本文将从Spring源码探讨2个问题,Spring 容器是如何管理bean,以及如何从容器中获取bean
BeanFactory接口 是Spring容器的基础,该接口提供了 getBean(String beanName) 来获取 instance实例
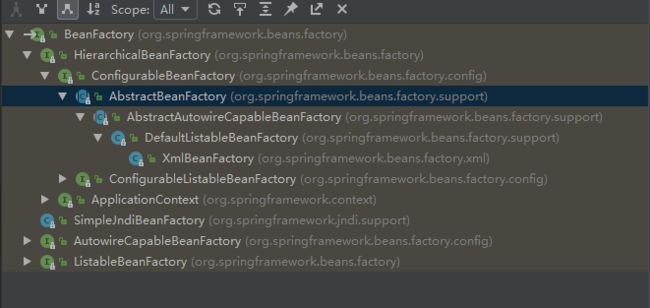
BeanFactory的继承体系如下:
getBean方法的实现是在AbstractBeanFactory抽象类中
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Implementation of BeanFactory interface
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
return doGetBean(name, null, null, false);
}
进入 doGetBean
/**
* Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean.
* @param name the name of the bean to retrieve
* @param requiredType the required type of the bean to retrieve
* @param args arguments to use when creating a bean instance using explicit arguments
* (only applied when creating a new instance as opposed to retrieving an existing one)
* @param typeCheckOnly whether the instance is obtained for a type check,
* not for actual use
* @return an instance of the bean
* @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T doGetBean(final String name, @Nullable final Class requiredType,
@Nullable final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException {
// 1.转换对应的beanName
final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
// 2.从缓存中获取原生实例
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.trace("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
}
else {
logger.trace("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
// 3.对原生instance进行处理 如果是正常bean直接返回,如果是FactoryBean beanName前有& 直接返回FactoryBean,否则返回FactoryBean.getObject()
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
// 4.原型模式下循环依赖的检测
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
// 5.如果有父工厂,并且当前工厂没有此bean则在父工厂中递归获取bean
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (parentBeanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) {
return ((AbstractBeanFactory) parentBeanFactory).doGetBean(
nameToLookup, requiredType, args, typeCheckOnly);
}
else if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
}
else if (requiredType != null) {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
else {
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup);
}
}
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
try {
// 6.将存储xml配置文件信息的GernericBeanDefinition转换成RootBeanDefinition
final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// 7.寻找依赖
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
// 记录依赖 dependenciesForBean.add(canonicalName); dependenciesForBean是个Set集合
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
getBean(dep);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);
}
}
}
// 8.根据不同模式下创建bean instance
// Create bean instance.
// 单例
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
// 原型模式
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
// 其他模式
else {
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " +
"defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",
ex);
}
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
// 9.类型检查
// Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {
try {
T convertedBean = getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
if (convertedBean == null) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
return convertedBean;
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex);
}
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
}
return (T) bean;
}
1.转换对应的beanName
final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
/**
* Return the bean name, stripping out the factory dereference prefix if necessary,
* and resolving aliases to canonical names.
* @param name the user-specified name
* @return the transformed bean name
*/
protected String transformedBeanName(String name) {
return canonicalName(BeanFactoryUtils.transformedBeanName(name));
}
从文档注释上可以看出 这部分逻辑 是转换bean的别名 或者如果是factorybean时 将beanName去除 前缀"&"
2. Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName); //从缓存中获取原生实例
/**
* Return the (raw) singleton object registered under the given name.
* Checks already instantiated singletons and also allows for an early
* reference to a currently created singleton (resolving a circular reference).
