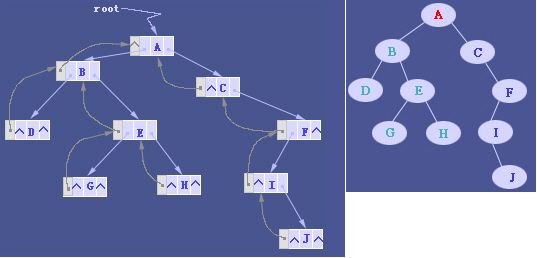
数据结构11.二叉树
引言
二叉树是一种非常重要的非线性结构,许多实际问题抽象出来的数据结构往往都是二叉树的形式.与树相比,二叉树更加规范并更具确定性,并且实现二叉树的存储结构及其算法都较为简单,因此二叉树就显得格外重要.
在计算机科学中,二叉树(Binary tree)是每个节点最多有两个子树的树结构。通常子树被称作“左子树”(left subtree)和“右子树”(right subtree)。二叉树常被用于实现二叉查找树和二元堆积。
一.二叉树的定义
I. 定义:
二叉树是n(n>=0)个节点的有限集合,它或者是空树(n=0),或者是由一个根节点及两颗互不相交,分别称作该根节点的"左子树"和"右子树"的二叉树构成.
II. 特点:
二叉树与树的定义一样,都是递归的.
并且,二叉树具有如下两个特点:
1. 二叉树不存在度大于2的结点.
2. 二叉树每个节点至多有两棵子树且有左,右之分,次序不能颠倒.
III. 区别:
与树的区别:
1. 树的节点个数至少为1,而二叉树的节点个数可以为0;
2. 树中节点的最大度数没有限制,而二叉树节点的最大度数为2;
3. 树的节点无左、右之分,而二叉树的节点有左、右之分。(二叉树任何一个节点的子树都要区分左右子数,即使这个节点只有一棵子树时也要明确指出它是左子树还是右子树.)
IV. 形态:
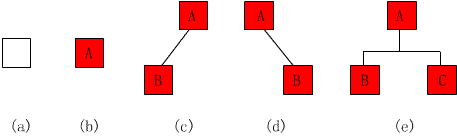
根据二叉树的定义,二叉树有如图的五种形态:
a. 为空二叉树(用Φ表示∅Ø )
b. 为只有一个根节点而无子树的二叉树
c. 为只有左子树而无右子树的二叉树
d. 为只有右子树而无左子树的二叉树
e. 为左右子树均非空的二叉树
v. 类型
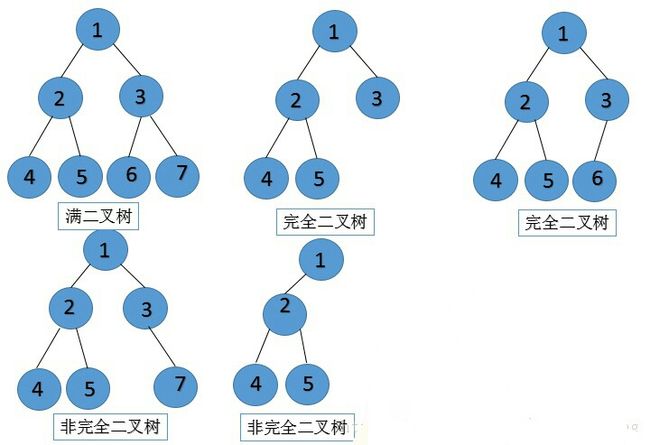
1). 满二叉树
我们将称具有如下性质的二叉树为满二叉树:
1. 不存在度为1的节点,即所有分支节点都有左子树和右子树.
2. 所有叶子节点都在同一层上.
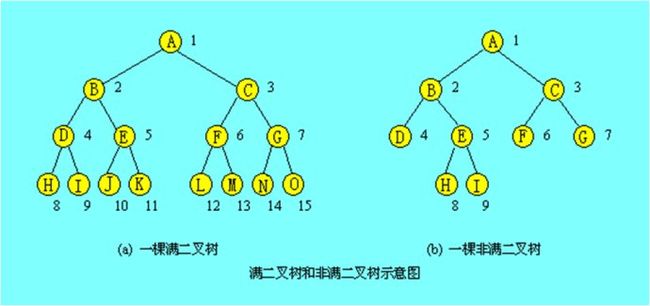
图a即为满二叉树,图b则不是满二叉树,因为其叶子节点不在同一层上.
一棵深度为k,且有 2^(k-1)个节点的二叉树,称为满二叉树(Full Binary Tree)。这种树的特点是每一层上的节点数都是最大节点数。
2). 完全二叉树
而在一棵二叉树中,除最后一层外,若其余层都是满的,并且最后一层或者是满的,或者是在右边缺少连续若干节点,则此二叉树为完全二叉树(Complete Binary Tree)。
对一棵具有n个节点的二叉树,将树中的节点按自上而下,从左向右的顺序进行编号,如果编号i(1 ≤ i ≤ n)的节点与满二叉树中的编号为i的节点在二叉树中的位置相同,则这棵二叉树成为完全二叉树.
二.二叉树的性质
(向下取整的运算称为Floor,用数学符号⌊⌋表示,
⌊x⌋表示不大于x的最大整数,如⌊3.7⌋=7;
与之相对的,向上取整的运算称为Ceiling,用数学符号⌈⌉表示。⌈x⌉表示不小于x的最小整数,⌈3.7⌉=4) ;
性质1.
非空二叉树的第i层上最多有2^(i-1)个节点(i≥1);性质2.
深度为k的二叉树最多有2^k-1个结点(k≥1),最少有h个结点;性质3.
对于任意一棵非空二叉树,如果其叶结点(度为0)数为n0,而度数为2的结点总数为n2,则n0=n2+1;性质4.
具有n个结点的完全二叉树的深度为⌊log2n⌋+1;性质5.
有n个结点的完全二叉树各结点如果按层次自上而下且每层从左到右用顺序方式存储,从1到n进行编号,则对任意序号为i的结点有如下关系:
1. 如果i>1,则其父结点的编号为⌊i/2⌋;若i=1,则i为根节点序号;
2. 如果2i ≤ n,则其左儿子(即左子树的根结点)的编号为2i;否则i无左儿子;
3. 如果2i+1 ≤ n,则其右儿子的结点编号为2i+1;否则i无右儿子。性质6.
给定n个节点,能构成h(n)种不同的二叉树。
h(n)为卡特兰数的第n项。
h(n)=C(2*n,n)/(n+1)。性质7.
