Day-8 YOLO3学习
Day-8 YOLO3(持续完善)
- 基础
- BoundingBox 预测
- 交并比与非极大值抑制
- YOLO3算法
- 预测
- 1.Darknet53
- 2.从特征层获取预测结果
- 3.预测结果解码
- 训练
- 1、loss值的计算
- 2、y_ture
- 3、loss值的计算过程
基础
BoundingBox 预测

图中3*3的方格中每个方格中的标签y为8维。
对于这里9个格子中任何一个,你都会得到一个8维输出向量,因为这里是3×3的网格,所以有9个格子,总的输出尺寸是3×3×8,所以目标输出是3×3×8。
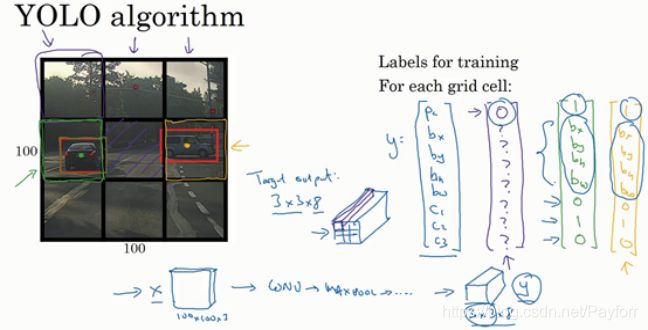
如果你现在要训练一个输入为100×100×3的神经网络,现在这是输入图像,然后你有一个普通的卷积网络,卷积层,最大池化层等等,最后你会有这个,选择卷积层和最大池化层,这样最后就映射到一个3×3×8输出尺寸。
这是在一次卷积中实现的。
交并比与非极大值抑制
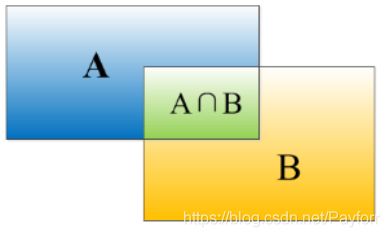
交并比称为IoU。在计算机检测任务中,如果IoU>=0.5,就说检测正确
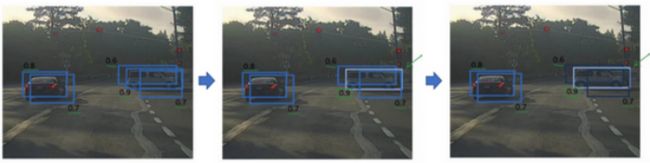
抛弃低概率的预测框,防止同一个目标被多次检测。
YOLO3算法
预测
1.Darknet53
2.从特征层获取预测结果
1、YOLO3会提取三个特征层,三个特征层的shape分别为(52,52,256)、(26,26,512)、(13,13,1024)
def yolo_body(inputs, num_anchors, num_classes):
# 生成darknet53的主干模型
feat1,feat2,feat3 = darknet_body(inputs)
darknet = Model(inputs, feat3)
# 第一个特征层
# y1=(batch_size,13,13,3,85)
x, y1 = make_last_layers(darknet.output, 512, num_anchors*(num_classes+5))
x = compose(
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(256, (1,1)),
UpSampling2D(2))(x)
x = Concatenate()([x,feat2])
# 第二个特征层
# y2=(batch_size,26,26,3,85)
x, y2 = make_last_layers(x, 256, num_anchors*(num_classes+5))
x = compose(
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(128, (1,1)),
UpSampling2D(2))(x)
x = Concatenate()([x,feat1])
# 第三个特征层
# y3=(batch_size,52,52,3,85)
x, y3 = make_last_layers(x, 128, num_anchors*(num_classes+5))
return Model(inputs, [y1,y2,y3])
2、三个特征层进行5次卷积处理,
处理完后一部分用于输出该特征层对应的预测结果:通过3×3的卷积与1×1的卷积来进行通道处理,来得到13×13(或26×26、52×52)的先验框的参数(下图)
下图y对应粉红色的框。
def make_last_layers(x, num_filters, out_filters):
# 五次卷积
x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters, (1,1))(x)
x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters*2, (3,3))(x)
x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters, (1,1))(x)
x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters*2, (3,3))(x)
x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters, (1,1))(x)
# 将最后的通道数调整为outfilter
y = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters*2, (3,3))(x)
y = DarknetConv2D(out_filters, (1,1))(y)
return x, y
一部分用于进行反卷积UmSampling2d后与其它特征层进行结合。
这一部分为特征金字塔
3、输出层的shape分别为(13,13,75),(26,26,75),(52,52,75),最后一个维度为75是因为该图是基于voc数据集的,它的类为20种,yolo3只有针对每一个特征层存在3个先验框,所以最后维度为3x25;
如果使用的是coco训练集,类则为80种,最后的维度应该为255 = 3x85,三个特征层的shape为(13,13,255),(26,26,255),(52,52,255)
输入N张416x416的图片,在经过多层的运算后,会输出三个shape分别为(N,13,13,255),(N,26,26,255),(N,52,52,255)的数据,对应每个图分为13x13、26x26、52x52的网格上3个先验框的位置。
3.预测结果解码
def generate(self):
#预训练好的模型的位置
model_path = os.path.expanduser(self.model_path)
assert model_path.endswith('.h5'), 'Keras model or weights must be a .h5 file.'