* @param beanName the name of the bean to look for
* @param allowEarlyReference whether early references should be created or not
* @return the registered singleton object, or {@code null} if none found
*/
@Nullable
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
ObjectFactory singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
a.首先尝试从单例缓存名为 singletonObjects Map中获取bean,
b. 获取不到,如果该实例正在创建中,则尝试从earlySingletonObjects Map中获取,
c.还获取不到,如果允许单例 循环依赖即boolean allowEarlyReference =true 时 尝试从singletonFactories 中获取ObjectFactory,返回 ObjectFactory.getObject()
如果Bean A 依赖Bean B Bean B 依赖 Bean A 那么就造成循环依赖
循环依赖分为 构造器依赖 和 setter方法依赖
Spring 只提供解决 单例模式下的setter方法循环依赖,其他模式下的循环依赖会抛BeanCurrentlyInCreationException异常
Spring解决bean循环依赖的思路是: 单例模式下默认是可以允许循环依赖的,解决办法时,在创建实例时,不等实例创建完成就会把创建该实例的Factory 暴露出去(放入到singletonFactories Map中),并且下一个bean可以通过暴露的ObjectFactory的 getObject()方法获取该实例,当然我们也可以通过AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext的setAllowCircularReferences()方法 来禁止循环引用
3. bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
对原生instance进行处理 如果是正常bean直接返回,如果是FactoryBean,传入的beanName前有& 也直接返回FactoryBean,否则返回FactoryBean.getObject()
Spring容器createBean创建完该实例后,只是原生的instance,放入到缓存中的实例也是这种状态,如果该实例是FactoryBean,而我们想要的是该工厂实例创建的实例,所以就有了getObjectForBeanInstance方法的处理
/**
* Get the object for the given bean instance, either the bean
* instance itself or its created object in case of a FactoryBean.
* @param beanInstance the shared bean instance
* @param name name that may include factory dereference prefix
* @param beanName the canonical bean name
* @param mbd the merged bean definition
* @return the object to expose for the bean
*/
protected Object getObjectForBeanInstance(
Object beanInstance, String name, String beanName, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
// Don't let calling code try to dereference the factory if the bean isn't a factory.
if (BeanFactoryUtils.isFactoryDereference(name)) {
if (beanInstance instanceof NullBean) {
return beanInstance;
}
if (!(beanInstance instanceof FactoryBean)) {
throw new BeanIsNotAFactoryException(transformedBeanName(name), beanInstance.getClass());
}
}
// 如果是正常bean 或者FactoryBean的beanName 加上前缀& 直接返回
// Now we have the bean instance, which may be a normal bean or a FactoryBean.
// If it's a FactoryBean, we use it to create a bean instance, unless the
// caller actually wants a reference to the factory.
if (!(beanInstance instanceof FactoryBean) || BeanFactoryUtils.isFactoryDereference(name)) {
return beanInstance;
}
Object object = null;
if (mbd == null) {
// 缓存FactoryBean.getObject
object = getCachedObjectForFactoryBean(beanName);
}
if (object == null) {
// Return bean instance from factory.
FactoryBean factory = (FactoryBean) beanInstance;
// Caches object obtained from FactoryBean if it is a singleton.
if (mbd == null && containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
boolean synthetic = (mbd != null && mbd.isSynthetic());
// 从FactoryBean中获取bean
object = getObjectFromFactoryBean(factory, beanName, !synthetic);
}
return object;
}
/**
* Return whether the given name is a factory dereference
* (beginning with the factory dereference prefix).
* @param name the name of the bean
* @return whether the given name is a factory dereference
* @see BeanFactory#FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX
*/
public static boolean isFactoryDereference(@Nullable String name) {
return (name != null && name.startsWith(BeanFactory.FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX));
}
/**
* Used to dereference a {@link FactoryBean} instance and distinguish it from
* beans created by the FactoryBean. For example, if the bean named
* {@code myJndiObject} is a FactoryBean, getting {@code &myJndiObject}
* will return the factory, not the instance returned by the factory.
*/
String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&";
/**
* Obtain an object to expose from the given FactoryBean.
* @param factory the FactoryBean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param shouldPostProcess whether the bean is subject to post-processing
* @return the object obtained from the FactoryBean
* @throws BeanCreationException if FactoryBean object creation failed
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean#getObject()
*/
protected Object getObjectFromFactoryBean(FactoryBean factory, String beanName, boolean shouldPostProcess) {
if (factory.isSingleton() && containsSingleton(beanName)) {
synchronized (getSingletonMutex()) {
Object object = this.factoryBeanObjectCache.get(beanName);
if (object == null) {
object = doGetObjectFromFactoryBean(factory, beanName);
// Only post-process and store if not put there already during getObject() call above
// (e.g. because of circular reference processing triggered by custom getBean calls)
Object alreadyThere = this.factoryBeanObjectCache.get(beanName);
if (alreadyThere != null) {
object = alreadyThere;
}
else {
if (shouldPostProcess) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
// Temporarily return non-post-processed object, not storing it yet..
