深入理解spring(spring的beanFactory与spring的factoryBean)(八 )
回顾:
上一篇我们自己写了山寨版本的SpringIOC容器,主要讲了。手动装配与自动装配的实现方式。还有XML得方式
这一篇主要讲,springIOC的注解实现方式
讲注解之前,我们先用一个问题引入,factoryBean与BeanFactory的区别有哪些?
相信 很多老哥,在面试中。或者网上都有看到这样的问题。
(面试)先来了解,什么是BeanFactory?
beanFactory是spring中产生类的一个工厂。
spring中如何声明一个bean?
1、XML方式
3、@service
4、声明一个类,实现factoryBean
先来看一段代码啊!
1、声明一个类,实现FactoryBean 将该类交给Spring管理
//将该类交给Spring管理
@Component("DaoFactoryBean")
public class DaoFactoryBean implements FactoryBean{
public void getTest(){
System.out.println("getTest");
}
@Override
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
return new TempFactoryBean();
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return TempFactoryBean.class;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
2、从容器中取出该类 调用getTest()方法,结果报错,类型转换异常。
但是我们明明容器中放的就是这个类呢,为什么会类型转换异常呢?
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
DaoFactoryBean daoFactoryBean = (DaoFactoryBean) annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("DaoFactoryBean");
daoFactoryBean.getTest();
}
-------------控制台输出----------------------
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassCastException: com.myspring.dao.impl.TempFactoryBean cannot be cast to com.myspring.dao.impl.DaoFactoryBean
at com.myspring.test.Test.main(Test.java:18)
3、在看,我们将GetBean 方法中加入一个“&”符号,这个时候。控制台又输出正常了?
这个是怎么回事呢?
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
DaoFactoryBean daoFactoryBean = (DaoFactoryBean) annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("&DaoFactoryBean");
daoFactoryBean.getTest();
}
-------------控制台输出----------------------
getTest
4、在看,我们将getBean(“DaoFactoryBean”) 强转成 TempFactoryBean。调用test方式这个时候输出又正常了?
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
TempFactoryBean daoFactoryBean = (TempFactoryBean) annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("DaoFactoryBean");
daoFactoryBean.test();
}
}
-------------控制台输出----------------------
test
到底是怎么回事呢、?为什么实现了FactoryBean 接口要想获取该对象就得加一个&符号呢?
通过观察我们可以发现,spring是通过FactoryBean 的getObject()去获取对象的。要想获取当前对象,就得在前面加上一个&符号?说明实现了FactoryBean 接口的类,在spring容器中有两个对象,一个是getObject()返回的对象,还有一个是当前对象。
那么Spring为什么要这样设计呢?
先看一段源码,我们调用getBean方法的时候。
TempFactoryBean daoFactoryBean = (TempFactoryBean) annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("DaoFactoryBean");
通过条件断点进入,可以发现。spring要通过name去获取beanName。但是name跟beanName明明相等,为什么还要这么做?不禁要问,spring是不是傻?