# 计算anchor数量
num_anchors = len(self.anchors)#9
num_classes = len(self.class_names)#80
# 载入模型,如果原来的模型里已经包括了模型结构则直接载入。
# 否则先构建模型再载入
try:
self.yolo_model = load_model(model_path, compile=False)
except:
#yolo_body建立yolo3的模型
self.yolo_model = yolo_body(Input(shape=(None,None,3)), num_anchors//3, num_classes)
#load_weights将模型的权重载入
self.yolo_model.load_weights(self.model_path)
else:
assert self.yolo_model.layers[-1].output_shape[-1] == \
num_anchors/len(self.yolo_model.output) * (num_classes + 5), \
'Mismatch between model and given anchor and class sizes'
print('{} model, anchors, and classes loaded.'.format(model_path))
# 画框设置不同的颜色
hsv_tuples = [(x / len(self.class_names), 1., 1.)
for x in range(len(self.class_names))]
self.colors = list(map(lambda x: colorsys.hsv_to_rgb(*x), hsv_tuples))
self.colors = list(
map(lambda x: (int(x[0] * 255), int(x[1] * 255), int(x[2] * 255)),
self.colors))
# 打乱颜色
np.random.seed(10101)
np.random.shuffle(self.colors)
np.random.seed(None)
self.input_image_shape = K.placeholder(shape=(2, ))
#yolo_eval将预测结果转换成图片上的位置
#self.yolo_model.output就是尚未处理的预测结果
boxes, scores, classes = yolo_eval(self.yolo_model.output, self.anchors,
num_classes, self.input_image_shape,
score_threshold=self.score, iou_threshold=self.iou)
return boxes, scores, classes
接下来看一下yolo_eval函数
def yolo_eval(yolo_outputs,
anchors,
num_classes,
image_shape,
max_boxes=20,
score_threshold=.6,
iou_threshold=.5):
# 获得特征层的数量
num_layers = len(yolo_outputs)
# 特征层1对应的anchor是678
# 特征层2对应的anchor是345
# 特征层3对应的anchor是012
anchor_mask = [[6,7,8], [3,4,5], [0,1,2]]
input_shape = K.shape(yolo_outputs[0])[1:3] * 32
boxes = []
box_scores = []
# 对每个特征层进行处理
#yolo_boxes_and_scores函数
for l in range(num_layers):
_boxes, _box_scores = yolo_boxes_and_scores(yolo_outputs[l], anchors[anchor_mask[l]], num_classes, input_shape, image_shape)
boxes.append(_boxes)
box_scores.append(_box_scores)
# 将每个特征层的结果进行堆叠
boxes = K.concatenate(boxes, axis=0)
box_scores = K.concatenate(box_scores, axis=0)
#通过查看得分来判断是否有东西
mask = box_scores >= score_threshold
max_boxes_tensor = K.constant(max_boxes, dtype='int32')
boxes_ = []
scores_ = []
classes_ = []
for c in range(num_classes):
# 取出所有box_scores >= score_threshold的框,和成绩
class_boxes = tf.boolean_mask(boxes, mask[:, c])
class_box_scores = tf.boolean_mask(box_scores[:, c], mask[:, c])
# 非极大抑制,去掉box重合程度高的那一些
nms_index = tf.image.non_max_suppression(
class_boxes, class_box_scores, max_boxes_tensor, iou_threshold=iou_threshold)
# 获取非极大抑制后的结果
# 下列三个分别是
# 框的位置,得分与种类
class_boxes = K.gather(class_boxes, nms_index)
class_box_scores = K.gather(class_box_scores, nms_index)
classes = K.ones_like(class_box_scores, 'int32') * c
boxes_.append(class_boxes)
scores_.append(class_box_scores)
classes_.append(classes)
boxes_ = K.concatenate(boxes_, axis=0)
scores_ = K.concatenate(scores_, axis=0)
classes_ = K.concatenate(classes_, axis=0)
return boxes_, scores_, classes_
下面看一下yolo_boxes_and_scores函数
def yolo_boxes_and_scores(feats, anchors, num_classes, input_shape, image_shape):