return object;
}
// singletonsCurrentlyInCreation.add(beanName) 记录正在创建的bean
beforeSingletonCreation(beanName);
try {
// 给后处理器PostProcessor一次覆写返回bean的逻辑 默认是正常返回FactoryBean.getObject
object = postProcessObjectFromFactoryBean(object, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Post-processing of FactoryBean's singleton object failed", ex);
}
finally {
// singletonsCurrentlyInCreation.remove(beanName) 从正在创建bean记录中移除
afterSingletonCreation(beanName);
}
}
if (containsSingleton(beanName)) {
// 将bean放入factoryBeanObjectCache.缓存
this.factoryBeanObjectCache.put(beanName, object);
}
}
}
return object;
}
}
else {
Object object = doGetObjectFromFactoryBean(factory, beanName);
if (shouldPostProcess) {
try {
object = postProcessObjectFromFactoryBean(object, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Post-processing of FactoryBean's object failed", ex);
}
}
return object;
}
}
/**
* Obtain an object to expose from the given FactoryBean.
* @param factory the FactoryBean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the object obtained from the FactoryBean
* @throws BeanCreationException if FactoryBean object creation failed
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean#getObject()
*/
private Object doGetObjectFromFactoryBean(final FactoryBean factory, final String beanName)
throws BeanCreationException {
Object object;
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessControlContext acc = getAccessControlContext();
try {
object = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction如果缓存中有原生实例,通过getObjectForBeanIntance()处理后直接返回了;
下面是单例缓存中没有实例的逻辑:
4.原型模式下循环依赖的检测
上面已经说到,Spring只支持单例模式下setter方法的循环依赖,如果是原型模式则直接抛出BeanCurrentlyInCreationException异常
5.如果当前工厂没有定义此bean,并且有父工厂,则在父工厂中递归获取bean 获取到则返回
6.将存储xml配置文件信息的GernericBeanDefinition转换成RootBeanDefinition
从xml读取到的bean信息定义在GernericBeanDefinition中,但是后续针对bean的处理都是使用RootBeanDefinition,所以将GernericBeanDefinition转换成RootBeanDefinition,转换过程中如果父bean不为空的话,也会合并父类的属性
7.在bean初始化之前,会通过getBean 先加载依赖的bean
8.根据不同的模式下 创建bean 这部分逻辑较长 稍后详解
9类型检查及转换
public T getBean(String name, Class requiredType) throws BeansException {
return doGetBean(name, requiredType, null, false);
}
如果getBean()方法中传入了类型,Spring在返回实例前,会进行类型检查或转换为requiredType所指定的类型,比如返回的bean是个String,requiredType却需要Integer 这时候就需要转换了
下面探讨在不同模式下创建bean的逻辑,
该逻辑的方法是个getSingleton((String beanName, ObjectFactory singletonFactory)重载方法
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
if (this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction) {
throw new BeanCreationNotAllowedException(beanName,
"Singleton bean creation not allowed while singletons of this factory are in destruction " +
"(Do not request a bean from a BeanFactory in a destroy method implementation!)");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating shared instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
// singletonsCurrentlyInCreation.add(beanName) 记录正在创建的bean
beforeSingletonCreation(beanName);
boolean newSingleton = false;
boolean recordSuppressedExceptions = (this.suppressedExceptions == null);
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
try {
// ObjectFactory来创建bean的方法 该方法的具体逻辑是在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.creatBean()中
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
newSingleton = true;
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// Has the singleton object implicitly appeared in the meantime ->
// if yes, proceed with it since the exception indicates that state.
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
throw ex;
}
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
for (Exception suppressedException : this.suppressedExceptions) {
ex.addRelatedCause(suppressedException);
}
}
throw ex;
}
finally {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = null;
}
// singletonsCurrentlyInCreation.remove(beanName) 从正在创建bean记录中移除
afterSingletonCreation(beanName);
}
if (newSingleton) {
//将创建的实例放入到singletonObjects缓存中,并且删除中间的各种记录
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
}
我们先来看看创建完成后 addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject)具体做了什么操作
/**
* Add the given singleton object to the singleton cache of this factory.
* To be called for eager registration of singletons.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param singletonObject the singleton object
*/
protected void addSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
this.singletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
很明显,在单例缓存singletonObjects中添加实例,将提前暴露的ObjectFactory移除缓存
再返回来看看具体创建bean的过程
ObjectFactory.getObject方法来创建bean,该方法的具体逻辑AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.creatBean()中,接下来我们就详细解析createBean的过程
/**
* Central method of this class: creates a bean instance,
* populates the bean instance, applies post-processors, etc.