设有i个枝点,i为所有枝点的道路长度总和,j为叶的道路长度总和j=i+2i
三.二叉树的存储
二叉树的存储方法有以下几种。
/* 二叉树的顺序存储表示 */
#define MAX_TREE_SIZE 100 /* 二叉树的最大节点数 */
typedef TElemType SqBiTree[MAX_TREE_SIZE]; /* 0号单元存储根节点 */
typedef struct
{
int level,order; /* 节点的层,本层序号(按满二叉树计算) */
}position; 用这种紧凑排列,如果一个节点的索引为i,它的子节点能在索引2i+1和2i+2找到,并且它的父节点(如果有)能在索引floor((i-1)/2)找到(假设根节点的索引为0)。
这种方法更有利于紧凑存储和更好的访问的局部性,特别是在[前序遍历]中。然而,它需要连续的存储空间,这样在存储高度为h的n个结点组成的一般普通树时将会浪费很多空间。一种最极坏的情况下如果深度为h的二叉树每个节点只有右孩子需要占用2的h次幂减1,而实际却只有h个结点,空间的浪费太大,这是顺序存储结构的一大缺点。
将数组下标作为结点名称(编号),就可将二叉树中所有结点的标号存储在一维数组中。
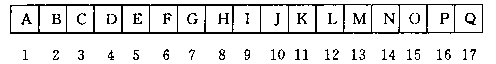
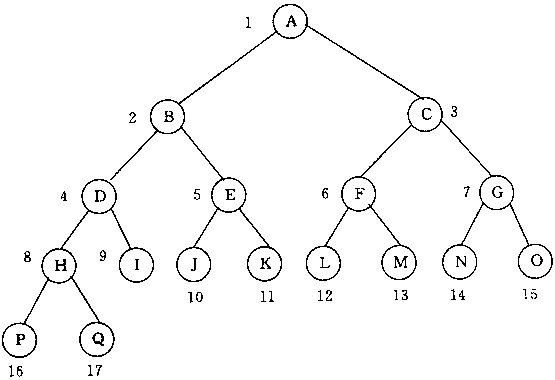
在二叉树的这种表示方式下,各结点之间的逻辑关系是隐含表示的。近似满二叉树中,除最下面一层外,各层都充满了结点。可能除最底层外,每一层的结点个数恰好是上一层结点个数的2倍。因此,从一个结点的编号就可推知其父亲,左、右儿子,和兄弟等结点的编号。例如,对于结点i我们有:
- 仅当i=1时,结点i为根结点;
- 当i>1时,结点i的父结点为i/2;
- 结点i的左儿子结点为2i;
- 结点i的右儿子结点为2i+1;
- 当i为奇数且不为1时,结点i的左兄弟结点为i-1;
- 当i为偶数时,结点i的右兄弟结点为i+1。
由上述关系可知,近似满二叉树中结点的层次关系足以反映结点之间的逻辑关系。因此,对近似满二叉树而言,顺序存储结构既简单又节省存储空间。
对于一般的二叉树,采用顺序存储时,为了能用结点在数组中的位置来表示结点之间的逻辑关系,也必须按近似满二叉树的形式来存储树中的结点。显然,这将造成存储空间的浪费。在最坏情况下,一个只有k个结点的右单枝树却需要2k-1个结点的存储空间。
例如,只有3个结点的右单枝树,如下图(a)所示,添上一些实际不存在的虚结点后,成为一棵近似满二叉树,相应的顺序存储结构如下图(b)所示。
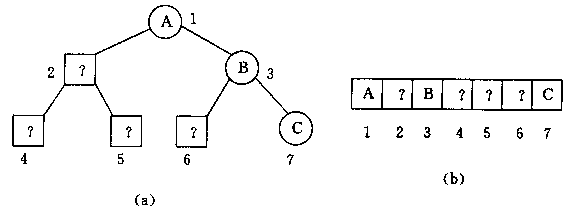
2. 二叉树的结点度表示法
二叉树的顺序存储结构可看作是二叉树的一种无边表示,即树中边信息是隐含的。二叉树的另一种无边表示称为二叉树的结点度表示。这种表示法将二叉树中所有结点依其后序列表排列,并在每个结点中附加一个0到3之间的整数,以表示结点的状态。该整数为0时,表示相应的结点为一叶结点;为1时,表示相应结点只有一个左儿子;为2时,表示相应结点只有一个右儿子;为3时,表示相应结点有两个儿子。例如,图(a)中的二叉树的结点度表示如图(b)所示。
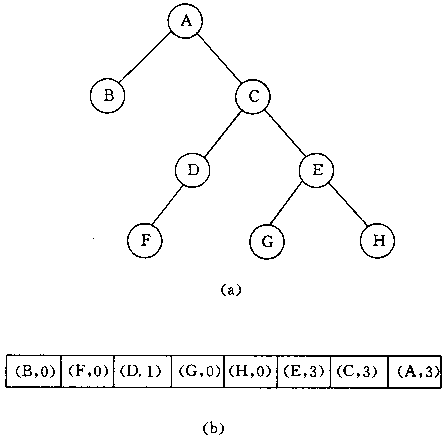
3. 二叉树的链式存储结构
在使用记录或内存地址指针的程序设计语言中,二叉树通常用树结点结构来存储。有时也包含指向唯一的父节点的指针。如果一个结点的子结点个数小于2,一些子结点指针可能为空值,或者为特殊的哨兵结点。 使用链表能避免顺序存储浪费空间的问题,算法和结构相对简单,但使用二叉链表,由于缺乏父链的指引,在找回父节点时需要重新扫描树得知父节点的节点地址。
/* 二叉树的二叉链表存储表示 */
typedef struct BiTNode
{
TElemType data;
struct BiTNode *lchild, /* 左孩子指針 */
struct BiTNode *rchild; /* 右孩子指針 */
}BiTNode,*BiTree; 

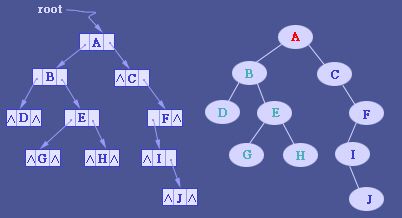
- 4. 三叉链表存储表示
改进于二叉链表,增加父节点的指引,能更好地实现节点间的访问,不过算法相对复杂。 当二叉树用三叉链表表示时,有N个结点,就会有N+2个空指针。
/* 二叉树的三叉链表存储表示 */
typedef struct BiTPNode
{
TElemType data;
struct BiTPNode *parent; /* 父孩子指針 */
struct BiTPNode *lchild; /* 左孩子指針 */
struct BiTPNode *rchild; /* 右孩子指針 */
}BiTPNode,*BiPTree;四.二叉树的遍历
我们经常希望访问树中的每一个结点并且查看它的值。有很多常见的顺序来访问所有的结点,而且每一种都有有用的性质。
由于二叉树的定义是递归的,因此一棵非空二叉树可以看作是由根节点,左子树和右子树这三个基本部分组成.如果能依次遍历这三个部分的信息,也就遍历了整个二叉树.因此,二叉树的遍历就是按某种策略访问二叉树中每一个节点并且访问一次的过程.
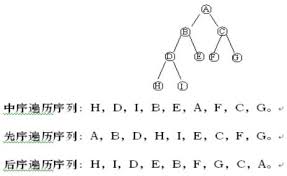
若以字母DLR分别表示访问根节点,遍历根节点的左子树,遍历根节点的右子树,则二叉树的遍历方式有六种:DLR,LDR,LRD,DRL,RDL和RLD.如果限定先左后右则只有前三种方式:DLR,LDR和LRD,分别被称之为先序(前序)遍历,中序遍历和后序遍历.
遍历二叉树的实质就是对二叉树线性化的过程.即遍历的结果是将非线性结构中的节点排成一个线性序列,而且三种遍历的结果都是线性序列.遍历二叉树的基本操作就是访问节点,对含有n个节点的二叉树不论按哪种次序遍历,其时间复杂度均为O(n),这是因为在遍历过程中实际是按照节点的左右指针遍历二叉树的每一个节点.此外,遍历所需的辅助空间为栈的容量,在遍历过程中每递归调用一次都要将有关节点的信息压入栈中,栈的容量恰为树的深度,最坏情况是n个节点的单支树,这时树的深度为n,所以空间复杂度为O(n).
