基于Spark通用计算平台,可以很好地扩展各种计算类型的应用,尤其是Spark提供了内建的计算库支持,像Spark Streaming、Spark SQL、MLlib、GraphX,这些内建库都提供了高级抽象,可以用非常简洁的代码实现复杂的计算逻辑、这也得益于Scala编程语言的简洁性。这里,我们基于1.3.0版本的Spark搭建了计算平台,实现基于Spark Streaming的实时计算。
我们的应用场景是分析用户使用手机App的行为,描述如下所示:
- 手机客户端会收集用户的行为事件(我们以点击事件为例),将数据发送到数据服务器,我们假设这里直接进入到Kafka消息队列
- 后端的实时服务会从Kafka消费数据,将数据读出来并进行实时分析,这里选择Spark Streaming,因为Spark Streaming提供了与Kafka整合的内置支持
- 经过Spark Streaming实时计算程序分析,将结果写入Redis,可以实时获取用户的行为数据,并可以导出进行离线综合统计分析
Spark Streaming介绍
Spark Streaming提供了一个叫做DStream(Discretized Stream)的高级抽象,DStream表示一个持续不断输入的数据流,可以基于Kafka、TCP Socket、Flume等输入数据流创建。在内部,一个DStream实际上是由一个RDD序列组成的。Sparking Streaming是基于Spark平台的,也就继承了Spark平台的各种特性,如容错(Fault-tolerant)、可扩展(Scalable)、高吞吐(High-throughput)等。
在Spark Streaming中,每个DStream包含了一个时间间隔之内的数据项的集合,我们可以理解为指定时间间隔之内的一个batch,每一个batch就构成一个RDD数据集,所以DStream就是一个个batch的有序序列,时间是连续的,按照时间间隔将数据流分割成一个个离散的RDD数据集,如图所示(来自官网):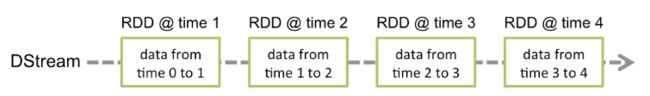
我们都知道,Spark支持两种类型操作:Transformations和Actions。Transformation从一个已知的RDD数据集经过转换得到一个新的RDD数据集,这些Transformation操作包括map、filter、flatMap、union、join等,而且Transformation具有lazy的特性,调用这些操作并没有立刻执行对已知RDD数据集的计算操作,而是在调用了另一类型的Action操作才会真正地执行。Action执行,会真正地对RDD数据集进行操作,返回一个计算结果给Driver程序,或者没有返回结果,如将计算结果数据进行持久化,Action操作包括reduceByKey、count、foreach、collect等。关于Transformations和Actions更详细内容,可以查看官网文档。
同样、Spark Streaming提供了类似Spark的两种操作类型,分别为Transformations和Output操作,它们的操作对象是DStream,作用也和Spark类似:Transformation从一个已知的DStream经过转换得到一个新的DStream,而且Spark Streaming还额外增加了一类针对Window的操作,当然它也是Transformation,但是可以更灵活地控制DStream的大小(时间间隔大小、数据元素个数),例如window(windowLength, slideInterval)、countByWindow(windowLength, slideInterval)、reduceByWindow(func, windowLength, slideInterval)等。Spark Streaming的Output操作允许我们将DStream数据输出到一个外部的存储系统,如数据库或文件系统等,执行Output操作类似执行Spark的Action操作,使得该操作之前lazy的Transformation操作序列真正地执行。
Kafka+Spark Streaming+Redis编程实践
下面,我们根据上面提到的应用场景,来编程实现这个实时计算应用。
首先,创建一个scala工程,创建方法见 三、使用maven创建scala工程(scala和java混一起)
引入kafka、redis、json等相关的包,pom.xml 如下:
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<parent>
<artifactId>fvpartifactId>
<groupId>com.sf.fvpgroupId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
parent>
<groupId>com.sfgroupId>
<artifactId>scalademo3artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
<name>${project.artifactId}name>
<description>My wonderfull scala appdescription>
<inceptionYear>2015inceptionYear>
<licenses>
<license>
<name>My Licensename>
<url>http://....url>
<distribution>repodistribution>
license>
licenses>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.6maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.6maven.compiler.target>
<encoding>UTF-8encoding>
<scala.version>2.11.5scala.version>
<scala.compat.version>2.11scala.compat.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.sparkgroupId>
<artifactId>spark-core_2.11artifactId>
<version>2.0.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.sparkgroupId>
<artifactId>spark-streaming_2.11artifactId>
<version>2.0.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.scala-langgroupId>
<artifactId>scala-libraryartifactId>
<version>${scala.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.sparkgroupId>
<artifactId>spark-streaming-kafka-0-8_2.11artifactId>
<version>2.0.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.json-libgroupId>
<artifactId>json-libartifactId>
<version>2.2.3version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.codehaus.jettisongroupId>
<artifactId>jettisonartifactId>
<version>1.3.8version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ezmorphgroupId>
<artifactId>ezmorphartifactId>
<version>1.0.6version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clientsgroupId>
<artifactId>jedisartifactId>
