MyBatis——动态SQL、if、where、set、foreach、sql片段
目录
- 一、动态SQL
- 1、if
- 2、choose、when、otherwise
- 3、trim(where,set)
- 3.1、where
- 3.2、set
- 3.3、trim
- 4、foreach
- 5、sql、include、bind
![]()
MyBatis源码及资料: https://github.com/coderZYGui/MyBatis-Study
MyBatis系列
- MyBatis — ORM思想、MyBatis概述、日志框架、OGNL
- MyBaits — MyBatis的CRUD操作、别名配置、属性配置、查询结果映射、Mapper组件、参数处理、注解开发
- MyBatis — 动态SQL、if、where、set、foreach、sql片段
- MyBatis — 对象关系映射、延迟加载、关联对象的配置选择
- MyBatis — 缓存机制、EhCache第三方缓存
- MyBatis — MyBatis Generator插件使用(配置详解)
一、 动态SQL
跳转到目录
-
MyBatis的强大特性之一便是它的
动态SQL。 -
动态sql是mybatis中的一个核心,什么是动态sql?
动态sql即对sql语句进行灵活操作,通过表达式进行判断,对sql进行灵活拼接、组装。 -
如果你有使用JDBC或其他类似框架的经验,你就能体会到根据不同条件拼接SQL语句有多么痛苦。
-
拼接的时候要确保不能忘了必要的空格, 还要注意省掉列名列表最后的逗号。利用动态SQL这一特性可以彻底摆脱这种痛苦。
-
通常使用动态SQL不可能是独立的一部分, MyBatis当然使用一-种强大的动态SQL语言来改进这种情形,这种语言可以被用在任意的SQL映射语句中。
-
和标签库
JSTL很像
1、if
跳转到目录
- if元素用于判断,一般用作
是否应该包含某一个查询条件
测试类
/**
* 查询工资大于等于1000的员工
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
EmployeeMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
BigDecimal minSalary = new BigDecimal("1001");
List<Employee> employees = mapper.query1(minSalary);
for (Employee employee : employees) {
System.out.println(employee);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
/**
* 查询工资在1000-2000之间的员工
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
EmployeeMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
BigDecimal minSalary = new BigDecimal("1000");
BigDecimal maxSalary = new BigDecimal("2000");
List<Employee> employees = mapper.query2(minSalary, maxSalary);
for (Employee employee : employees) {
System.out.println(employee);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
Employee接口
/**
* 查询工资大于1000的员工
*/
List<Employee> query1(@Param("minSalary") BigDecimal minSalary);
/**
* 查询工资在1000-2000之间
* @param minSalary
* @param maxSalary
* @return
*/
List<Employee> query2(
@Param("minSalary") BigDecimal minSalary,
@Param("maxSalary") BigDecimal maxSalary
);
EmployeeMapper.xml
<select id="query1" resultType="Employee">
SELECT * FROM employee
<if test="minSalary!=null">
WHERE salary >= #{minSalary}
if>
select>
<select id="query2" resultType="Employee">
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE 1 = 1
<if test="minSalary!=null">
AND salary >= #{minSalary}
if>
<if test="maxSalary!=null">
AND salary <= #{maxSalary};
if>
select>
注意: 如果minSalary和maxSalary条件是可选择的,也就是说当minSalary传入null时,SQL就会出现问题.就不确定使用WHERE还是AND来连接查询条件.
解决方案: 使用WHERE 1 = 1方式,其他的查询条件都使用AND或OR连接,但是WHERE 1 = 1 会影响查询性能.
2、choose、when、otherwise
跳转到目录
- 相当于switch判断
测试方法
/**
* 查询指定部门的员工信息
*/
@Test
public void test3(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
EmployeeMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
BigDecimal minSalary = new BigDecimal("100");
BigDecimal maxSalary = new BigDecimal("1000");
List<Employee> employees = mapper.query3(minSalary, maxSalary, 20L);
for (Employee employee : employees) {
System.out.println(employee);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
Employee接口中的方法
List<Employee> query3(
@Param("minSalary") BigDecimal minSalary,
@Param("maxSalary") BigDecimal maxSalary,
@Param("deptId") Long deptId
);
EmployeeMapper.xml
<select id="query3" resultType="Employee">
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE 1 = 1
<if test="minSalary!=null">
AND salary >= #{minSalary}
if>
<if test="maxSalary!=null">
AND salary <= #{maxSalary}
if>
<choose>
<when test="deptId > 0">AND deptId = #{deptId}when>
<otherwise>AND deptId IS NOT NULLotherwise>
choose>
select>
3、trim(where,set)
跳转到目录
3.1、where
跳转到目录
- where元素: 判断查询条件是否有WHERE关键字,如果没有,则在第一个查询条件之前,插入一个WHERE, 如果发现查询条件AND 或者 OR开头,也会把第一个查询条件前的AND/OR 替换成WHERE
- 这种方式避免了 WHERE 1 = 1的形式
查询指定部门的员工信息
<select id="query3" resultType="Employee">
SELECT * FROM employee
<where>
<if test="minSalary!=null">
AND salary >= #{minSalary}
if>
<if test="maxSalary!=null">
AND salary <= #{maxSalary}
if>
<choose>
<when test="deptId > 0">AND deptId = #{deptId}when>
<otherwise>AND deptId IS NOT NULLotherwise>
choose>
where>
select>
3.2、set
跳转到目录
- set元素和where元素相似,也能根据set中的sql动态的去掉
最后的逗号,并在前面添加set关键字,如过没有内容,也会选择忽略set语句.
