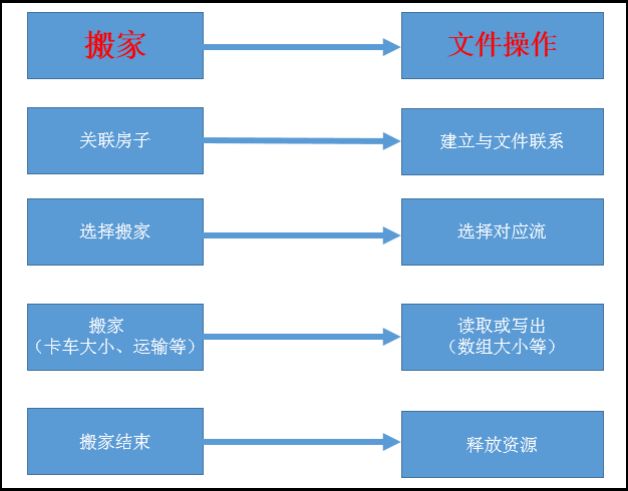
Java IO字符流与字节流
一、基本概念
流:从一端流向另一端,从源头到目的地。
始终与程序为中心,都是程序与文件|数组|网络连接|数据库进行操作。
二、IO流分类
1.流向:
输入流和输出流
2.数据:
字节流:二进制,可以处理文本文件,视频,音频等 。
字符流:文本文件,只能处理纯文本,全款为可见字符(.txt、.html)。
3.功能:
节点:包裹源头
处理:增强功能,提高性能。
三、字节流与字符流
1.字节流
输入流:InputStream
int read(byte[] b)
int read(byte[] b, int off, int len)
void close() FileInputStream
输出流:OutputStream
void write(byte[] b)
void write(byte[] b, int off, int len)
void close()
void flush() FileOutputStream
2.字符流
输入流:Reader
int read(char[] cbuf)
abstract int read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)
abstract void close() FileReader
输出流:Writer
void write(char[] cbuf)
abstract void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)
void write(String str, int off, int len)
abstract void flush()
abstract void close()FileWriter
四、基本操作步骤
五、读取文件(字节流)
1、建立联系 –> File对象 源头
2、选择流 –> 文件输入流InputStream、FileInputStream
3、操作 –> byte[] car = new byte[1024];+read+读取大小、输出
4、释放资源–>关闭
package IO;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* 文件的读取
* 1、建立联系
* 2、选择流
* 3、操作 不断读取
* 4、释放资源
*
* String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length)
* 通过使用平台的 默认字符集解码 指定的byte子数组,构造一个新的 String。
*/
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "g:/love.txt";
//1、建立联系
File src= new File(path);
//2、选择流
InputStream is= null;//提升作用域
try {
//is = new FileInputStream(path);
is = new FileInputStream(src);
//3、操作不断读取 缓冲数组
byte[] car = new byte[20];
int len = 0;//接收实际读取的大小
//循环读取
while(-1!=(len=is.read(car)))
{
//输出 字节数组转成字符串(默认字符集解码)
String info = new String(car,0,len);
System.out.print(info);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("文件不存在");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("读取文件失败");
}
finally
{
//4、释放资源
if(null!=is)
{
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("关闭输入流文件失败");
}
}
}
}
}
运行结果:
if LOVE,
Please deeping LOVE.六、写出文件(字节流)
1、建立联系 –> File对象 目的地
2、选择流 –> 文件输出流OutputStream、FileOutputStream
3、操作 –> write+flush
4、释放资源–>关闭
package IO;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
/**
* 文件的写出
* 1、建立联系
* 2、选择流
* 3、操作 不断写出
* 4、释放资源
*/
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "g:/oo.txt";
//1、建立联系
File dest= new File(path);
//2、选择文件输出流 OutputStream、FileOutputStream
OutputStream os = null;
try {
//以追加的形式写出文件为true 覆盖为false 默认是false
os = new FileOutputStream(dest, true);
//3、操作 \r\n回车
String str = "Ladygaga is my nvshen.\r\n";
//字符集转字符数组
byte[] data = str.getBytes();
os.write(data,0,data.length);
os.flush();//强制刷新出去
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("文件不存在");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("文件写出失败");
}
finally
{
//4、释放资源
if(null!=os)
{
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("关闭输出流失败");
}
}
}
}
}七、文件拷贝(字节流)
1、建立联系 File对象 源头 目的地
2、选择流
文件输入流
文件输出流3、操作
byte[] flush = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while(-1!=(len=输入流.read(flush)))
{
输出流.write(flush,0,len);
}
输出流.flush4、释放资源:关闭两个流
package IO;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
/**
* 拷贝文件
* 1、建立联系 File对象 源头 目的地
* 2、选择流
* 文件输入流
* 文件输出流
* 3、操作 拷贝
* byte[] flush = new byte[1024];
* int len = 0;
* while(-1!=(len=输入流.read(flush)))
* {
* 输出流.write(flush,0,len);
* }
* 输出流.flush
* 4、释放资源:关闭两个流
*/
public class Demo03 {
final static String pathsrc = "G:/picture/520.jpg";
final static String pathdest = "G:/1314.jpg";
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
copyFile(pathsrc,pathdest);//源-->目的地
} catch(FileNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("文件不存在");
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("拷贝文件失败|关闭输出流失败");