<version>2.5.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commonsgroupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2artifactId>
<version>2.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>4.11version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.specs2groupId>
<artifactId>specs2-core_${scala.compat.version}artifactId>
<version>2.4.16version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.scalatestgroupId>
<artifactId>scalatest_${scala.compat.version}artifactId>
<version>2.2.4version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
<build>
<sourceDirectory>src/main/scalasourceDirectory>
<testSourceDirectory>src/test/scalatestSourceDirectory>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>net.alchim31.mavengroupId>
<artifactId>scala-maven-pluginartifactId>
<version>3.2.0version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>compilegoal>
<goal>testCompilegoal>
goals>
<configuration>
<args>
<arg>-make:transitivearg>
<arg>-dependencyfilearg>
<arg>${project.build.directory}/.scala_dependenciesarg>
args>
configuration>
execution>
executions>
plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.pluginsgroupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-pluginartifactId>
<version>2.18.1version>
<configuration>
<useFile>falseuseFile>
<disableXmlReport>truedisableXmlReport>
<includes>
<include>**/*Test.*include>
<include>**/*Suite.*include>
includes>
configuration>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
project>
二、写了一个Kafka Producer模拟程序,用来模拟向Kafka实时写入用户行为的事件数据,数据是JSON格式,示例如下:
{"uid":"068b746ed4620d25e26055a9f804385f","event_time":"1430204612405","os_type":"Android","click_count":6}
一个事件包含4个字段:
- uid:用户编号
- event_time:事件发生时间戳
- os_type:手机App操作系统类型
- click_count:点击次数
下面是我们实现的代码,如下所示:
package com.sf.scalademo3 import java.util.Properties import scala.util.Properties import org.codehaus.jettison.json.JSONObject import kafka.javaapi.producer.Producer import kafka.producer.KeyedMessage import kafka.producer.KeyedMessage import kafka.producer.ProducerConfig import scala.util.Random object KafkaEventProducer { private val users = Array( "4A4D769EB9679C054DE81B973ED5D768", "8dfeb5aaafc027d89349ac9a20b3930f", "011BBF43B89BFBF266C865DF0397AA71", "f2a8474bf7bd94f0aabbd4cdd2c06dcf", "068b746ed4620d25e26055a9f804385f", "97edfc08311c70143401745a03a50706", "d7f141563005d1b5d0d3dd30138f3f62", "c8ee90aade1671a21336c721512b817a", "6b67c8c700427dee7552f81f3228c927", "a95f22eabc4fd4b580c011a3161a9d9d") private val random = new Random() private var pointer = -1 def getUserID(): String = { pointer = pointer + 1 if (pointer >= users.length) { pointer = 0 users(pointer) } else { users(pointer) } } def click(): Double = { random.nextInt(10) } // bin/kafka-topics.sh --zookeeper zk1:2181,zk2:2181,zk3:2181/kafka --create --topic user_events --replication-factor 2 --partitions 2 // bin/kafka-topics.sh --zookeeper zk1:2181,zk2:2181,zk3:2181/kafka --list // bin/kafka-topics.sh --zookeeper zk1:2181,zk2:2181,zk3:2181/kafka --describe user_events // bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --zookeeper zk1:2181,zk2:2181,zk3:22181/kafka --topic test_json_basis_event --from-beginning def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val topic = "user_events" val brokers = "localhost:9092" val props = new Properties() props.put("metadata.broker.list", brokers) props.put("serializer.class", "kafka.serializer.StringEncoder") val kafkaConfig = new ProducerConfig(props) val producer = new Producer[String, String](kafkaConfig) while (true) { // prepare event data val event = new JSONObject() event .put("uid", getUserID) .put("event_time", System.currentTimeMillis.toString) .put("os_type", "Android") .put("click_count", click) // produce event message producer.send(new KeyedMessage[String, String](topic, event.toString)) println("Message sent: " + event) Thread.sleep(200) } } }
