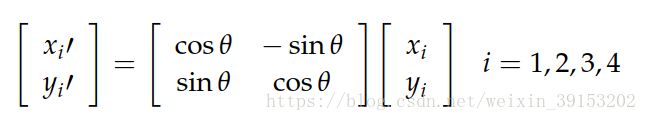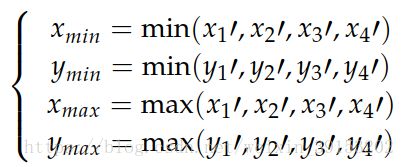通过旋转角度扩充数据集
tensorflow 的object detection api有一系列预处理方法(如flip等),但不包括旋转rotation,这可能是因为常规项目不会涉及到图像的360度旋转。但旋转在某些特定任务中尤为重要,笔者最近的遥感图像检测和血细胞检测项目采用的都是俯瞰视角,这种情况下,训练数据集的旋转操作可以使得网络具有方向的鲁棒性。
初步发现,api中常规的预处理操作是封装在.proto文件里面了,再通过.config文件设置、选择,preprogress.py等文件集成、调用。要直接添加,需要修改最初的配置文件,笔者水平有限,程序改不了那么深。。。
因此,直接在数据集上进行操作,对图像进行旋转,并对相应的annotation中的.xml文件进行修改,使得图像和目标按特定角度旋转。暂定每张图像旋转20次,每次18度。这样,原来的一张图像就生成了20张旋转后的图像,同时也进行了数据集的扩充。方法也比较粗暴,但简单可行。
首先是图像旋转的程序,
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Oct 9 09:57:04 2018
@author: PC
"""
import tensorflow as tf
from scipy import misc
import numpy as np
import os
from skimage import transform
global angle
angle = 0.0
#文件名
def file_name_original(file):
return os.path.splitext(file)[0]
#扩展名
def file_name_extension(file):
return os.path.splitext(file)[1]
#随机旋转图片
def random_rotate_image(image_input_path, image_output_path, image_file, num):
global angle
with tf.Graph().as_default():
# tf.set_random_seed(666)
file_contents = tf.read_file(os.path.join(image_input_path, image_file))
image = tf.image.decode_image(file_contents, channels=3)
image_rotate_en_list = []
def random_rotate_image_func(image, angle):
return misc.imrotate(image, angle, 'bicubic')
# return transform.rotate(image, angle,resize=True)
for i in range(num):
image_rotate = tf.py_func(random_rotate_image_func, [image, angle], tf.uint8)
angle = (angle + 18)
# image_rotate = misc.imrotate(image, 90, 'bicubic')
image_rotate_en_list.append(tf.image.encode_png(image_rotate))
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
sess.run(tf.local_variables_initializer())
results = sess.run(image_rotate_en_list)
for idx,re in enumerate(results):
with open(image_output_path + '/' + file_name_original(image_file)+ '_' + str(idx) + '.jpg','wb') as f:
print(image_output_path + '/' + file_name_original(image_file)+ '_' + str(idx) + '.jpg')
f.write(re)
if __name__ == '__main__':
#处理图片,进行20次随机处理,并将处理后的图片保存到输入图片相同的路径下
path_input = 'D:/object_detection/research/object_detection/CELL/VOCdevkit/CELL/JPEGImages'
path_output = 'D:/object_detection/research/object_detection/CELL/VOCdevkit/CELL_expand1/JPEGImages'
files=os.listdir(path_input)
for file in files:
if not os.path.isdir(file):
if file_name_extension(os.path.join(path_input, file)) == '.jpg' or file_name_extension(os.path.join(path_input, file)) == '.JPG':
random_rotate_image(path_input, path_output, file, 20)
print('Done')
然后是对.xml进行修改。旋转公式为
对应.xml中boundingbox的参数调整为
此处的公式是针对坐标原点进行旋转,而misc.imrotate函数是以(width/2, height/2)为中心进行旋转,因此在程序中需要对坐标进行校正,
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Oct 9 09:57:04 2018
@author: PC
"""
import tensorflow as tf
from scipy import misc
import numpy as np
import os
import xml.dom.minidom
import xml.etree.cElementTree as et
import math
#文件名
def file_name_original(file):