二叉树三种遍历的方法如表所示.
| 遍历方式 | 操作步骤 |
|---|---|
| 先序遍历 | 若二叉树非空: |
| 1.访问根节点 2.按先序遍历左子树 3.按先序遍历右子树 | |
| 中序便利 | 若二叉树非空: |
| 按中序遍历左子树 2.访问根节点 3.按中序遍历右子树 | |
| 后序便利 | 若二叉树非空: |
| 按后序遍历左子树 2.按后序遍历右子树 3.访问根节点 |
此外,二叉树的遍历还可以采用层次遍历的方法.
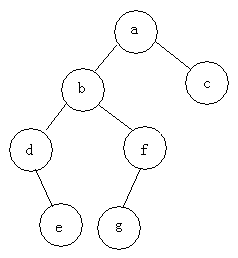
前序遍历:abdefgc
中序遍历:debgfac
后序遍历:edgfbca
I. 遍历二叉树的递归算法及遍历示例
1. 先序遍历二叉树的递归算法
void Preorder(BSTree *p) //先序遍历二叉树 { if(NULL != p) { printf("%3c",p->data); //访问根节点 Preorder(p->lchild); //先序遍历左子树 Preorder(p->rchild); //先序遍历右子树 } }2. 中序遍历二叉树的递归算法
void Inorder(BSTree *p) //中序遍历二叉树 { if(NULL != p) { Inorder(p->lchild); //中序遍历左子树 printf("%3c",p->data); //访问根节点 Inorder(p->rchild); //中序遍历右子树 } }3. 后序遍历二叉树的递归算法
void Postorder(BSTree *p) //后序遍历二叉树 { if(NULL != p) { Postorder(p->lchild); //后序遍历左子树 Postorder(p->rchild); //后序遍历右子树 printf("%3c",p->data); //访问根节点 } }
II.遍历二叉树的非递归算法
递归算法虽然简洁,但可读性较差且执行效率不高.因此,就存在着如何把遍历二叉树的递归算法转化为非递归算法的问题.
由二叉树的遍历可知,先序,中序和后序遍历都是从根节点开始的,并且在遍历过程中所经历的节点路线都是一样的,只不过访问节点信息的时机不同.也即,二叉树的遍历路线是从根节点开始沿左子树向下深入,当深入到最左端节点时,则因无法继续深入下去而返回,然后再逐一进入刚才深入时所遇节点的右子树,并且重复前面深入和返回的过程,直到最后从根节点的右子树返回到根节点时为止.由于节点返回的顺序正好和节点深入的顺序相反,即后深入先返回,它恰好符合栈结构的后进先入特点,因此可以用栈来实现遍历二叉树的非递归算法.注意,在三种便利方式中,先序遍历是在深入过程中饭凡遇到节点就访问该节点信息,中序遍历则是从左子树返回时访问该节点信息,而后序遍历是从右子树返回时访问节点信息.
- 1. 先序遍历二叉树的非递归算法
先序非递归遍历二叉树的方法是:由根节点沿左子树(即p->lchild`所指)一直遍历下去,在遍历过程中每经过一个节点时就输出(访问)该节点的信息并且同时将其压栈,当某个节点无左子树时就将这个节点由栈中弹出,并由这个节点的右子树的根开始继续沿其左子树向下遍历(对此时右子树的根节点也进行输出和压栈操作),直到栈中无任何节点时就实现了先序遍历.先序遍历的非递归算法如下:
void Preorder(BSTree *p) //先序遍历二叉树
{
BSTree *stack[MAXSIZE]; //MAXSIZE为大于二叉树节点个数的容量
int i = 0;
stack[0] = NULL; //栈初始化
while(p!= NULL || i>0) //当指针p不为空或栈stack不空(i>0)时
{
if(p!=NULL) //当指针p不为空时
{
printf("%3c", p->data);//输出该节点信息
stack[++i] = p; //将该节点压栈
p = p->lchild; //沿左子树向下遍历
}
else //当指针p为空时
{
p = stack[i--]; //将这个无左子树的节点由栈中弹出
p = p->rchild; //从该节点右子树的根开始沿左子树向下遍历
}
}
}- 2. 中序遍历二叉树的非递归算法
中序非递归遍历二叉树与先序非递归遍历二叉树的过程基本相同,仅是输出节点信息的语句位置发生了变化,即每当需要沿当前节点的右子树根开始继续沿其左子树向下遍历时(即此时已经遍历过当前节点的左子树了),就先输出这个当前节点的信息.中序便利二叉树非递归算法如下:
void Inorder(BSTree *p) //中序遍历二叉树
{
BSTree *stack[MAXSIZE]; //MAXSIZE为大于二叉树节点个数的容量
int i = 0;
stack[0] = NULL; //栈初始化
while(i > 0) //栈stack不空(i>0)时
{
if(p!=NULL) //当指针p不为空时
{
stack[++i] = p; //将该节点压栈
p = p->lchild; //沿左子树向下遍历
}
else //当指针p为空时
{
p = stack[i--]; //将这个无左子树的节点由栈中弹出
printf("%3c", p->data);//输出该节点信息
p = p->rchild; //从该节点右子树的根开始沿左子树向下遍历
}
if(p == NULL && i == 0) //当指针p为空且栈stack也为空时结束循环
break;
}
}- 3. 后序遍历二叉树的非递归算法
后序非遍历二叉树与前面两种非递归遍历算法有所不同,它除了使用栈stack之外,还需使用一个数组b来记录二叉树中节点i(i=1,2,3,…n)当前遍历的情况:如果b[i]为0,则表示仅遍历过节点i的左子树,它的右子树还没遍历过;如果b[i]为1,则表示节点i的左右子树都被遍历过~~
右序非递归便利二叉树的过程仍然是由根节点开始沿左子树向下进行遍历,并且将遇到的所有节点顺序压栈.当某个节点j无左子树时就将节点j由栈stack中弹出,然后检查b[j]是否为0,如果b[j]为0则表示节点j的右子树还未遍历过,也即必须遍历过节点j的右子树后方可输出节点j的信息,所以必须先节点j的右子树,即将节点j重新压栈并置b[j]为1(作为遍历过左右子数的标识),然后再将节点j的右孩子压栈并沿右孩子的左子树继续向下遍历.直到某一时刻该节点j再次由栈中弹出,因为此时b[j]已经为1,即表示此时节点j的左右子树都已遍历过(节点j的左右子树上的所有节点信息都已经输出),或者j本身就是一个叶节点,这时就可以输出节点j的信息了.为了统一,对于前者,在输出了节点j的信息后即置节点j的父节点指向节点j的指针值为NULL.这样,当某个节点的左右孩子指针都已为NULL时,则意味着或者该节点本身就为叶节点,或者该节点左右子树中的节点信息都已输出过,此时就可以输出该节点的信息了.后序遍历二叉树非递归算法如下:
void Postorder(BSTree *p) //后序遍历二叉树
{
int i = 0;
int b[MAXSIZE]; //数组b用于标识每个节点是否已遍历过其左右子树
BSTree *stack[MAXSIZE]; //MAXSIZE为大于二叉树节点个数的容量
stack[0] = NULL; //栈初始化
do
{
if(p != NULL) //当指针p不为空时
{
stack[++i] = p; //将遍历中遇到的所有节点依次压栈
b[i] = 0; //置该节点右子树未访问过的标志
p = p->lchild; //沿该节点左子树继续向下遍历
}
else //当指针p为空时
{
p = stack[i--]; //将这个无左子树(或左子树已遍历过)的当前节点由栈中弹出
if(!b[i+1]) //b[i+1]为0则当前节点的右子树未遍历
{
stack[++i] = p; //将当前节点重新压栈
b[i] = 1; //置当前节点右子树已访问过标志
p = p->rchild; //沿当前节点右孩子继续向下遍历
}
else //当前节点的左右子树都已遍历(即节点信息都已输出)
{
printf("%3c", p->data);//输出当前节点信息
p = NULL; //将指向当前节点的指针置为空
}
}
}while(p != NULL || i > 0) //当指针p 不空或栈stack不空(i>0)时继续遍历
}这种后序遍历二叉树的非递归算法,其优点是只需一重循环即可实现,而缺点是遍历之后二叉树就被破坏.另一种不破坏二叉树却需两重循环实现的后序遍历非递归算法如下:
void Postorder1(BSTree *p)
{
int b = 0;
int i = -1;
BSTree *q ;
BSTree *stack[MAXSIZE]; //MAXSIZE为大于二叉树节点个数的常量
do
{
while(p != NULL) //将*p节点左分支上的所有左孩子入栈
{
stack[++i] = p;
p = p->lchild;
}
//栈顶节点已没有左孩子或其左子树上的节点都已访问过
q = NULL;
b = 1; //置已访问过的标记
while(i >= 0 && b) //栈stack不空且当前栈顶节点的左子树已经遍历过
{
p = stack[i]; //取出当前栈顶节点
if(p->rchild == q) //当前栈顶节点*p无右孩子或*p的右孩子已经遍历过
{
printf("%3c", p->data);//输出当前节点*p的值
i --;
q = p; //q指向刚访问过的节点*p
}
else //当前栈顶节点*p有右子树
{
p = p->rchild; //p指向当前栈顶节点*p的右孩子节点
b = 0; //置该右孩子节点未遍历过其右子树标记
}
}
}while(i >= 0) //当栈stack非空时继续遍历