这里通过Name获取BeanName主要有两个原因:
1、name可能会以&字符来区分,调用者是想回去实现FactoryBean本身的对象,而非factoryBean的getobject所创建的对象。
2、别名的问题,我们都知道spring.XML的方式,可以给类配置一个别名(这里就不做演示。大家可以自己去查一些资料)
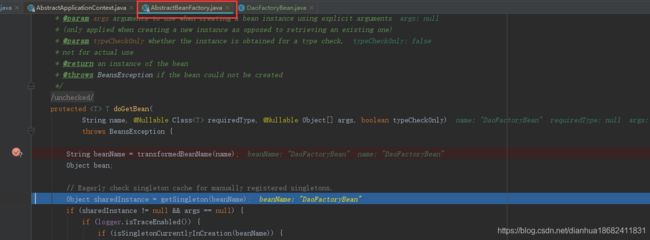
我们传入&DaoFactoryBean的时候 beanName跟name就不相等了。
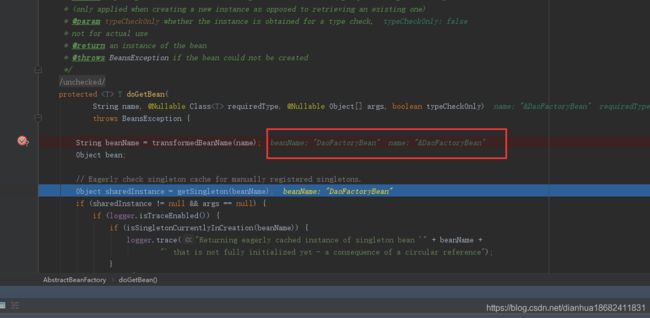
再看这段源码,如果name不以&开头则直接return 否则进入下面的逻辑,截取&的部分
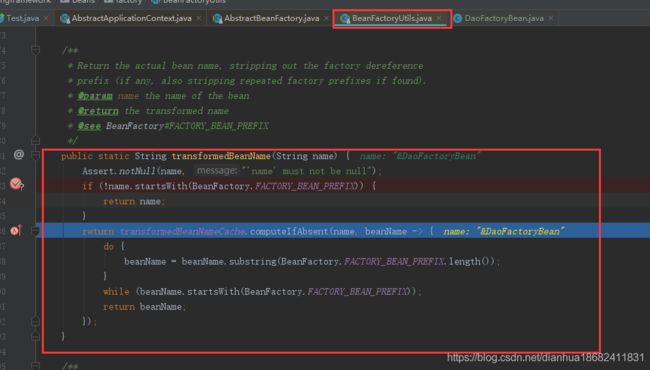
现在大家应该明白spring为什么要这样设计,也可以下去尝试,若没实现FactoryBean 注入的名称首字母只要带&这个字符都会报错,因为spring会认为你要去查找 FactoryBean 本身,会找不到。
那么FactoryBean 有哪些用途呢?
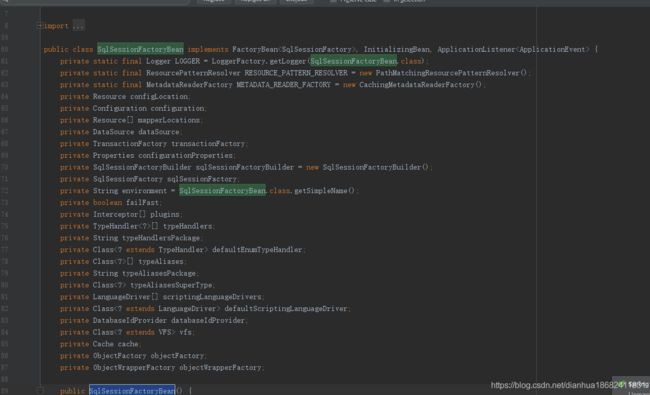
下面这一段代码,大家应该不陌生,下面是配置mybatis的SQLSessionFactoryBean的核心配置。
1、大家试想一下,如果一个外部的框架,或者自己写的类,不属于spring。怎么将对象交给spring管理。
A:@Bean B:spring.xml C:service 注解
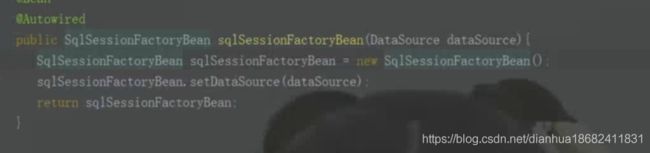
2、如果这个类相当复杂呢,这个类又依赖了,外部的其他类。是不是还得把这个类依赖的其他类信息,常量信息。全部实例化传入,才能得到我们要用的类的对象。
如下,就比如Mybatis的 SqlSessionFactoryBean,如果我们要用这个类。不得全部实现它依赖的所有类,常量信息。我们根本维护不了这个类,里面依赖太多东西。
那么现在我们该怎么办?
