LeetCode刷题总结101~150
LeetCode刷题总结101~150
- 101. Symmetric Tree
- 121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
- 122. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
- 125. Valid Palindrome
- 136. Single Number
- 147. Insertion Sort List
- 150. Evaluate Reverse Polish Notation
101. Symmetric Tree
思路:
分析到此题并不是简单的把一个结点划分为左右子树就可以的,因而使用递归时必定需要重新定义一个函数,函数的参数即为需要比较的两个树,该树的特征即a的左子树与b的右子树相同,同理a的右子树与b的左子树相同,此时即为true。
需要注意的一点是,分析好逻辑关系,如下:
if(lf==NULL&&rt==NULL)
return true;
if((lf==NULL&&rt!=NULL)||(rt==NULL&&lf!=NULL))
return false;
if(lf->val!=rt->val)
return false;
逻辑不能错误,即三个if语句的顺序不能颠倒。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)
return true;
return judge(root->left,root->right);
}
bool judge(TreeNode* lf,TreeNode* rt){
if(lf==NULL&&rt==NULL)
return true;
if((lf==NULL&&rt!=NULL)||(rt==NULL&&lf!=NULL))
return false;
if(lf->val!=rt->val)
return false;
bool islf=judge(lf->left,rt->right);
bool isrt=judge(lf->right,rt->left);
if(islf&&isrt)
return true;
return false;
}
};
121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock

该题较为简单,问题在于怎么简化。
常规方法两层循环的情况下,就算剪枝了也达不到很好的效果,因此我们使用一层循环来做。
一层循环思路如下:
遍历数组,记录min,并定义max=price[i]-min,此时max即为最大差值。
class Solution {
public:
// 15.07
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int max=0,min=0x3f3f3f3f;
for(int i=0;i<prices.size();i++){
if(prices[i]<min)
min=prices[i];
else if(prices[i]-min>max)
max=prices[i]-min;
}
return max;
}
};
122. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II

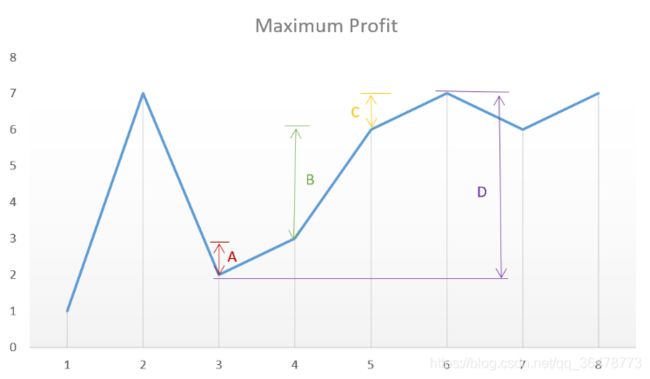
该题最直观也是最高效的方法即为把收益图画出来,可以证明第i个点到第j个点的直接涨幅一定小于等于i到j的断续涨幅之和,故我们只要每次累积求和两连续点之间的增幅即可,O(N)复杂度。
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int maxProfit=0;
for(int i=1;i<prices.size();i++){
if(prices[i]>prices[i-1])
maxProfit += prices[i]-prices[i-1];
}
return maxProfit;
}
};
125. Valid Palindrome
一个最容易想到的方法就是对字符串一次变量,筛选出不是alphanumeric characters的字符并删去,另外对于大写字符我们转换成小写字符,最后对处理后的字符串我们反转它并与原来的字符串去做比较即可。
知识点:
isalpha(s[i])、isdigit(s[i])、isupper(s[i])分别判断该字符是否为字母、数字、大写字母;
tolower()将字符转化成小写字母
string类中的删除方法:s.erase(pos,n),即从pos处删除字符s中长为n的子串,并返回修改后的string对象引用。注意,删除时s.size()的大小也发生变化,需要对下标进行处理才能正常使用。
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(string s) {
int ct=0;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++){
if(isalpha(s[i])||isdigit(s[i]))
{
if(isupper(s[i])){
s[i]=tolower(s[i]);
}
}
else{ // 其他字符删除
s.erase(i,1);
i--;
}
}
string ans=s;
reverse(s.begin(),s.end());
return s==ans;
}
};
136. Single Number
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
ans=ans^nums[i];
}
return ans;
}
};
147. Insertion Sort List

此题为单链表插入排序的模拟,我们新建一个单链表,为了规范,依旧使用带头结点的单链表。注意,结点的使用需要重新定义,不能定义临时结点为外部变量,应设置为局部变量,当不用时下一次重新初始化(简单的更新会错误覆盖,即指针地址被错误更改)。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* }ListNode;
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* insertionSortList(ListNode* head) {
if(head==NULL||head->next==NULL)
return head;
// 申请一个单链表存储答案
ListNode* ans=new ListNode(0); // 指向新单链表最后一个结点
ListNode* p=new ListNode(0);; // 用来对往下推目标链表
ListNode* head1=new ListNode(0); // 新链表头结点,最终返回值
head1->next=ans;
ans->val=head->val;
p=head;
ListNode* t=new ListNode(0);
int ct=0,ct1=0,ct2=0;
while(p->next){ // 目标单链表非空
p=p->next;
if(p->val>ans->val){ // 新节点大了,插在后面
ListNode* temp=new ListNode(p->val);
ans->next=temp;
ans=temp; //ans始终指向最后一个结点
}
else{ //新的结点小了,插入相应的位置
t=head1;
while(t->next&&(t->next->val)<p->val){ // 4 2 1 3
t=t->next;
} // 插在t之后
ListNode* cur=new ListNode(p->val);
cur->next=t->next;
t->next=cur;
// temp->val=p->val; //该种写法不对,会被错误覆盖
// temp->next=t->next;
// t->next=temp;
}
}
return head1->next;
}
};
150. Evaluate Reverse Polish Notation
class Solution {
public:
// 20. 19
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {
stack<int> stack1;
for(int i=0;i<tokens.size();i++){
int temp=0,flag=1;
if(tokens[i].size()>=2&&tokens[i][0]=='-'){
flag=-1;
tokens[i].erase(0,1);
}
for(int j=0;j<tokens[i].size();j++){
temp=temp*10+tokens[i][j]-'0';
}
temp=temp*flag;
if(isdigit(tokens[i][0])) // 操作数则压入栈中
stack1.push(temp);
// 操作符则取栈顶的两个元素
else{
int b=stack1.top();stack1.pop();
int a=stack1.top();stack1.pop();
int ans=0;
switch(tokens[i][0]){
case '+':ans=a+b;break;
case '-':ans=a-b;break;
case '*':ans=a*b;break;
case '/':ans=a/b;break;
}
stack1.push(ans);
}
}
return stack1.top();
}
};