}算法中,表达式p->rchild == q的含义是:若q等于NULL,则表示节点*p的右孩子不存在且*p的左子树或不存在或已遍历过,所以现在可以访问节点*p了;若q不等于NULL,则表示*p的右孩子已访问过(因为q指向p的右子树中刚被访问过的节点,而*q此时又是*p的右孩子,即意味着p 的右子树中所有节点都已访问过),所以现在可以访问*p.
III. 二叉树的层次遍历算法
二叉树的层次遍历是指从二叉树的第一层(即根节点开始),对整棵二叉树进行自上而下的逐层遍历.在同一层中,则按从左到右的顺序逐个访问该层的每一个节点.
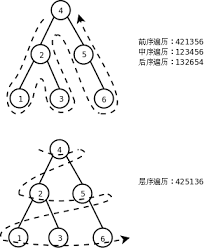
在进行层次遍历时,对某一层节点访问完后,再按照它们的访问次序对各个节点的左孩子和右孩子顺序访问.这样一层一层的进行,先访问的节点其左右孩子也必定先访问,这恰好与队列的操作相吻合.因此,在进行层次遍历时可设置一个队列结构,遍历从二叉树的根节点开始,即首先访问根节点并同时将根节点的指针t入队,然后在队不为空的情况下循环执行下述操作:
先从队头取出一个节点*p,若*p有左孩子则访问左孩子并将指向左孩子的指针入队;若*p有右孩子则访问右孩子并将指向右孩子的指针入队.
这种不断入队,出队的操作一直持续到队空为止,而此时二叉树的所有节点都已遍历.
void Transleve(BSTree *t) //层次遍历二叉树
{
SeQueue *Q;
BSTree *p;
Init_SeQueue(&Q); //队列Q初始化
if(t != NULL) //二叉树t非空
printf("%2c", t->data); //输出根节点信息
In_SeQueue(Q, t); //指针t 入队
while(!Empty_SeQueue(Q)) //队Q非空
{
Out_SeQueue(Q, &p); //从头节点(即指针值)出队并赋给p
if(p->lchild !=NULL) //*p有左孩子
{
printf("%2c", p->lchild->data); //输出左孩子信息
In_SeQueue(Q, p->lchild); //*p左孩子指针入队
}
if(p->rchild !=NULL) //*p有右孩子
{
printf("%2c", p->rchild->data); //输出右孩子信息
In_SeQueue(Q, p->rchild); //*p右孩子指针入队
}
}
}五.二叉树的操作接口及程序代码
binary_tree.h
#ifndef _BINARY_TREE_H_
#define _BINARY_TREE_H_
#include "tools.h"
#define END ('#')
#define ONE (1)
typedef struct Tree_node Tree_node;
struct Tree_node{
char data; //数据区域
Tree_node * left_child;
Tree_node *right_child;
};
typedef Tree_node *Bin_tree; //二叉树的根节点
//
//二叉树的接口
//一.创建二叉树
Bin_tree create_tree(char **str); //一.1.创建二叉树
Bin_tree create_tree_by_pre_mid(char *pre_str, char *mid_str, int length); //一.2.通过前序和中序创建二叉树
Bin_tree create_tree_by_mid_last(char *mid_str, char *last_str, int length);//一.3.通过中序和后序创建二叉树
//二.销毁二叉树
void destroy_tree(Bin_tree *root); //二.1.销毁二叉树
void destroy_tree_nr(Bin_tree *root); //二.2.非递归销毁二叉树
//三.遍历二叉树
// A | A
// / \ | / \
// B C | C B
// / \ \ | / / \
// D E F | F E D //镜像
//
// 先序(根、左、右) A B D E C F
// 中序(左、根、右) D B E A C F
// 后序(左、右、根) D E B F C A
// 层序 (1----h) A B C D E F
void pre_order_print(Bin_tree root); //三.1.前序递归遍历
void mid_order_print(Bin_tree root); //三.2.中序递归遍历
void last_order_print(Bin_tree root); //三.3.后序递归遍历
void pre_order_print_nr(Bin_tree root); //三.4.前序非递归遍历
void mid_order_print_nr(Bin_tree root); //三.5.中序非递归遍历
void last_order_print_nr(Bin_tree root); //三.6.后序非递归遍历
void level_order_print(Bin_tree root); //三.7.层序遍历
//四.二叉树的性质
Boolean is_full_binary_tree(Bin_tree root); //四.1.判断是否是满二叉树
Boolean is_complete_binary_tree(Bin_tree root); //四.2.判断是否是完全二叉树
Boolean is_balance_binary_tree(Bin_tree root); //四.3.判断是否是平衡二叉树
Boolean is_include_tree(Bin_tree root1,
Bin_tree root2); //四.4.判断二叉树是否包含
Boolean is_binarytree_equal(Bin_tree root1,
Bin_tree root2); //四.5.判断二叉树是否相等
//五.二叉树的变量
void swap_left_right(Bin_tree root); //五.1.得到二叉树的镜像
int get_binarytree_height(Bin_tree root); //五.2.得到二叉树的高度
int get_largest_dir_count(Bin_tree root); //五.3.得到二叉树的最大路径
int get_binarytree_node_count(Bin_tree root); //五.4.得到二叉树的节点个数
int get_binarytree_leaf_count(Bin_tree root); //五.5.得到二叉树的叶子节点个数
int get_binarytree_level_count(Bin_tree root, int level); //五.6.得到指定层级的节点个数
Bin_tree copy_binary_tree(Bin_tree root); //五.7.二叉树的拷贝
//六.二叉树的查找
Tree_node *find_value(Bin_tree root, char value); //六.1.找到指定值所在的节点
Tree_node *find_parent(Bin_tree root,
Tree_node *node); //六.2.找到指定节点的双亲节点
Tree_node *find_common_node(Bin_tree root, Tree_node *node1,
Tree_node *node2 ); //六.3.找到两个节点的最近公共节点
#endif六.二叉树操作接口实现:
binary_tree.c
//非操作接口声明及实现
//二叉树的接口
static int max(int a, int b);
static Tree_node *create_node(void);
static int get_index(char *string, char value);
static void destroy(Bin_tree root);
static Tree_node *find_common(Bin_tree root,
Tree_node *node1, Tree_node *node2);
static int max(int a, int b)
{
return b > a ? b : a;
}
//创建节点
static Tree_node *create_node(void)
{
Tree_node *node = (Tree_node *)Malloc(sizeof(Tree_node));
bzero(node, sizeof(Tree_node));
return node;
}
//获得索引
static int get_index(char *string, char value)
{
// abcdefg
//
// e
char *local = strchr(string, value);
return local == NULL ? -1 : (local - string) / sizeof(char);
}一.创建二叉树
- (1.普通string创建,2.先序中序,3.中序后序)
//一.创建二叉树
//Bin_tree create_tree(char **str);
// A
// / \
// B G
// / \ / \
// C D H J
// / \ \
// E F I
//
// ABC##DE##F##GH#I##J##
// A
// A->left = BC##DE##F##GH#I##J##
// B->left = C##DE ..