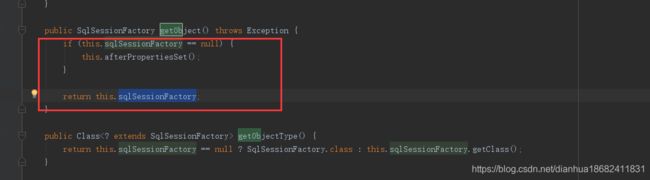
再看这一段源码,getObject()它只用把当前对象交给调用者就行了。。他自己都把他的依赖都完成了。
我们只用传入一个数据源。就可以使用了。。这就是mybatis通过FactoryBean接口的无缝对接。
以上只是FactoryBean使用的一个场景,包括hibernate也是通过这种方式完成无缝对接。在我们项目实战中,如果一个项目。依赖到另一个项目的类或者对象,我们要交给spring来管理。或者提供简单的实现方式,同样可以使用这样的方式。 现在大家应该对spring为什么要这么设计,有更深层次的理解了吧。
总结一下: 那么什么是FactoryBean 什么是BeanFactory?
FactoryBean 上面已经讲了,他是一个由spring管理的对象,但是它也是一个特殊的对象。特殊在于,他有一个getObject方法,他也能创建出一个对象。所以需要用&来区分,是他的对象本身,还是它创造的对象
BeanFactory 其实是我们的spring工厂。它只能创造对象。我们的annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean就是由他创造出来的对象。。它不受spring管理。
初始化Spring的环境,有哪些方式?
1、xml 方式 需要借助:ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
2、javaConfig方式 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
3、 Annotation 方式。需要借助XML 或者javaConfig才能完成初始化
以上方式,最后都会做一个动作就是类的扫描。然后把我们交给spring管理的类,进行实例化。
如果,我们只想让spring管理我们的部分类,或者某一个类的时候,该怎么办呢?
XML的方式,可以直接声明一个类。然后交给spring来管理。。
那么注解的方式。该怎么做呢?
如下图所以,我们通过看spring的源码,发现spring也是通过register,refresh方法完成扫描 与注册。
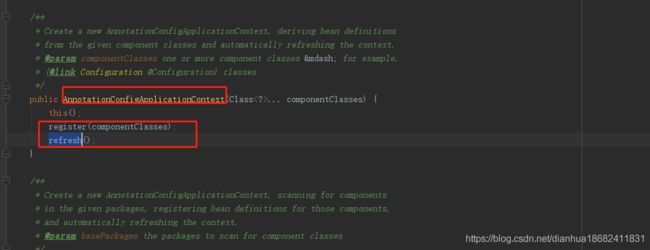
如以下代码片段,注解方式我们也可以只注册一个UserDaoImpl 指定它交给spring来管理。其他的类,不交给spring来管理。。
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
annotationConfigApplicationContext.register(UserDaoImpl.class);
annotationConfigApplicationContext.refresh();
UserDaoImpl bean = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(UserDaoImpl.class);
bean.query();
System.out.println(annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(UserDaoImpl.class).getClass().getName());
-------------控制台输出----------------------
假装查询数据库
com.bing.li.dao.UserDaoImpl
如以下代码片段,注解方式。我们也可以指定spring去扫描哪一个包下的类信息。。
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
annotationConfigApplicationContext.scan("com.myspring.dao");
annotationConfigApplicationContext.refresh();
UserDaoImpl1 bean = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(UserDaoImpl1.class);
bean.query();