* @see #doCreateBean
*/
@Override
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
//1.根据设置的class属性或者className来解析class对象
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and
// clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class
// which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition.
Class resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
// Prepare method overrides.
// 2.对xml配置中lookupMethod和replaceMethod的配置进行处理 主要是统计MethodOverrides方法对应方法名的个数,来设置是否有重载的标志
try {
mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(),
beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);
}
try {
//3.在真正实例化bean之前,给后处理器BeanPostProcessors 一次返回代理实例的机会
// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
try {
//4.真正实例化的逻辑
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) {
// A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already,
// or illegal singleton state to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex);
}
}
从createBean()方法中可以看到该方法主要有4部分逻辑,
1.根据设置的class属性或者className来解析class对象
2.对xml配置中lookupMethod和replaceMethod的配置进行处理 主要是统计MethodOverrides方法对应方法名的个数,来设置是否有重载的标志
3.在真正实例化bean之前,给后处理器BeanPostProcessors 一次返回代理实例的机会
4.真正实例化的逻辑doCreateBean
我们详细看看第3,4部分
/**
* Apply before-instantiation post-processors, resolving whether there is a
* before-instantiation shortcut for the specified bean.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @return the shortcut-determined bean instance, or {@code null} if none
*/
@Nullable
protected Object resolveBeforeInstantiation(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
Object bean = null;
if (!Boolean.FALSE.equals(mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved)) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
Class targetType = determineTargetType(beanName, mbd);
if (targetType != null) {
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(targetType, beanName);
if (bean != null) {
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
}
}
mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved = (bean != null);
}
return bean;
}
该方法是在真正实例化实例前的短路操作,如果有InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor后处理器的实现,就会走这部分逻辑
/**
* Apply InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors to the specified bean definition
* (by class and name), invoking their {@code postProcessBeforeInstantiation} methods.
* Any returned object will be used as the bean instead of actually instantiating
* the target bean. A {@code null} return value from the post-processor will
* result in the target bean being instantiated.
* @param beanClass the class of the bean to be instantiated
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean object to use instead of a default instance of the target bean, or {@code null}
* @see InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation
*/
@Nullable
protected Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(Class beanClass, String beanName) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
Object result = ibp.postProcessBeforeInstantiation(beanClass, beanName);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
}
return null;
}
从方法中我们可以看到只是寻找InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor后处理器,然后调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法,(注意该后处理器的postProcessAfterInstantiation方法是在真正初始化实例过程中在填充属性populateBean前调用)
在调用完InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor后处理器方法后,还会继续调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization实例化后的后处理方法,Spring创建bean有个特点就是尽量保证所有bean在初始化完成后都有机会调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization()方法,所以实际开发中可针对这个特性进行设计自己的业务逻辑.
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}
以上就是有InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor后处理器的短路逻辑,如果没有这个后处理器,则进行真正实例化
doCreateBean().
/**
* Actually create the specified bean. Pre-creation processing has already happened
* at this point, e.g. checking {@code postProcessBeforeInstantiation} callbacks.
* Differentiates between default bean instantiation, use of a
* factory method, and autowiring a constructor.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean
* @param args explicit arguments to use for constructor or factory method invocation
* @return a new instance of the bean
* @throws BeanCreationException if the bean could not be created
* @see #instantiateBean
* @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod
* @see #autowireConstructor
*/
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 1.根据指定的策略创建bean,如工厂方法,构造函数,简单初始化
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
//2.MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors后处理器逻辑
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
//3.不等bean创建完成,就将创建该bean的Factory暴露出去,以解决单例模式下的循环依赖
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
//4.填充属性
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
//5. 处理ware接口逻辑和 配置的init-method方法逻辑
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
//此处bean初始化逻辑已经走完,如果还有依赖的bean没有创建完成,即actualDependentBeans不为空说明存在循环依赖
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// 6 注册销毁bean,处理配置的destory-method方法或者DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor后处理器的逻辑
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
1.根据指定的策略创建bean,如工厂方法,构造函数,简单初始化,这个过程将BeanDefinition转换成了BeanWapper
/**
* Create a new instance for the specified bean, using an appropriate instantiation strategy:
* factory method, constructor autowiring, or simple instantiation.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @param args explicit arguments to use for constructor or factory method invocation
* @return a BeanWrapper for the new instance
* @see #obtainFromSupplier
* @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod
* @see #autowireConstructor
* @see #instantiateBean
*/
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
Class beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName());
}
Supplier instanceSupplier = mbd.getInstanceSupplier();
if (instanceSupplier != null) {
return obtainFromSupplier(instanceSupplier, beanName);
}
if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// Shortcut when re-creating the same bean...