// C->left = # = NULL
// C->rigth = # = NULL
// B->rigth = DE##F ..
// D ->left = E##F#..
// E->left = # = NULL
// E->rigth = # = NULL
// D ->right = F##GH..
// F ->left = # = NULL
// F ->right= # = NULL
// A ->rigth = GH#I..
// G ->left = H#I..
// H->left = # = NULL
// H->rigth = I##J
// I->left = # =NULL
// I->rigth = # = NULL
// G ->rigth = J##
// J ->left = NULL
// J->rigth = NULL
//
//
Bin_tree create_tree(char **str)
{
Bin_tree root = NULL;
if(str != NULL && *str != NULL && **str != END){
root = create_node();
root->data = **str;
//处理完当前节点,然后递归地创建其左右孩子
//++*str;
(*str)++;
root->left_child = create_tree(str);
//++*str;
(*str)++;
root->right_child = create_tree(str);
}
return root;
}
//一.2.通过前序和中序创建二叉树
//Bin_tree create_tree_by_pre_mid(char *pre_str, char *mid_str, int length);
// A
// / \
// B G
// / \ / \
// C D H J
// / \ \
// E F I
// 先序: ABCDEFGHIJ 确定当前序列中根地位置
// 中序: CBEDFAHIGJ 得到某个节点地左右子树部分
//
// 1.先序确定出 A 为根,则CBEDF为左子树内容,HIGJ为右子树内容
// 先序: (A) BCDEF GHIJ
// 中序: CBEDF (A) HIGJ
//
// A
// / \
// CBEDF HIGJ
//
// 2.先序中确定 B 为A的左子树的根,则C为B左子树内容,EDF为B右子树内容,
// 且,通过先序中剩下的元素可知,G为A的右子树的根.且HI为G的左子树,J为G的右子树,即
// 先序: (A) [B]CDEF [G]HIJ
// 中序: C [B] EDF (A) HI[G]J
//
// A
// / \
// B G
// / \ / \
// C EDF HI J
//
// 3.先序中确定 C 为B左子树的根,则D为B右子树的根,E为D左子树内容,F为D右子树内容,
// 且,通过先序中剩下的元素可知,H是G为左子树的根.且J为G的右子树,I为H的右子树,即
// 先序: (A) [B]C D E F [G]H IJ
// 中序: C [B] E D F (A) H I[G]J
// A
// / \
// B G
// / \ / \
// C D H J
// / \ \
// E F I
Bin_tree create_tree_by_pre_mid(char *pre_str,
char *mid_str, int length) //通过先序和中序构建二叉树
{
// 先序: ABCDEFGHIJ 确定当前序列中根地位置
// 中序: CBEDFAHIGJ 得到某个节点地左右子树部分
Bin_tree root = NULL;
char root_value = 0;
int index = -1;
if(pre_str == NULL || mid_str == NULL || length <= 0)
{
return root;
}
root_value = pre_str[0]; //获取当前序列地根节点数值
root = create_node();
root->data = root_value;
index = get_index(mid_str, root_value);
//创建完根结点后递归处理其左右子树序列
root->left_child = create_tree_by_pre_mid(pre_str + 1, mid_str, index);
root->right_child = create_tree_by_pre_mid(pre_str + index + 1,
mid_str + index + 1,
length - index - 1);
return root;
}
//一.3.通过中序和后序创建二叉树
//Bin_tree create_tree_by_mid_last(char *mid_str, char *last_str, int length);
// A
// / \
// B G
// / \ / \
// C D H J
// / \ \
// E F I
//
//
// 中序: CBEDFAHIGJ 得到某个节点地左右子树部分
// 后序: CEFDBIHJGA
//
// 1.后序确定出 A 为根,则CBEDF为左子树内容,HIGJ为右子树内容
// 中序: CBEDF (A) HIGJ
// 后序: CEFDB IHJG (A)
// A
// / \
// CBEDF HIGJ
//
// 2.后序中确定 G为A的右子树的根. 后序中确定 B 为A的左子树的根,
// 中序: C [B] EDF (A) HI [G] J
// 后序: CEFD[B] IHJ[G] (A)
// C为B的左子树,EDF为B的右子树;J为G的右子树,HI为G的左子树.
//
// A
// / \
// B G
// / \ / \
// C EDF HI J
//
// 3.后序中判断出D是B的右子树根节点,且E为D的左子树,F为D的右子树.
// H,从后序中看出H是G的左子树根节点,且I为其右子树.