return os.path.splitext(file)[0]
#扩展名
def file_name_extension(file):
return os.path.splitext(file)[1]
#随机旋转图片
angle = np.zeros(20)
for i in range(20):
angle[i] = 18 * i
if __name__ == '__main__':
#处理图片,进行20次随机处理,并将处理后的图片保存到输入图片相同的路径下
annotation_input = 'D:/object_detection/research/object_detection/CELL/VOCdevkit/CELL/Annotations'
annottation_output = 'D:/object_detection/research/object_detection/CELL/VOCdevkit/CELL_expand1/Annotations'
files=os.listdir(annotation_input)
for xmlFile in files:
for id in range(20):
if not os.path.isdir(xmlFile):
if file_name_extension(os.path.join(annotation_input, xmlFile)) == '.xml':
print(os.path.join(annotation_input,xmlFile))
tree=et.parse(os.path.join(annotation_input,xmlFile))
root=tree.getroot()
for Size in root.findall('size'):
Width = int(Size.find('width').text)
Height = int(Size.find('height').text)
for Object in root.findall('object'):
# name=Object.find('name').text
# print("Object name is ", name)
bndbox=Object.find('bndbox')
xmin=int(bndbox.find('xmin').text)
ymin=int(bndbox.find('ymin').text)
xmax=int(bndbox.find('xmax').text)
ymax=int(bndbox.find('ymax').text)
x1 = (xmin-Width/2) * math.cos(angle[id]/180*np.pi) + (ymin-Height/2) * math.sin(angle[id]/180*np.pi) + Width/2 #注意加上旋转中心的误差修正
y1 = (ymin-Height/2) * math.cos(angle[id]/180*np.pi) - (xmin-Width/2) * math.sin(angle[id]/180*np.pi) + Height/2
x2 = (xmin-Width/2) * math.cos(angle[id]/180*np.pi) + (ymax-Height/2) * math.sin(angle[id]/180*np.pi) + Width/2
y2 = (ymax-Height/2) * math.cos(angle[id]/180*np.pi) - (xmin-Width/2) * math.sin(angle[id]/180*np.pi) + Height/2
x3 = (xmax-Width/2) * math.cos(angle[id]/180*np.pi) + (ymin-Height/2) * math.sin(angle[id]/180*np.pi) + Width/2
y3 = (ymin-Height/2) * math.cos(angle[id]/180*np.pi) - (xmax-Width/2) * math.sin(angle[id]/180*np.pi) + Height/2
x4 = (xmax-Width/2) * math.cos(angle[id]/180*np.pi) + (ymax-Height/2) * math.sin(angle[id]/180*np.pi) + Width/2
y4 = (ymax-Height/2) * math.cos(angle[id]/180*np.pi) - (xmax-Width/2) * math.sin(angle[id]/180*np.pi) + Height/2
x_min = min(x1, x2, x3, x4)
x_max = max(x1, x2, x3, x4)
y_min = min(y1, y2, y3, y4)
y_max = max(y1, y2, y3, y4)
# if (x_min>Width) or (x_max<0) or (y_min>Height) or (y_max<0):
# parant.remove(Object)
# else:
# x_min = (x_min>0) * x_min
# x_max = (x_max=Width) * Width
# y_min = (x_min>0) * y_min
# y_max = (y_max=Height) * Height
#
bndbox.find('xmin').text = str(int(x_min))
bndbox.find('ymin').text = str(int(y_min))
bndbox.find('xmax').text = str(int(x_max))
bndbox.find('ymax').text = str(int(y_max))
Object.find('pose').text = str(angle[id])
File = file_name_original(xmlFile) + '_' + str(id) + '.xml'
tree.write(os.path.join(annottation_output,File), encoding="utf-8", xml_declaration=True)
print('Done') 用labelImg进行数据集验证,任一张图像
在旋转之后得到
随图像旋转,在.xml中存放标签的boundingbox的坐标也随之调整,使得boundingbox始终落在目标上。