boolean resolved = false;
boolean autowireNecessary = false;
if (args == null) {
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null) {
resolved = true;
autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved;
}
}
}
if (resolved) {
if (autowireNecessary) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null);
}
else {
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
}
// Candidate constructors for autowiring?
Constructor[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName);
if (ctors != null || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR ||
mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args);
}
// Preferred constructors for default construction?
ctors = mbd.getPreferredConstructors();
if (ctors != null) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, null);
}
// No special handling: simply use no-arg constructor.
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
该过程的大致逻辑是:
如果存在工厂方法则使用工厂方法进行初始化,
如果有多个构造函数,则根据具体的参数选择具体的构造函数并进行初始化
如果没有工厂方法,也没有带参构造,则选用默认的构造函数
@Override
public Object instantiate(RootBeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String beanName, BeanFactory owner) {
// Don't override the class with CGLIB if no overrides.
if (!bd.hasMethodOverrides()) {
Constructor constructorToUse;
synchronized (bd.constructorArgumentLock) {
constructorToUse = (Constructor) bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod;
if (constructorToUse == null) {
final Class clazz = bd.getBeanClass();
if (clazz.isInterface()) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "Specified class is an interface");
}
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
constructorToUse = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedExceptionAction>) clazz::getDeclaredConstructor);
}
else {
constructorToUse = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor();
}
bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod = constructorToUse;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "No default constructor found", ex);
}
}
}
return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructorToUse);
}
else {
// Must generate CGLIB subclass.
return instantiateWithMethodInjection(bd, beanName, owner);
}
}
上述初始化的逻辑可以很清楚的看到,如果有override的方法也就是有配置lookup-method或replace-method,则使用CGLB进行动态代理,如果没有override 则简单的使用反射来初始化bean
2.MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors后处理器逻辑
/**
* Apply MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors to the specified bean definition,
* invoking their {@code postProcessMergedBeanDefinition} methods.
* @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean
* @param beanType the actual type of the managed bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @see MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor#postProcessMergedBeanDefinition
*/
protected void applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(RootBeanDefinition mbd, Class beanType, String beanName) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor bdp = (MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) bp;
bdp.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
}
}
在刚初始化之后,有次使用MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition()来定义bean的机会
3.不等bean创建完成,就将创建该bean的Factory暴露出去,以解决单例模式下的循环依赖
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
/**
* Add the given singleton factory for building the specified singleton
* if necessary.
* To be called for eager registration of singletons, e.g. to be able to
* resolve circular references.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param singletonFactory the factory for the singleton object
*/
protected void addSingletonFactory(String beanName, ObjectFactory singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(singletonFactory, "Singleton factory must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
if (!this.singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName)) {
this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, singletonFactory);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
}
逻辑很简单,就是不等bean创建完成就将该ObjectFactory放入到singletonFactories Map中进行提前暴露,下一个bean依赖该bean时,即可通过该ObjectFactory来getObject()获取bean,那我们再看看getObject()里的具体实现
/**
* Obtain a reference for early access to the specified bean,
* typically for the purpose of resolving a circular reference.