应用场景
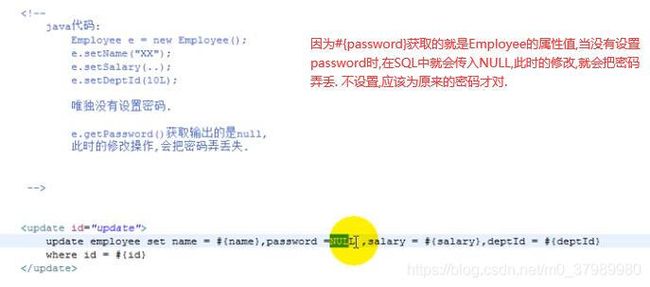
因为password没有设置值,所以就要采用if来动态判断password是否为空,如果为空,则不拼接,但是此时会出现问题,上面拼接的语句最后会存在一个,.

这个时候就采用set元素来操作了,可以去掉后面的,.
测试方法
/**
* 更新指定id的员工信息
*/
@Test
public void test4(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
EmployeeMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(6L);
employee.setSn("6238");
// employee.setName("桂阳");
employee.setSalary(new BigDecimal("8888"));
int update = mapper.update(employee);
if (update > 0){
System.out.println("成功修改"+update+"条用户信息!");
}
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
EmployeeMapper接口
int update(Employee employee);
EmployeeMapper.xml
<update id="update">
UPDATE employee
<set>
<if test="name!=null">
name = #{name},
if>
<if test="sn!=null">
sn = #{sn},
if>
<if test="salary!=null">
salary = #{salary},
if>
set>
WHERE id = #{id};
update>
3.3、trim
跳转到目录
trim是更强大的格式化SQL的标签:
<trim prefix="" prefixOverrides="" suffix="" suffixOverrides="">
trim>
前提如果trim元素包含内容返回一个字符串,则
-
prefix : 在这个字符串之前插入prefix属性值
-
prefixOverrides : 字符串内容以prefixOverrides中的内容开头(可以包含管道符号|),那么使用prefix属性值替换内容的开头.
-
suffix : 在这个字符串之后插入suffix属性值
-
suffixOverrides : 字符串的内容以suffixOverrides中的内容结尾(可以包含管道符号|),那么使用suffix属性值替换内容的结尾;

-
使用where等价于
<trim prefix="WHERE" prefixOverrides="AND |OR "> trim><select id="query3" resultType="Employee"> SELECT * FROM employee <trim prefix="WHERE" prefixOverrides="AND|OR"> <if test="minSalary!=null"> AND salary >= #{minSalary} if> <if test="maxSalary!=null"> AND salary <= #{maxSalary} if> <choose> <when test="deptId > 0">AND deptId = #{deptId}when> <otherwise>AND deptId IS NOT NULLotherwise> choose> trim> select>注意: 此时AND后面有一个空格
-
使用set等价于
<trim prefix="WHERE" suffix="" suffixOverrides=","> trim>trim prefix="SET" suffix="" suffixOverrides=","> <if test="name!=null"> name = #{name}, if> <if test="sn!=null"> sn = #{sn}, if> <if test="salary!=null"> salary = #{salary}, if> trim>
4、foreach
跳转到目录
SQL中有时候使用IN关键字,如WHERE id IN(10,20,30),此时可以使用${ids}直接拼接SQL ,但是会导致SQL注入问题,要避免SQL注入,只能使用#{}方式,此时就可以配合使用foreach元素了。foreach元素用于迭代-个集合/数组, 通常是构建在IN运算符条件中。
- foreach元素:
- collection属性:表示对哪一个集合或数组做迭代
如果参数是数组类型,此时Map的key为array;
如果参数是List类型,此时Map的key为list; - open属性:在迭代集合之前,拼接什么符号
- close属性:在迭代集合之后,拼接什么符号
- separactor属性:在迭代元素时,每一个元素之间使用什么符号分割开来
- item属性:被迭代的每一个元素的变量
- index属性:迭代的索引
- collection属性:表示对哪一个集合或数组做迭代
需求: 批量插入语法
注意: 当传递一个List对象或数字对象参数给MyBatis时,(这里可以看前面讲MyBatis参数处理的部分),MyBatis会自动把它包装到一个Map中,当是List对象时会以list作为key, 数组对象会以array作为key. 一般使用Param注解设置key名.