# 将预测值解码后调成真实值
# box_xy对应框的中心点偏移量
# box_wh对应框的宽和高
# -1,13,13,3,2; -1,13,13,3,2; -1,13,13,3,1; -1,13,13,3,80
#box_confidence置信度
#box_class_probs物体预测结果的可能性
box_xy, box_wh, box_confidence, box_class_probs = yolo_head(feats, anchors, num_classes, input_shape)
# 将box_xy、和box_wh调节成y_min,y_max,xmin,xmax
boxes = yolo_correct_boxes(box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape)
# 获得得分和box
boxes = K.reshape(boxes, [-1, 4])
box_scores = box_confidence * box_class_probs
box_scores = K.reshape(box_scores, [-1, num_classes])
return boxes, box_scores
下面进入yolo_head
def yolo_head(feats, anchors, num_classes, input_shape, calc_loss=False):
num_anchors = len(anchors)
# [1, 1, 1, num_anchors, 2]
#对先验框进行reshape
anchors_tensor = K.reshape(K.constant(anchors), [1, 1, 1, num_anchors, 2])
# 获得x,y的网格
# (13, 13, 1, 2)
grid_shape = K.shape(feats)[1:3] # height, width
grid_y = K.tile(K.reshape(K.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[0]), [-1, 1, 1, 1]),
[1, grid_shape[1], 1, 1])
grid_x = K.tile(K.reshape(K.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[1]), [1, -1, 1, 1]),
[grid_shape[0], 1, 1, 1])
grid = K.concatenate([grid_x, grid_y])
grid = K.cast(grid, K.dtype(feats))
# (batch_size,13,13,3,85)
feats = K.reshape(feats, [-1, grid_shape[0], grid_shape[1], num_anchors, num_classes + 5])
# 将预测值调成真实值
# box_xy对应框的中心点
# box_wh对应框的宽和高
box_xy = (K.sigmoid(feats[..., :2]) + grid) / K.cast(grid_shape[::-1], K.dtype(feats))
box_wh = K.exp(feats[..., 2:4]) * anchors_tensor / K.cast(input_shape[::-1], K.dtype(feats))
box_confidence = K.sigmoid(feats[..., 4:5])
box_class_probs = K.sigmoid(feats[..., 5:])
# 在计算loss的时候返回如下参数
if calc_loss == True:
return grid, feats, box_xy, box_wh
return box_xy, box_wh, box_confidence, box_class_probs
进入yolo_correct_boxes
在这个函数中将会去除图片的灰边且不会使图片失真,在处理过后求出框的位置
def yolo_correct_boxes(box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape):
box_yx = box_xy[..., ::-1]
box_hw = box_wh[..., ::-1]
#转换类型
input_shape = K.cast(input_shape, K.dtype(box_yx))
image_shape = K.cast(image_shape, K.dtype(box_yx))
new_shape = K.round(image_shape * K.min(input_shape/image_shape))
offset = (input_shape-new_shape)/2./input_shape
scale = input_shape/new_shape
box_yx = (box_yx - offset) * scale
box_hw *= scale
box_mins = box_yx - (box_hw / 2.)
box_maxes = box_yx + (box_hw / 2.)
boxes = K.concatenate([
box_mins[..., 0:1], # y_min
box_mins[..., 1:2], # x_min
box_maxes[..., 0:1], # y_max
box_maxes[..., 1:2] # x_max
])
boxes *= K.concatenate([image_shape, image_shape])
return boxes
经过这些 再看回yolo_eval函数中
yolo_eval最后返回的结果返回到yolo.py的self中
进入yolo.py的detect_image中
def detect_image(self, image):
start = timer()
# 调整图片使其符合输入要求
new_image_size = (image.width - (image.width % 32),
image.height - (image.height % 32))
boxed_image = letterbox_image(image, new_image_size)
image_data = np.array(boxed_image, dtype='float32')
image_data /= 255.
image_data = np.expand_dims(image_data, 0) # Add batch dimension.