System.out.println(annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(UserDaoImpl1.class).getClass().getName());
上一篇 我们已经讲了山寨版本,springXML方式 实例化对象的方式。当时我们是将 ,spring实例化好的对象,存放在Map中,实际上spring 不是用Map来存放,它是用一个对象来描述。。因为我们的类中会有很多信息,map不能完全描述出来,比如是否懒加载,是否加描述的注解,等等等。。。
如下图,spring源码部分,我们传入一个class com.bing.li.dao.UserDaoImpl ,Spring要如来来描述这个类的信息。Map显然是完全不够的。。
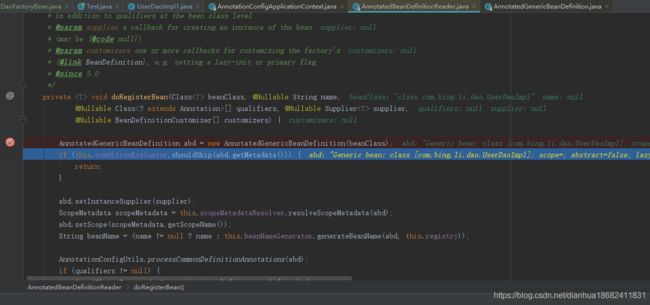
如下图,spring中描述了类的 这么多信息。什么spring是用对象来存储。。这是一种数据结构。。后面源码部分会做一些介绍。。
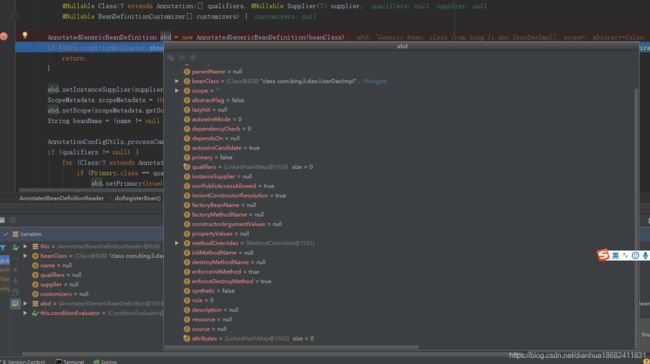
spring doRegisterBean方法的源码。首先是描述类信息,然后。对类做一些判断,比如下面 懒加载啊。qualifier注解的判断啊,等等等。。。
private <T> void doRegisterBean(Class<T> beanClass, @Nullable String name,
@Nullable Class<? extends Annotation>[] qualifiers, @Nullable Supplier<T> supplier,
@Nullable BeanDefinitionCustomizer[] customizers) {
AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition abd = new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(beanClass);
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(abd.getMetadata())) {
return;
}
abd.setInstanceSupplier(supplier);
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(abd);
abd.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = (name != null ? name : this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(abd, this.registry));
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(abd);
if (qualifiers != null) {
for (Class<? extends Annotation> qualifier : qualifiers) {
if (Primary.class == qualifier) {
abd.setPrimary(true);
}
else if (Lazy.class == qualifier) {
abd.setLazyInit(true);
}
else {
abd.addQualifier(new AutowireCandidateQualifier(qualifier));
}
}
}
if (customizers != null) {
for (BeanDefinitionCustomizer customizer : customizers) {
customizer.customize(abd);
}
}
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(abd, beanName);
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
试想一下,我们只传给spring一个包名称、、spring是怎么完成扫描的呢?怎么把包下带了,@service 或者其他注解的类都拿出来的呢?