// 中序: C [B] E{D}F (A) {H}I [G] J
// 后序: CEF{D}[B] I{H}J[G] (A)
// A
// / \
// B G
// / \ / \
// C D H J
// / \ \
// E F I
Bin_tree create_tree_by_mid_last(char *mid_str, char *last_str, int length)
{
// 中序: CBEDFAHIGJ 得到某个节点地左右子树部分
// 后序: CEFDBIHJGA 得到根节点
Bin_tree root = NULL;
char root_value = 0;
int index = -1;
if(last_str == NULL || mid_str == NULL || length <= 0)
{
return root;
}
root_value = last_str[length -1]; //获取当前序列地根节点数值
root = create_node();
root->data = root_value;
index = get_index(mid_str, root_value);
//创建完根结点后递归处理其左右子树序列
root->left_child = create_tree_by_mid_last(mid_str , last_str, index);
root->right_child = create_tree_by_mid_last(mid_str + index +1,
last_str + index ,
length - index - 1);
return root;
}二.销毁二叉树
- 递归/非递归
//二.销毁二叉树
//void destroy_tree(Bin_tree *root);
void destroy_tree(Bin_tree *root)
{
if(root == NULL || *root == NULL){
return ;
}
destroy(*root);
*root = NULL;
}
static void destroy(Bin_tree root)
{
if(root != NULL){
destroy(root->left_child);
destroy(root->right_child);
free(root);
}
}
//二.2.非递归销毁二叉树
//void destroy_tree_nr(Bin_tree *root);
//思路:
//
//
// A
// / \
// B C
// / \ \
// D E F
//
// A B C
// | A | | B | | B | | C | | D | | D | | E | | F | | |
// | | | C | | C | | D | | E | | E | | F | | | | |
// | | | | | | | E | | | | F | | | | | | |
// | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
// | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
//
// 在销毁n层节点之前,首先把n + 1的节点入队进行地址保存
//
void destroy_tree_nr(Bin_tree *root) //非递归销毁二叉树
{
Queue *queue = init_queue();
Tree_node *p_node = NULL;
if(root == NULL || *root == NULL)
{
return ;
}
p_node = *root;
*root = NULL;
in_queue(queue, p_node);
while(!is_queue_empty(queue))
{
get_front_queue(queue, (void **)&p_node);
out_queue(queue);
//先记录p_node对应的下一层节点的地址,再销毁p_node
if(p_node->left_child != NULL)
{
in_queue(queue, p_node->left_child);
}
if(p_node->right_child != NULL)
{
in_queue(queue, p_node->right_child);
}
free(p_node);
}
destroy_queue(&queue);
}
三.遍历二叉树
1.前序递归遍历,2.中序递归遍历,3.后序递归遍历
4.前序非递归遍历,5.中序非递归遍历,6.后序非递归遍历
7.层序遍历
//三.遍历二叉树
// A | A
// / \ | / \
// B C | C B
// / \ \ | / / \
// D E F | F E D
//
// 先序(根、左、右) A B D E C F
// 中序(左、根、右) D B E A C F
// 后序(左、右、根) D E B F C A
// 层序 (1----h) A B C D E F
// A
// / \
// B G
// / \ / \
// C D H J
// / \ \
// E F I
//
//
// 先序: ABCDEFGHIJ 确定当前序列中根地位置
// 中序: CBEDFAHIGJ 得到某个节点地左右子树部分
// 后序: CEFDBIHJGA
//
//
//
// A
// / \
// B C
// / \
// D E
//
// ABDEC pre
// DEBCA last
//
// A
// /
// B
// / \
// D E
//
// ABDE
//
// DEBA
//
// A A
// / \
// B B
// / / \
// D D E
// /
// E
//
//
//三.1.前序递归遍历
//void pre_order_print(Bin_tree root);
void pre_order_print(Bin_tree root) //前序递归遍历
{
if(root != NULL){
printf("%c ", root->data);
pre_order_print(root->left_child);
pre_order_print(root->right_child);
}
}
//三.2.中序递归遍历
//void mid_order_print(Bin_tree root);
void mid_order_print(Bin_tree root) //中序递归遍历
{
if(root != NULL){
mid_order_print(root->left_child);
printf("%c ", root->data);
mid_order_print(root->right_child);
}
}
//三.3.后序递归遍历
//void last_order_print(Bin_tree root);
void last_order_print(Bin_tree root) //后序递归遍历
{
if(root != NULL){
last_order_print(root->left_child);
last_order_print(root->right_child);
printf("%c ", root->data);
}
}
//三.4.前序非递归遍历
//void pre_order_print_nr(Bin_tree root);
//
// A
// / \
// B G
// / \ / \
// C D H J
// / \ \
// E F I
//
// 先序: ABCDEFGHIJ 确定当前序列中根地位置
//
// 借助栈,在打印当前节点后分别记录其右、左孩子
// A
// A B
// A B C
// A B C D
// A B C D E
// A B C D E F
// A B C D E F G
// A B C D E F G H
// A A B C D E F G H I
// A B B C D E F G H I J
// | A | | B | | G | | C | | D | | E | | F | | G | | H | | I | | J | | |
// | | | G | | | | D | | G | | F | | G | | | | J | | J | | | | |
// | | | | | | | G | | | | G | | | | | | | | | | | | |
// | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
// | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
// A B C D E F G H I J
void pre_order_print_nr(Bin_tree root) //前序非递归遍历
{
Stack *stack = init_stack();
Tree_node *p_node = NULL;
if(root == NULL)
{
return ;
}
p_node = root;
push_stack(stack, p_node);
while(!is_stack_empty(stack))
{
get_top_stack(stack, (void **)&p_node);
printf("%c ", p_node->data);
pop_stack(stack);
if(p_node->right_child != NULL)
{
push_stack(stack, p_node->right_child);
}
if(p_node->left_child != NULL)
{
push_stack(stack, p_node->left_child);
}
}
destroy_stack(&stack);
}
//三.5.中序非递归遍历
//void mid_order_print_nr(Bin_tree root);
// A
// / \
// B G
// / \ / \
// C D H J
// / \ \
// E F I
//
// CBEDFAHIGJ
//
// 思路:
//
// 1.使用栈进行回溯
// 2.每打印完一个节点,要对其右孩子做处理
// 3.每个节点都需要不断找到最左边的孩子进行打印
//
//
// C B E D F A H I G J
// | A | | B | | C | | B | | A | | D | | E | | D | | A | | F | | A | | | | G | | H | | G | | I | | G | | | | J | | |
// | | | A | | B | | A | | | | A | | D | | A | | | | A | | | | | | | | G | | | | G | | | | | | | | |
// | | | | | A | | | | | | | | A | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
// | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
// | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
// C B E D F A H I G J
//
void mid_order_print_nr(Bin_tree root) //中序非递归遍历
{
Stack *stack = NULL;
Tree_node *p_node = NULL;
if(root == NULL){
return ;
}
stack = init_stack();
p_node = root;
while(!is_stack_empty(stack) || p_node != NULL)
{
while(p_node != NULL)
{ //首先找到当前节点最左边的节点
push_stack(stack, p_node);
p_node = p_node->left_child;
}
get_top_stack(stack, (void **)&p_node);
printf("%c ", p_node->data);
pop_stack(stack);
p_node = p_node->right_child;
}
destroy_stack(&stack);
}
//三.6.后序非递归遍历
//void last_order_print_nr(Bin_tree root)
void last_order_print_nr(Bin_tree root)
{
int tag = 0;
Stack *stack = NULL;
Tree_node *p_node = NULL;
Tree_node *q_node = NULL;
if(root == NULL){
return ;
}
stack = init_stack();
p_node = root;
do
{
while(p_node != NULL)
{ //首先找到当前节点最左边的节点
push_stack(stack, p_node);
p_node = p_node->left_child;
}
q_node = NULL;
tag = 1;
while(!is_stack_empty(stack) && tag )
{
get_top_stack(stack, (void **)&p_node);
if(p_node -> right_child == q_node)