# 预测结果
out_boxes, out_scores, out_classes = self.sess.run(
[self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes],
feed_dict={
self.yolo_model.input: image_data,
self.input_image_shape: [image.size[1], image.size[0]],
K.learning_phase(): 0
})
print('Found {} boxes for {}'.format(len(out_boxes), 'img'))
# 设置字体
font = ImageFont.truetype(font='font/simhei.ttf',
size=np.floor(3e-2 * image.size[1] + 0.5).astype('int32'))
thickness = (image.size[0] + image.size[1]) // 300
small_pic=[]
for i, c in list(enumerate(out_classes)):
predicted_class = self.class_names[c]
box = out_boxes[i]
score = out_scores[i]
top, left, bottom, right = box
top = top - 5
left = left - 5
bottom = bottom + 5
right = right + 5
top = max(0, np.floor(top + 0.5).astype('int32'))
left = max(0, np.floor(left + 0.5).astype('int32'))
bottom = min(image.size[1], np.floor(bottom + 0.5).astype('int32'))
right = min(image.size[0], np.floor(right + 0.5).astype('int32'))
# 画框框
label = '{} {:.2f}'.format(predicted_class, score)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
label_size = draw.textsize(label, font)
label = label.encode('utf-8')
print(label)
if top - label_size[1] >= 0:
text_origin = np.array([left, top - label_size[1]])
else:
text_origin = np.array([left, top + 1])
for i in range(thickness):
draw.rectangle(
[left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i],
outline=self.colors[c])
draw.rectangle(
[tuple(text_origin), tuple(text_origin + label_size)],
fill=self.colors[c])
draw.text(text_origin, str(label,'UTF-8'), fill=(0, 0, 0), font=font)
del draw
end = timer()
print(end - start)
return image
训练
1、loss值的计算
在计算loss的时候,实际上是y_pre和y_true之间的对比
2、y_ture
y_true就是一个真实图像中,它的每个真实框对应的(13,13)、(26,26)、(52,52)网格上的偏移位置、长宽与种类。其仍需要编码才能与y_pred的结构一致
在yolo3中,其使用了一个专门的函数用于处理读取进来的图片的框的真实情况。
def preprocess_true_boxes(true_boxes, input_shape, anchors, num_classes):
3、loss值的计算过程
在得到了y_pre和y_true后怎么对比呢?不是简单的减一下就可以的呢。
loss值需要对三个特征层进行处理,这里以最小的特征层为例。
1、利用y_true取出该特征层中真实存在目标的点的位置(m,13,13,3,1)及其对应的种类(m,13,13,3,80)。
2、将yolo_outputs的预测值输出进行处理,得到reshape后的预测值y_pre,shape分别为(m,13,13,3,85),(m,26,26,3,85),(m,52,52,3,85)。还有解码后的xy,wh。
3、获取真实框编码后的值,后面用于计算loss,编码后的值其含义与y_pre相同,可用于计算loss。
4、对于每一幅图,计算其中所有真实框与预测框的IOU,取出每个网络点中IOU最大的先验框,如果这个最大的IOU都小于ignore_thresh,则保留,一般来说ignore_thresh取0.5,该步的目的是为了平衡负样本。
5、计算xy和wh上的loss,其计算的是实际上存在目标的,利用第三步真实框编码后的的结果和未处理的预测结果进行对比得到loss。
6、计算置信度的loss,其有两部分构成,第一部分是实际上存在目标的,预测结果中置信度的值与1对比;第二部分是实际上不存在目标的,在第四步中得到其最大IOU的值与0对比。
7、计算预测种类的loss,其计算的是实际上存在目标的,预测类与真实类的差距。
其实际上计算的总的loss是三个loss的和,这三个loss分别是:
实际存在的框,编码后的长宽与xy轴偏移量与预测值的差距。
实际存在的框,预测结果中置信度的值与1对比;实际不存在的框,在上述步骤中,在第四步中得到其最大IOU的值与0对比。
实际存在的框,种类预测结果与实际结果的对比。