通过控制上面程序最后一行的时间间隔来控制模拟写入速度。
三、下面我们来讨论实现实时统计每个用户的点击次数,它是按照用户分组进行累加次数,逻辑比较简单,关键是在实现过程中要注意一些问题,如对象序列化等。先看实现代码,稍后我们再详细讨论,代码实现如下所示:
package com.sf.scalademo3 import kafka.serializer.StringDecoder import org.apache.spark.SparkConf import org.apache.spark.streaming._ import org.apache.spark.streaming.kafka.KafkaUtils import net.sf.json.JSONObject import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool import org.apache.commons.pool2.impl.GenericObjectPoolConfig object UserClickCountAnalytics { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { var masterUrl = "local[1]" if (args.length > 0) { masterUrl = args(0) } // Create a StreamingContext with the given master URL val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster(masterUrl).setAppName("UserClickCountStat") val ssc = new StreamingContext(conf, Seconds(5)) // Kafka configurations val topics = Set("user_events") val brokers = "localhost:9092" val kafkaParams = Map[String, String]( "metadata.broker.list" -> brokers, "serializer.class" -> "kafka.serializer.StringEncoder") val dbIndex = 1 val clickHashKey = "app::users::click" // Create a direct stream val kafkaStream = KafkaUtils.createDirectStream[String, String, StringDecoder, StringDecoder](ssc, kafkaParams, topics) val events = kafkaStream.flatMap(line => { val data = JSONObject.fromObject(line._2) Some(data) }) // Compute user click times val userClicks = events.map(x => (x.getString("uid"), x.getInt("click_count"))).reduceByKey(_ + _) userClicks.foreachRDD(rdd => { rdd.foreachPartition(partitionOfRecords => { partitionOfRecords.foreach(pair => { val uid = pair._1 val clickCount = pair._2 val jedis = RedisClient.pool.getResource jedis.select(dbIndex) jedis.hincrBy(clickHashKey, uid, clickCount) RedisClient.pool.returnResource(jedis) }) }) }) ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() } }
上面代码使用了Jedis客户端来操作Redis,将分组计数结果数据累加写入Redis存储,如果其他系统需要实时获取该数据,直接从Redis实时读取即可。RedisClient实现代码如下所示:
package com.sf.scalademo3 import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool import org.apache.commons.pool2.impl.GenericObjectPoolConfig object RedisClient extends Serializable { val redisHost = "10.202.34.232" val redisPort = 6383 val redisTimeout = 30000 lazy val pool = new JedisPool(new GenericObjectPoolConfig(), redisHost, redisPort, redisTimeout) lazy val hook = new Thread { override def run = { println("Execute hook thread: " + this) pool.destroy() } } sys.addShutdownHook(hook.run) }
上面代码我们分别在local[K]和Spark Standalone集群模式下运行通过。
如果我们是在开发环境进行调试的时候,也就是使用local[K]部署模式,在本地启动K个Worker线程来计算,这K个Worker在同一个JVM实例里,上面的代码默认情况是,如果没有传参数则是local[K]模式,所以如果使用这种方式在创建Redis连接池或连接的时候,可能非常容易调试通过,但是在使用Spark Standalone、YARN Client(YARN Cluster)或Mesos集群部署模式的时候,就会报错,主要是由于在处理Redis连接池或连接的时候出错了。我们可以看一下Spark架构,如图所示(来自官网):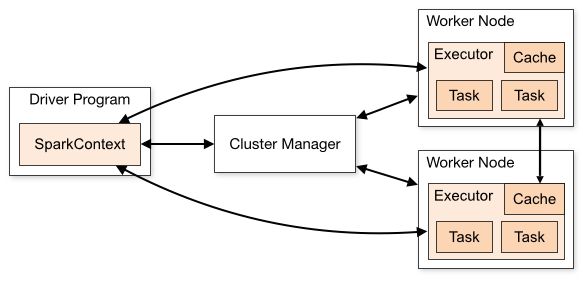
无论是在本地模式、Standalone模式,还是在Mesos或YARN模式下,整个Spark集群的结构都可以用上图抽象表示,只是各个组件的运行环境不同,导致组件可能是分布式的,或本地的,或单个JVM实例的。如在本地模式,则上图表现为在同一节点上的单个进程之内的多个组件;而在YARN Client模式下,Driver程序是在YARN集群之外的一个节点上提交Spark Application,其他的组件都运行在YARN集群管理的节点上。
在Spark集群环境部署Application后,在进行计算的时候会将作用于RDD数据集上的函数(Functions)发送到集群中Worker上的Executor上(在Spark Streaming中是作用于DStream的操作),那么这些函数操作所作用的对象(Elements)必须是可序列化的,通过Scala也可以使用lazy引用来解决,否则这些对象(Elements)在跨节点序列化传输后,无法正确地执行反序列化重构成实际可用的对象。上面代码我们使用lazy引用(Lazy Reference)来实现的,代码如下所示:
package com.sf.scalademo3 import org.apache.commons.pool2.impl.GenericObjectPoolConfig import org.apache.spark.SparkConf import org.apache.spark.streaming.Seconds import org.apache.spark.streaming.StreamingContext import org.apache.spark.streaming.dstream.DStream.toPairDStreamFunctions import org.apache.spark.streaming.kafka.KafkaUtils import kafka.serializer.StringDecoder import net.sf.json.JSONObject import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool object UserClickCountAnalytics2 { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { var masterUrl = "local[1]" if (args.length > 0) { masterUrl = args(0) } // Create a StreamingContext with the given master URL val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster(masterUrl).setAppName("UserClickCountStat") val ssc = new StreamingContext(conf, Seconds(5)) // Kafka configurations val topics = Set("user_events") val brokers = "localhost:9092" val kafkaParams = Map[String, String]( "metadata.broker.list" -> brokers, "serializer.class" -> "kafka.serializer.StringEncoder") val dbIndex = 1 val clickHashKey = "app::users::click" // Create a direct stream val kafkaStream = KafkaUtils.createDirectStream[String, String, StringDecoder, StringDecoder](ssc, kafkaParams, topics) val events = kafkaStream.flatMap(line => { val data = JSONObject.fromObject(line._2) Some(data) }) // Compute user click times val userClicks = events.map(x => (x.getString("uid"), x.getInt("click_count"))).reduceByKey(_ + _) userClicks.foreachRDD(rdd => { rdd.foreachPartition(partitionOfRecords => { partitionOfRecords.foreach(pair => { /** * Internal Redis client for managing Redis connection {@link Jedis} based on {@link RedisPool} */ object InternalRedisClient extends Serializable { @transient private var pool: JedisPool = null def makePool(redisHost: String, redisPort: Int, redisTimeout: Int, maxTotal: Int, maxIdle: Int, minIdle: Int): Unit = { makePool(redisHost, redisPort, redisTimeout, maxTotal, maxIdle, minIdle, true, false, 10000) } def makePool(redisHost: String, redisPort: Int, redisTimeout: Int, maxTotal: Int, maxIdle: Int, minIdle: Int, testOnBorrow: Boolean, testOnReturn: Boolean, maxWaitMillis: Long): Unit = { if (pool == null) { val poolConfig = new GenericObjectPoolConfig() poolConfig.setMaxTotal(maxTotal) poolConfig.setMaxIdle(maxIdle) poolConfig.setMinIdle(minIdle) poolConfig.setTestOnBorrow(testOnBorrow) poolConfig.setTestOnReturn(testOnReturn) poolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(maxWaitMillis) pool = new JedisPool(poolConfig, redisHost, redisPort, redisTimeout) val hook = new Thread { override def run = pool.destroy() } sys.addShutdownHook(hook.run) } } def getPool: JedisPool = { assert(pool != null) pool } } // Redis configurations val maxTotal = 10 val maxIdle = 10 val minIdle = 1 val redisHost = "10.202.34.232" val redisPort = 6383 val redisTimeout = 30000 val dbIndex = 1 InternalRedisClient.makePool(redisHost, redisPort, redisTimeout, maxTotal, maxIdle, minIdle) val uid = pair._1 val clickCount = pair._2 val jedis = InternalRedisClient.getPool.getResource jedis.select(dbIndex) //原子操作--Redis HINCRBY命令用于增加存储在字段中存储由增量键哈希的数量。 //如果键不存在,新的key被哈希创建。如果字段不存在,值被设置为0之前进行操作。 jedis.hincrBy(clickHashKey, uid, clickCount) InternalRedisClient.getPool.returnResource(jedis) }) }) }) ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() } }
上面代码实现,得益于Scala语言的特性,可以在代码中任何位置进行class或object的定义,我们将用来管理Redis连接的代码放在了特定操作的内部,就避免了瞬态(Transient)对象跨节点序列化的问题。这样做还要求我们能够了解Spark内部是如何操作RDD数据集的,更多可以参考RDD或Spark相关文档。
在集群上,以Standalone模式运行,执行如下命令:
cd /usr/local/spark 2 ./bin/spark-submit --class org.shirdrn.spark.streaming.UserClickCountAnalytics --master spark://hadoop1:7077 --executor-memory 1G --total-executor-cores 2 ~/spark-0.0.SNAPSHOT.jar spark://hadoop1:7077
可以查看集群中各个Worker节点执行计算任务的状态,也可以非常方便地通过Web页面查看。
下面,看一下我们存储到Redis中的计算结果,如下所示:
有关更多关于Spark Streaming的详细内容,可以参考官方文档。
附录
这里,附上前面开发的应用所对应的依赖,以及打包Spark Streaming应用程序的Maven配置,以供参考。如果使用maven-shade-plugin插件,配置有问题的话,打包后在Spark集群上提交Application时候可能会报错Invalid signature file digest for Manifest main attributes。