{
printf("%c ", p_node->data);
pop_stack(stack);
q_node = p_node;
}
else
{
tag =0;
p_node = p_node->right_child;
}
}
}while(!is_stack_empty(stack));
destroy_stack(&stack);
}
//三.7.层序遍历
//void level_order_print(Bin_tree root);
//
// A
// / \
// B G
// / \ / \
// C D H J
// / \ \
// E F I
//
// A B G C D H J E F I
//
// 队列进行层序遍历:
//
// ^ A B G C D H J E F I
// | | A | | | | G | | G | | C | | D | | H | | J | | E | | F | | I | | |
// ^ | | | | | | | C | | D | | H | | J | | E | | F | | I | | | | |
// | | | | | | | | D | | H | | J | | E | | F | | I | | | | | | |
// ^ | | | | | | | | | J | | | | F | | I | | | | | | | | |
// | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
// ^ A B G C D H J E F I
//
void level_order_print(Bin_tree root) //层序遍历
{
Queue *queue = NULL;
Tree_node *p_node = NULL;
if(root == NULL){
return ;
}
queue = init_queue();
p_node = root;
in_queue(queue, p_node);
while(!is_queue_empty(queue))
{
get_front_queue(queue, (void **)&p_node);
out_queue(queue);
printf("%c ", p_node->data);
if(p_node->left_child != NULL)
{
in_queue(queue, p_node->left_child);
}
if(p_node->right_child != NULL)
{
in_queue(queue, p_node->right_child);
}
}
destroy_queue(&queue);
}
四.二叉树的变量
1.得到二叉树的镜像
2.得到二叉树的高度
3.得到二叉树的最大路径
4.得到二叉树的节点个数
5.得到二叉树的叶子节点个数
6.得到指定层级的节点个数
7.二叉树的拷贝
//四.二叉树的变量
//四.1.得到二叉树的镜像
//void swap_left_right(Bin_tree root);
void swap_left_right(Bin_tree root) //得到二叉树的镜像
{
// A | A
// / \ | / \
// B C | C B
// / \ \ | / / \
// D E F | F E D
if(root == NULL || (root->left_child == NULL
&& root->right_child == NULL)){
return ;
}
swap(&(root->left_child), &(root->right_child), sizeof(Tree_node *));
swap_left_right(root->left_child);
swap_left_right(root->right_child);
}
//四.2.得到二叉树的高度
//int get_binarytree_height(Bin_tree root);
int get_binarytree_height(Bin_tree root) //得到二叉树的高度
{
// A
// / \
// B G
// / \ / \
// C D H J
// / \ \
// E F I
if(root == NULL){
return 0;
}
return 1 + max(get_binarytree_height(root->left_child),
get_binarytree_height(root->right_child));
}
//四.3.得到二叉树的最大路径
//int get_largest_dir_count(Bin_tree root);
//
//
// A A A
// / \ / / \
// B G B B C
// / \ / \ / \ / \
// C D H J C D D E
// / \ \ / \ / \
// E F I E F F G
//
// 最大路径:
// EDBAGHI ECBDF FDBAC
// 长度为6 长度为4 长度为4
//
// 情况A:路径经过左子树的最深节点,通过根节点,再到右子树的最深节点;
// 情况B:路径不穿过根节点,而是左子树(或右子树)的最大距离路径,取其大者.
//
// 这两种情况的最大值就是该二叉树的最大路径.
//
//
int get_largest_dir_count(Bin_tree root)
{
int distence = 0;
if(root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else if(root->left_child == NULL && root->right_child == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
distence = max(get_binarytree_height(root->left_child)+get_binarytree_height(root->right_child),
max(get_largest_dir_count(root->left_child), get_largest_dir_count(root->right_child)));
return distence;
}
//
//四.4.得到二叉树的节点个数
//int get_binarytree_node_count(Bin_tree root);
int get_binarytree_node_count(Bin_tree root) //得到二叉树的节点个数
{
if(root == NULL){
return 0;
}
//1 + 左(右)子树节点个数
return 1 + get_binarytree_node_count(root->left_child)
+ get_binarytree_node_count(root->right_child);
}
//四.5.得到二叉树的叶子节点个数
//int get_binarytree_leaf_count(Bin_tree root);
int get_binarytree_leaf_count(Bin_tree root) //得到二叉树的叶子节点个数
{
//root->left_child == NULL && root->right_child == NULL
if(root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else if(root->left_child == NULL && root->right_child == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return get_binarytree_leaf_count(root->left_child)
+ get_binarytree_leaf_count(root->right_child);
}
}
//四.6.得到指定层级的节点个数
//int get_binarytree_level_count(Bin_tree root, int level);
int get_binarytree_level_count(Bin_tree root, int level) //得到指定层级的节点个数
{
// A
// / \
// B G
// / \ / \
// C D H J
// / \ \
// E F I
int num_left = 0;
int num_right = 0;
if(root == NULL || level < ONE || level > get_binarytree_height(root))
{
return 0;
}
if(level == ONE)
{
return 1;
}
num_left = get_binarytree_level_count(root->left_child, level - 1);
num_right = get_binarytree_level_count(root->right_child, level - 1);
return num_left + num_right;
}
//四.7.二叉树的拷贝
//Bin_tree copy_binary_tree(Bin_tree root);
Bin_tree copy_binary_tree(Bin_tree root) //二叉树的拷贝
{
Bin_tree result = NULL;
//1.如果当前节点存在,则构建当前节点,
//然后递归地创建当前节点地左右子树部分
if(root != NULL)
{
result = create_node();
result->data = root->data;
result->left_child = copy_binary_tree(root->left_child);
result->right_child = copy_binary_tree(root->right_child);
}
return result;
}五.二叉树的性质
1.判断是否是满二叉树
2.判断是否是完全二叉树
3.判断是否是平衡二叉树
4.判断二叉树是否包含
5.判断二叉树是否相等
//五.二叉树的性质
//五.1.判断是否是满二叉树
//Boolean is_full_binary_tree(Bin_tree root);
Boolean is_full_binary_tree(Bin_tree root) //判断是否是满二叉树
{
int height = 0;
int count = 0;
if(root == NULL){
return TRUE;
}
//得到二叉树的高度h和节点个数n
//
//判断:
// if (2^h - 1) == n, 满二叉树
// else 不是满二叉树
height = get_binarytree_height(root);
count = get_binarytree_node_count(root);
return ( ((int)pow(2, height) - 1) == count) ;
}
//五.2.判断是否是完全二叉树
//Boolean is_complete_binary_tree(Bin_tree root);
// A
// / \
// B G
// / \ /
// C D H
//
// 1.层序遍历:
//
// 2.分两个状态:
// 从根节点开始,入队列,如果队列不为空,循环。
// 遇到第一个没有左儿子或者右儿子的节点,设置标志位,
// 如果之后再遇到有左/右儿子的节点,那么这不是一颗完全二叉树。
//
// A
// / \
// B G
// / \ / \
// C D H J
// / \ / \
// K L E F
Boolean is_complete_binary_tree(Bin_tree root) //判断是否是完全二叉树
{
int flag = 0;
Queue *queue = NULL;
Tree_node *p_node = NULL;
if(root == NULL){
return FALSE;
}
queue = init_queue();
p_node = root;
in_queue(queue, p_node);
while(!is_queue_empty(queue))
{
get_front_queue(queue, (void **)&p_node);
out_queue(queue);
//printf("%c ", p_node->data);
if(p_node->left_child == NULL || p_node->right_child == NULL)
{
flag = 1;
}
if(p_node->left_child != NULL || p_node->right_child != NULL)
{
if(flag == 1)
{
//printf("not complete \n");
return FALSE;
}
}
if(p_node->left_child != NULL)
{
in_queue(queue, p_node->left_child);
}
if(p_node->right_child != NULL)
{
in_queue(queue, p_node->right_child);
}
}
//printf("complete\n");
destroy_queue(&queue);
return TRUE;
}
//五.3.判断是否是平衡二叉树