* @param beanName the name of the bean (for error handling purposes)
* @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean
* @param bean the raw bean instance
* @return the object to expose as bean reference
*/
protected Object getEarlyBeanReference(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object bean) {
Object exposedObject = bean;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
exposedObject = ibp.getEarlyBeanReference(exposedObject, beanName);
}
}
}
return exposedObject;
}
可以看到是通过SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 后处理器的getEarlyBeanReference()方法返回一个未实例化结束的bean,以此来解决单例模式下的循环依赖
4.填充属性 populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
/**
* Populate the bean instance in the given BeanWrapper with the property values
* from the bean definition.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @param bw the BeanWrapper with bean instance
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation") // for postProcessPropertyValues
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
if (bw == null) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor后处理器来设置是否继续需要填充
// postProcessAfterInstantiation()方法返回false 该属性表示不需要继续填充
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return;
}
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
// 根据名称 获取属性 // pvs.add(propertyName, bean);
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// 根据类型 获取属性 // pvs.add(propertyName, autowiredArgument);
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
if (pvs != null) {
// 将PropertyValues 记录的属性填充到beanWrapper中
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}
上述的方法 有以下逻辑:
a.通过InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor后处理器来设置是否继续需要填充 postProcessAfterInstantiation()方法返回false 该属性表示不需要继续填充
b.根据名称或者类型,进行属性获取,记录在PropertyValues pvs对象中
c.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的postProcessPropertyValues方法对获取属性后,填充前对属性进行再次处理,典型应用是在RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类中对属性进行验证
d.将PropertyValues 记录的属性填充到beanWrapper中
5. 处理ware接口逻辑和 配置的init-method方法逻辑
到此处,Spring的bean已经完成了初步初始化,以及属性填充,接下来就是Aware相关方法的处理,以及用户自定义的初始化方法
/**
* Initialize the given bean instance, applying factory callbacks
* as well as init methods and bean post processors.
* Called from {@link #createBean} for traditionally defined beans,
* and from {@link #initializeBean} for existing bean instances.
* @param beanName the bean name in the factory (for debugging purposes)
* @param bean the new bean instance we may need to initialize
* @param mbd the bean definition that the bean was created with
* (can also be {@code null}, if given an existing bean instance)
* @return the initialized bean instance (potentially wrapped)
* @see BeanNameAware
* @see BeanClassLoaderAware
* @see BeanFactoryAware
* @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization
* @see #invokeInitMethods
* @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
*/
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction
可以看到initializeBean主要有一下逻辑:
a.处理Aware接口相关方法
private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
ClassLoader bcl = getBeanClassLoader();
if (bcl != null) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl);
}
}
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
}
设置setBeanName ,setBeanClassLoader,setBeanFactory
b.invokeInitMethods 用户自定义初始化处理
在invokeInitMethods 前后有BeanPostProcessor后处理器BeforeInitialization和AfterInitialization方法的处理
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}
再返回来看invokeInitMethods 方法的逻辑
/**
* Give a bean a chance to react now all its properties are set,
* and a chance to know about its owning bean factory (this object).
* This means checking whether the bean implements InitializingBean or defines
* a custom init method, and invoking the necessary callback(s) if it does.
* @param beanName the bean name in the factory (for debugging purposes)
* @param bean the new bean instance we may need to initialize
* @param mbd the merged bean definition that the bean was created with
* (can also be {@code null}, if given an existing bean instance)
* @throws Throwable if thrown by init methods or by the invocation process
* @see #invokeCustomInitMethod
*/
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction可以清晰看到执行用户初始化方法时,先执行InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet()方法,再执行配置的init-method
6 注册销毁bean,处理配置的destory-method方法或者DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor后处理器的逻辑
/**
* Add the given bean to the list of disposable beans in this factory,
* registering its DisposableBean interface and/or the given destroy method
* to be called on factory shutdown (if applicable). Only applies to singletons.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param bean the bean instance
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @see RootBeanDefinition#isSingleton
* @see RootBeanDefinition#getDependsOn
* @see #registerDisposableBean
* @see #registerDependentBean
*/
protected void registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(String beanName, Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
AccessControlContext acc = (System.getSecurityManager() != null ? getAccessControlContext() : null);
if (!mbd.isPrototype() && requiresDestruction(bean, mbd)) {
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// Register a DisposableBean implementation that performs all destruction
// work for the given bean: DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors,
// DisposableBean interface, custom destroy method.
registerDisposableBean(beanName,
new DisposableBeanAdapter(bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessors(), acc));
}
else {
// A bean with a custom scope...
Scope scope = this.scopes.get(mbd.getScope());
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + mbd.getScope() + "'");
}
scope.registerDestructionCallback(beanName,
new DisposableBeanAdapter(bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessors(), acc));
}
}
}
可以看到处理DisposableBean的destory()方法
至此,Spring bean 从创建 到获取的问题已经探讨完,希望你能有所收获.
由于笔者水平有限,文中如有错误请各路大神多多指正.
原创不易,如有转载请标明原处