}
}
/**
* 文件的拷贝
*/
public static void copyFile(String srcPath,String destPath)
throws FileNotFoundException,IOException
{
//1、建立联系 源存在(且为文件)+目的地(文件可以不存在)
File src = new File(srcPath);
File dest = new File(destPath);
if(!src.isFile())
{
System.out.println("只能拷贝文件");
throw new IOException("只能拷贝文件");
}
//2、选择流
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(src);
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(dest);
//3、文件拷贝 循环(读取+写出)
byte[] flush = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while(-1!=(len = is.read(flush)))//读入
{
//写出
os.write(flush,0,len);
}
os.flush();//强制刷出
//关闭流 先打开后关闭
os.close();
is.close();
}
}八、文件夹拷贝(字节流)
1、递归查找子孙级文件|文件夹
2、如果是文件 复制(IO流复制)
如果是文件夹 创建,递归
package IO;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
/**
* 文件夹的拷贝
* 1、文件 复制
* 2、文件夹 创建mkdirs()
* 3、递归查找子孙级
* @author Administrator
*/
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String srcPath = "g:/try/123/432";//源目录
String destPath = "g:/try/";//目标目录
//File dest =null;
//copyDir(srcPath,destPath);
//FileUtil.copyDir(srcPath,destPath);
copyDir(new File(srcPath),new File(destPath));
}
/**
* 拷贝文件夹
* src 源文件对象
* dest 目标文件对象
*/
public static void copyDir(File src,File dest)
{
if(src.isDirectory())//文件夹
{
dest = new File(dest,src.getName());//****
//如果父目录不能拷贝到子目录中,这样会造成死循环。
if(dest.getAbsolutePath().contains(src.getAbsolutePath()))
{
System.out.println("父目录不能拷贝到子目录中");
return;
}
}
copyDirDetail(src,dest);
}
/**
* 拷贝文件夹细节
* @param src
* @param dest
*/
public static void copyDirDetail(File src,File dest)
{
if(src.isFile())//如果是文件,直接拷贝。
{
try {
copyFile(src, dest);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
else if(src.isDirectory())//如果是文件夹,递归。
{
//确保目标文件夹存在
dest.mkdirs();//****
//获取下一级目录文件夹
for(File sub:src.listFiles())
{
copyDirDetail(sub, new File(dest,sub.getName()));
}
}
}
/**
* 文件的拷贝
* 源文件的File对象
* 目标文件的File对象
*/
public static void copyFile(File src,File dest) throws IOException
{
if(!src.isFile())
{
System.out.println("只能拷贝文件");
throw new IOException("只能拷贝文件");
}
//如果过dest为已经存在的文件件,不能建立同名的文件
if(dest.isDirectory())
{
System.out.println("不能建立同名的文件");
throw new IOException("不能建立同名的文件");
}
//2、选择流
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(src);
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(dest);
//3、文件拷贝 循环+读取+写出
byte[] flush = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while(-1!=(len = is.read(flush)))
{
//写出
os.write(flush,0,len);
}
os.flush();//强制刷出
//关闭流 先打开后关闭
os.close();
is.close();
}
}九、自制文件|文件夹拷贝工具
package IO;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
/**
* 文件操作综合更加完整,健壮
* 1、文件拷贝
* 2、文件夹拷贝
*/
public class FileUtil {
/**
* 文件的拷贝
* 源文件的String对象
* 目标文件的String对象
*/
public static void copyFile(String srcPath,String destPath) throws IOException
{
//1、建立联系 源存在(且为文件)+目的地(文件可以不存在)
copyFile(new File(srcPath),new File(destPath));
}
/**
* 文件的拷贝
* 源文件的File对象
* 目标文件的File对象
*/
public static void copyFile(File src,File dest) throws IOException
{
if(!src.isFile()||null==src)//不是文件或者为null
{
System.out.println("只能拷贝文件");
throw new IOException("只能拷贝文件");
}
//如果dest为已经存在的文件夹,不能建立与文件夹同名的文件。
if(dest.isDirectory())
{
System.out.println(dest.getAbsolutePath()+"不能建立与文件夹同名的文件");
throw new IOException(dest.getAbsolutePath()+"不能建立与文件夹同名的文件");
}
//2、选择流
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(src);
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(dest);
//3、文件拷贝 循环+读取+写出
byte[] flush = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while(-1!=(len = is.read(flush)))
{
//写出
os.write(flush,0,len);