通过以下源码片段,发现。。我们传入一个包名com.myspring.dao 以上一行代码 就能拿到,该包下 添加过注解的类。。以及类的描述。。拿到类的全信息。。要实例化,就只剩反射就完事了。当然spring做得更复杂。我们先学习核心的部分。。。那我们就一探究竟。。spring这一行代码到底做了什么事。
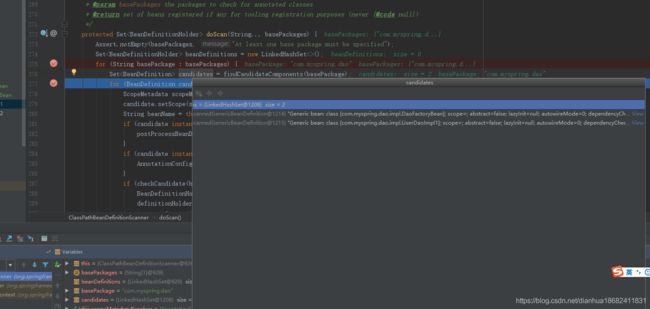
以下代码 就是spring 核心扫描。。包下面文件的类。。。
第一步,spring组装好packageSearchPath 这里的包的全路径就是 classpath*:com/myspring/dao/**/*.class
第二步。Resource[] resources = getResourcePatternResolver().getResources(packageSearchPath);
这一段代码就是获取这个路径下的所有文件。
第三步。遍历 判断文件是否带有 @service注解 等等其他的一些判断。。如果是我们要扫描的类则加入到上面
Set candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>();这个 集合中然后返回。。
private Set<BeanDefinition> scanCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>();
try {
String packageSearchPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX +
resolveBasePackage(basePackage) + '/' + this.resourcePattern;
Resource[] resources = getResourcePatternResolver().getResources(packageSearchPath);
boolean traceEnabled = logger.isTraceEnabled();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
for (Resource resource : resources) {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Scanning " + resource);
}
if (resource.isReadable()) {
try {
MetadataReader metadataReader = getMetadataReaderFactory().getMetadataReader(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(metadataReader)) {
ScannedGenericBeanDefinition sbd = new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(metadataReader);
sbd.setSource(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(sbd)) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Identified candidate component class: " + resource);
}
candidates.add(sbd);
}
else {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Ignored because not a concrete top-level class: " + resource);
}
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not matching any filter: " + resource);
}
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to read candidate component class: " + resource, ex);
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not readable: " + resource);
}
}
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("I/O failure during classpath scanning", ex);
}
return candidates;
}
总结,spring扫描的部分 核心就是干了这三件事。现在了解了spring的扫描部分。。我们拿到扫描的类的全路劲,剩下的就是反射,实例化就行了。我们可以试着来写一个山寨版本的
步骤o如下:
第一步先,自定义一个注解。@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 表示运行时注解 我们用得最多 的 spring的叫@service 我们可以叫 serviceAA
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ServiceAA {
public String value();
}
第二步 ,随便写几个类。加上我们自定义的注解。
@ServiceAA("TempFactoryBean")
public class TempFactoryBean {
public void test(){
System.out.println("test");
}
}
第三步,我们自己写一个AnnotationConfigApplicationContext类,scan方法。。传入包路径。扫描包下面带有serviceAA注解的类信息。然后把它实例化。。山寨版代码如下。
public class AnnotationConfigApplicationContext {
public void scan(String basePackage){
//拿到代码的当前路劲
String rootPath = this.getClass().getResource("/").getPath();
String basePackagePath =basePackage.replaceAll("\\.","\\\\");
//当前路劲加上我们 传过来的包名,就是我们要扫描的类信息
File file = new File(rootPath+"//"+basePackagePath);
String names[]=file.list();
for (String name : names) {
if (name.endsWith(".class")) {
name = name.replaceAll(".class", "");
try {
Class clazz = Class.forName(basePackage + "." + name);
//判断是否属于 ServiceAA注解的类
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(ServiceAA.class)) {
ServiceAA luban = (ServiceAA) clazz.getAnnotation(ServiceAA.class);
System.out.println("拿到类的名称" + luban.value());
System.out.println("实例化类对象。" + clazz.newInstance());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
测试
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
applicationContext.scan("com.myspring.dao.impl");
-------------控制台输出----------------------
拿到类的名称TempFactoryBean
实例化类对象。com.myspring.dao.impl.TempFactoryBean@f5f2bb7
总结:beanfactory 与 factoryBean 这个很重要。。上面已经讲过,我们自己实现 Annotation注解扫描。实例化、、是为了后面。。会写一些更深层次的 源码分析。。最近也还在整理中。我觉得有必要先出一篇。。我们自己的方式。直接上深层次的源码。spring 不熟悉的朋友,未必能理解。。
源代码地址