EmployeeMapperTest测试类
/**
* 批量删除指定id的员工信息
*/
@Test
public void test5(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
EmployeeMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
mapper.batchDelete(new Long[]{10L,20L,30L});
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
/**
* 批量插入员工信息
*/
@Test
public void test6(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
EmployeeMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
List<Employee> list = new ArrayList<Employee>();
list.add(new Employee(null, "周", "10001", new BigDecimal("5555.00"), 50L));
list.add(new Employee(null, "吴", "10002", new BigDecimal("6666.00"), 60L));
list.add(new Employee(null, "郑", "10003", new BigDecimal("7777.00"), 70L));
int count = mapper.batchInsert(list);
if (count > 0){
System.out.println("成功插入了:"+count+"条用户信息!");
}
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
EmployeeMapper接口
/**
* 使用foreach元素批量删除
* @param ids
* param注解原理还是Map,Map的key
*/
void batchDelete(@Param("ids") Long[] ids);
/**
* 批量插入用户信息
* @param list
* @return
* 当参数是数组或集合时,一般要加上@Param注解,写死
*/
int batchInsert(@Param("emps") List<Employee> emps);
EmployeeMapper.xml
<delete id="batchDelete">
DELETE FROM employee WHERE id IN
<foreach collection="ids" open="(" close=")" separator="," item="id">
#{id}
foreach>
delete>
<insert id="batchInsert">
INSERT INTO employee(id, name, sn, salary, deptId) VALUES
<foreach collection="emps" separator="," item="e">
(#{e.id}, #{e.name}, #{e.sn}, #{e.salary}, #{e.deptId})
foreach>
insert>
5、sql、include、bind
跳转到目录
- 使用sql可以把相同的sql片段起一个名字,并使用include在sql任意位置使用.
- bind: 使用OGNL表达式创建一个变量,并将其绑定在上下文中.
需求: 按照员工的关键字、工资范围、所属部门来查询
需求: 按照查询条件了查询员工的人数
注意: 要封装一个查询条件类,用来设置条件使用
EmployeeQueryObject 封装查询条件的
package com.sunny.query;
import lombok.Data;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
/**
* 封装员工的高级查询信息--->封装查询条件
*/
@Data
public class EmployeeQueryObject {
private String keyword; // 根据keyword来查询,员工名字或编号
private BigDecimal minSalary; // 最低工资
private BigDecimal maxSalary; // 最高工资
private Long deptId = -1L; // 部门ID,缺省为-1;表示所有部门
/**
* 重写keyword的get方法,如果
* @return
*/
public String getKeyword(){
// 防止传的条件是空或空字符
return empty2null(keyword);
}
// 如果字符串为空串,也应该设置为null
private String empty2null(String str){
return hasLength(str) ? str : null;
}
// 判断这个字符串是否有数据
private boolean hasLength(String str){
// str不为空 并且 str trim()后不和""相等
/**
* 判断非空,假如str为zy
* zy!=null ---> true
* "".equals(zy.trim()) --> false
* !"".equals(zy.trim()) ---> !false ---> true
* 所以
* true && true ---> true 不为空
*/
return str!=null && !"".equals(str.trim());
}
}
EmployeeMapper接口
public interface EmployeeMapper {
/**
* 根据查询条件来查询员工
* @param qo 封装查询条件的类对象
* @return
*/
List<Employee> queryForList(EmployeeQueryObject qo);
/**
* 根据查询条件来查询员工人数
* @param qo 封装查询条件的类对象
* @return
*/
int queryForEmpCount(EmployeeQueryObject qo);
}
EmployeeMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.sunny.dao.EmployeeMapper">
<sql id="Base_where">
<where>
<if test="keyword!=null">
<bind name="keywordLike" value="'%' + keyword +'%'"/>
AND (name LIKE #{keywordLike} OR sn LIKE #{keywordLike})
if>
<if test="minSalary!=null">
AND salary >= #{minSalary}
if>
<if test="maxSalary!=null">
AND salary <=#{maxSalary}
if>
<if test="deptId!=null">
AND deptId = #{deptId}
if>
where>
sql>
<select id="queryForList" resultType="Employee">
SELECT * FROM employee
<include refid="Base_where">include>
select>
<select id="queryForEmpCount" resultType="int">
SELECT count(*) FROM employee
<include refid="Base_where">include>
select>
mapper>
EmployeeMapperTest测试类
public class EmployeeMapperTest {
/**
* 按照员工的关键字、工资范围、所属部门来查询
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
EmployeeMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
EmployeeQueryObject qo = new EmployeeQueryObject();
qo.setKeyword("2");
qo.setMinSalary(new BigDecimal("1000"));
qo.setMaxSalary(new BigDecimal("9000"));
qo.setDeptId(30L);
List<Employee> employees = mapper.queryForList(qo);
for (Employee employee : employees) {
System.out.println(employee);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
/**
* 按照查询条件了查询员工的人数
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
EmployeeMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
EmployeeQueryObject qo = new EmployeeQueryObject();
qo.setKeyword("2");
qo.setMinSalary(new BigDecimal("1000"));
qo.setMaxSalary(new BigDecimal("9000"));
qo.setDeptId(30L);
int i = mapper.queryForEmpCount(qo);
if (i > 0) {
System.out.println("符合条件的一共有:"+i+"人!");
}
sqlSession.close();
}
}