}
os.flush();//强制刷出
//4、关闭流 先打开后关闭
os.close();
is.close();
}
/**
* 拷贝文件夹
* 原路径
* 目标路径
*/
public static void copyDir(String srcPath,String destPath)
{
File src = new File(srcPath);
File dest = new File(destPath);
copyDir(src,dest);
}
/**
* 拷贝文件夹
* src 源文件对象
* dest 目标文件对象
*/
public static void copyDir(File src,File dest)
{
if(src.isDirectory())//文件夹
{
dest = new File(dest,src.getName());
if(dest.getAbsolutePath().contains(src.getAbsolutePath()))
{
System.out.println("父目录不能拷贝到子目录中");
return;
}
}
copyDirDetail(src,dest);
}
/**
* 拷贝文件夹细节
* @param src
* @param dest
*/
public static void copyDirDetail(File src,File dest)
{
if(src.isFile())
{
try {
FileUtil.copyFile(src, dest);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
else if(src.isDirectory())//文件夹
{
//确保目标文件夹存在
dest.mkdirs();
//获取下一级目录文件夹
for(File sub:src.listFiles())
{
copyDirDetail(sub, new File(dest,sub.getName()));
}
}
}
}十、读取纯文本(字符流)
1、建立联系 –> File对象 源头
2、选择流 –> 文件输入流Reader、FileReader
3、操作 –> char[] car = new char[1024];+read+读取大小、输出
4、释放资源–>关闭
package IOChar;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Reader;
/**
* 纯文本读取
* String(char[] value, int offset, int count)
* 分配一个新的 String,它包含取自字符数组参数一个子数组的字符。
*/
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "G:/kfcv.txt";
//1、创建源
File src = new File(path);
//2、选择流
Reader reader = null;
try {
reader = new FileReader(src);
//3、读取操作
char[] flush = new char[10];
int len = 0;
while(-1!=(len = reader.read(flush)))
{
//字符数组转成字符串
String str = new String(flush,0,len);
System.out.print(str);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("文件不存在");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("文件读取失败");
}
finally
{
if(null!=reader)
{
try {
//4、关闭
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
运行结果:
机会对于不能利用它的人又有什么用呢?
正如风只对于能利用它的人才是动力。十、纯文本写出(字符流)
1、建立联系 –> File对象 目的地
2、选择流 –> 文件输出流Writer、FileWriter
3、操作 –> write(字符数组,0,长度)+flush
4、释放资源–>关闭
package IOChar;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Writer;
/**
* 纯文件的写出
* write(char[] cbuf) 写入字符数组。
* void write(String str) 写入字符串。
* abstract void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)
*/
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "G:/output.txt";
//创建源
File dest = new File(path);
//选择流
Writer wr = null;
try {
//wr = new FileWriter(dest,true);//true表示追加文件 默认是false,覆盖文件。
wr = new FileWriter(dest);
//写出
String msg = "每个人都有青春,\r\n每个青春都有一个故事,\r\n每个故事都有一个遗憾,\r\n每个遗憾却都存在着他的美好。";
wr.write(msg);
wr.append("ouye");
wr.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
if(null!=wr)
{
try {
wr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}十一、纯文本拷贝(字符流)
package IOChar;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Reader;
import java.io.Writer;
/**
* 纯文件的拷贝
* @author liguodong
*/
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String srcPath = "G:/output.txt";
String destPath = "G:/writer.txt";
//创建源
File src = new File(srcPath);
//创建源
File dest = new File(destPath);
//选择流
Reader reader = null;
//选择流
Writer writer = null;
try {
reader = new FileReader(src);
writer = new FileWriter(dest);
//读取操作
char[] flush = new char[10];
int len = 0;
while(-1!=(len = reader.read(flush)))
{
//字符数组转成字符串
//String str = new String(flush,0,len);
//writer = new FileWriter(dest,true);
//writer.write(str);
writer.write(flush,0,len);
}
writer.flush();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("文件不存在");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("文件读写失败");
}
finally
{
if(null!=reader)
{
try {
writer.close();
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}