//Boolean is_balance_binary_tree(Bin_tree root);
//1.平衡条件:
//
// 左右子树高度差小于等于1,左右子树内部也要平衡
Boolean is_balance_binary_tree(Bin_tree root) //判断是否是平衡二叉树
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return TRUE;
}
int left_height = get_binarytree_height(root->left_child);
int right_height = get_binarytree_height(root->right_child);
if(abs(left_height - right_height) > 1)
{
return FALSE;
}
else
{
return is_balance_binary_tree(root->left_child) && is_balance_binary_tree(root->right_child);
}
}
//五.4.判断二叉树是否包含
//Boolean is_include_tree(Bin_tree root1, Bin_tree root2);
// A
// / \
// B G
// / \ / \
// C D H J
// / \ \
// E F I
//
// B
// / \
// C D
// 1.找root2在root1中的位置,如果存在,则在root1对于
// 的位置开始(p_node),递归地对root2的左右子树部分进行
// 查找,如果root2遍历结束,则认为root2包含于root1
//
Boolean is_include_tree(Bin_tree root1,
Bin_tree root2) //二叉树是否包含
{
if(root1 == NULL || root2 == NULL)
{
return TRUE;
}
Tree_node *p_node = NULL;
if((p_node = find_value(root1, root2->data)) == NULL)
{
return FALSE;
}
return (is_include_tree(p_node, root2->left_child) && is_include_tree(p_node, root2->right_child));
return TRUE;
}
//五.5.判断二叉树是否相等
//Boolean is_binarytree_equal(Bin_tree root1, Bin_tree root2);
Boolean is_binarytree_equal(Bin_tree root1,
Bin_tree root2) //二叉树是否相等
{
//1.相等:
//(1)root1和root2都为NULL,相等
//(2)root1和root2都存在,并且data相等,并且左(右)子树部分都相等
if(root1 == NULL && root2 == NULL)
{
return TRUE;
}
else if( (root1 != NULL && root2 != NULL)
&& root1->data == root2->data
&& is_binarytree_equal(root1->left_child, root2->left_child)
&& is_binarytree_equal(root1->right_child, root2->right_child) )
{
return TRUE;
}
else
{
return FALSE;
}
}
六.二叉树的查找
1.找到指定值所在的节点
2.找到指定节点的双亲节点
3.找到两个节点的最近公共节点
//六.二叉树的查找
//六.1.找到指定值所在的节点
//Tree_node *find_value(Bin_tree root, char value);
Tree_node *find_value(Bin_tree root, char value) //找到指定值所在的节点
{
Tree_node *p_node = NULL;
if(root == NULL || root->data == value)
{
return root;
}
p_node = find_value(root->left_child, value);
if(p_node == NULL)
{
p_node = find_value(root->right_child, value);
}
return p_node;
}
//六.2.找到指定节点的双亲节点
//Tree_node *find_parent(Bin_tree root, Tree_node *node);
Tree_node *find_parent(Bin_tree root,
Tree_node *node) //找到指定节点的双亲节点
{
Tree_node *p_node = NULL;
if(root == NULL || root->left_child == node
|| root->right_child == node){
//root不存在或者root是所要找的双亲节点
return root;
}
p_node = find_parent(root->left_child, node);
if(p_node == NULL){
p_node = find_parent(root->right_child, node);
}
return p_node;
}
//六.3.找到两个节点的最近公共节点
//Tree_node *find_common_node(Bin_tree root, Tree_node *node1, Tree_node *node2 );
static Tree_node *find_common(Bin_tree root,
Tree_node *node1, Tree_node *node2){
// 从根节点开始:
//
// 如果node1和node2分别在root左右子树部分,则root为最近公共祖先;
//
// 如果在左(右),则对root的左(右)子树部分进行递归的处理,直到满足
//
// node1 和node2在不同侧的情况
if(find_value(root->left_child, node1->data))
{
if(find_value(root->right_child, node2->data))
{
return root;
}
else
{
return find_common(root->left_child, node1, node2);
}
}
else
{
if(find_value(root->left_child, node2->data))
{
return root;
}
else
{
return find_common(root->right_child, node1, node2);
}
}
}
Tree_node *find_common_node(Bin_tree root, Tree_node *node1,
Tree_node *node2 ) //找到两个节点的最近公共节点
{
// A
// / \
// B G
// / \ / \
// C D H J
// / \ \
// E F I
//
// 1.如果出现node1和node2有继承关系,则返回高度较高节点的双亲节点
//
// find_value
// find_parent
//
int height1 = get_binarytree_height(node1);
int height2 = get_binarytree_height(node2);
//处理包含关系
if(height1 > height2)
{
if(find_value(node1, node2->data) != NULL)
{
return find_parent(root, node1);
}
}
else if(height1 < height2)
{
if(find_value(node2, node1->data) != NULL)
{
return find_parent(root, node2);
}
}
//处理非包含关系
return find_common(root, node1, node2);
}七.功能检测
main.c
#include - 运行结果:
root@aemonair:~binary_tree# cc.sh *.c
Compiling ...
-e CC binary_tree.c dlist.c main.c queue.c stack.c tools.c -g -lpthread -lm
-e Completed .
-e Thu Aug 4 23:52:07 CST 2016
root@aemonair:~/binary_tree# ./binary_tree
**********************************************************************************
一.1.创建二叉树
root,root2: root1: root4:
A A
/ \ / \
B G B G B
/ \ / \ / \ / \ / \
C D H J C D H J C D
/ \ \ /\ /\
E F I K L E F
**********************************************************************************
二.遍历二叉树:
pre order root:
A B C D E F G H I J
pre order nr root:
A B C D E F G H I J
mid order root:
C B E D F A H I G J
mid order nr root:
C B E D F A H I G J
last order root:
C E F D B I H J G A
last order nr root:
C E F D B I H J G A
last order root1:
K L C E F D B H J G A
last order nr root1:
K L C E F D B H J G A
level order root1:
A B G C D H J K L E F
**********************************************************************************
三.二叉树的变量:
mid order root :
C B E D F A H I G J
mid order coped root2:
C B E D F A H I G J
the height of root2:4
the count of root2:10
the leaves count of root2:5
the largest dir count of root2:6
the 3 level count is:4
pre order root2:
A B C D E F G H I J
swap pre order root2:
A G J H I B D F E C
root3 = copy_binary_tree(root1)
mid order root1 :
K C L B E D F A H G J
mid order root3 :
K C L B E D F A H G J
**********************************************************************************
四.二叉树的性质:
root, root2: root1,root3: root4:
A | A A
/ \ | / \ / \
B G | G B B G B
/ \ / \ | / \ / \ / \ / \ / \
C D H J | J H D C C D H J C D
/ \ \ | / / \ /\ /\
E F I | I F E K L E F
root1 is not full!
root1 is complete!
root1 is balance!
mid order root :
C B E D F A H I G J
mid order root4 :
C B D
root4 is include root!
root1 root3 two trees are equal!
**********************************************************************************
五.二叉树的查找
mid order root :
C B E D F A H I G J
H is found!
(B and I) parent is:A
**********************************************************************************
总结:
上次说树,是数据结构中非常重要的非线性结构.
我们总算是对二叉树的各种操作做了这么多详细研究,呼~
嗯…然后呢…
我们创建二叉树时可以通过字符串创建,可以通过前序中序,或者中序后序创建.
我们可以看,在非遍历的过程中,我们对节点要进行各种前后操作,于是用到了栈,用到了队列,还好以前实现过,这里就直接用啦,对不对.
二叉树的各种性质,也可以直接用来判断某些类别,递归实现的求高度,求节点都可以利用性质.
嗯~还有,在二叉树里用到了大量递归的概念~好好想想,觉得,嗯,二叉树好厉害~
Hey ~ 继续加油.