粒子滤波器的Matlab实现
前言:粒子滤波器相较于卡尔曼滤波器或者UKF无迹卡尔曼滤波器而言,可以表达强非线性的变换且无需假设后验分布为高斯分布,在描述多峰分布时具有非常大的优势。粒子滤波器被广泛的应用于机器人系统中,如著名的Gmapping算法便是在粒子滤波器的基础上实现的,但是当前网络中对粒子滤波器的描述往往浅尝则止或长篇大论,导致学习起来往往是了解大概流程而不懂实际代码实现,无法应用于自己机器人中或困于理论推导。因此本文将简要的说明粒子滤波器的流程,然后在matlab中一步步的实现粒子滤波器,其中核心代码仅有20行,非常便于理解从而打通由理论到实际的过程。
原理介绍
算法流程
- 根据上一次的粒子分布和控制命令更新粒子位置
- 对更新后的粒子计算在该粒子的情况下,获得传感器观测的概率作为权重
- 根据权重进行重采样
一、根据上一次分布和控制指令更新粒子位置
假设某一粒子位置为![]() ,控制命令为
,控制命令为![]() ,即旋转一定角度后前进一定的距离。跟新粒子的位置如下
,即旋转一定角度后前进一定的距离。跟新粒子的位置如下
![]()
%控制机器人前进
function pos = move(robot_pos,set_w,set_v,control_noise)
% 先进行旋转,加上噪声,并归一化到0~pi*2
pos(3) = mod(robot_pos(3) + set_w + control_noise*rand(),2*pi);
% 前进距离+噪声
V = set_v + control_noise*rand();
% 坐标变换,因为前进距离是车体坐标系而要求的是世界坐标系下的
pos(1) = mod(robot_pos(1) - V*sin(pos(3)),200);
pos(2) = mod(robot_pos(2) + V*cos(pos(3)),200);
end二、对更新后的粒子计算在该粒子的情况下,获得传感器观测的概率作为权重
计算权重的公式为
![]()
对于某一时刻真实的测量值为![]() ,而对于其中一个粒子假设也进行了一次同样的测量根据地图估计出测量值为
,而对于其中一个粒子假设也进行了一次同样的测量根据地图估计出测量值为![]() ,则认为传感器的测量噪声是满足高斯分布的,因此该粒子测量值的概率分布为
,则认为传感器的测量噪声是满足高斯分布的,因此该粒子测量值的概率分布为
其中x带入传感器测量的真实值,而![]() 为当前粒子根据地图信息估计出最可能的测量值,而协方差矩阵为测量传感器的设定的误差。
为当前粒子根据地图信息估计出最可能的测量值,而协方差矩阵为测量传感器的设定的误差。
% 获取机器人在当前位置观测到对应数据的概率
function weight = get_probability(P,Z,landMark,sensor_noise)
particle_Z = getDistance(P,landMark,sensor_noise);%根据地图获取理论上最有可能的观测结果
distance = particle_Z - Z;%计算和真实值之间的差值
noise = zeros([1,12]) + sensor_noise*sensor_noise;%根据设定观测噪声,构建协方差
sigma = diag(noise);
%带入多维高斯分布的公式中,这里去掉了归一化常数项
weight = exp(-1/2 * (distance)' / (sigma) * (distance));
end三、根据权重进行重采样
使用如下的重采样策略,假设由M个样本,每个样本的权重为![]() ,则根据权重进行归一化
,则根据权重进行归一化
将0~1的圆弧分成![]() 份,每一份的长度为
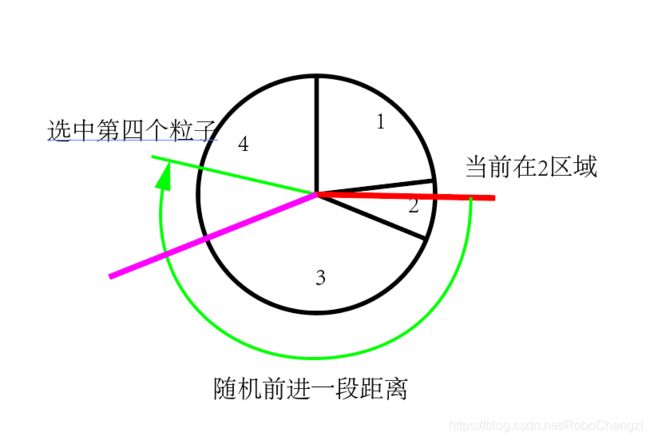
份,每一份的长度为![]() ,然后在该圆上随机取值,落到哪一段则选取该段对应的粒子,如图所示当前落在2区域内,然后随机生成前进距离,然后根据随机距离进入了第四个粒子的范围则选中第四个粒子,然后不断重复直至找到M个粒子。
,然后在该圆上随机取值,落到哪一段则选取该段对应的粒子,如图所示当前落在2区域内,然后随机生成前进距离,然后根据随机距离进入了第四个粒子的范围则选中第四个粒子,然后不断重复直至找到M个粒子。
% 粒子滤波:根据权重进行重采样
sum_weight = sum(weight);
weight = weight./sum_weight;%归一化权重
max_weight = max(weight);
index = ceil(rand()*particle_num);%开始时随机选取一个位置
for i = 1:particle_num %随机采样的过程
beta = rand() * 2 * max_weight;%随机生成前进距离,避免太远处或太近,设置为最大值的两倍
while beta > weight(index+1)%重采样过程
beta = beta - weight(index+1);
index = mod(index + 1,particle_num-1);
end
temp_particle(:,i) = particle(:,index+1);
end
particle = temp_particle;Matlab代码实现
%% begin
clc;
clear;
%% set param
map_length = 200;%场地范围为200m
% 路标
landMarkNum = 12;%设定12个路标
%随机生成路标作为地图
landMark = [rand()*map_length rand()*map_length rand()*map_length rand()*map_length rand()*map_length rand()*map_length rand()*map_length rand()*map_length rand()*map_length rand()*map_length rand()*map_length rand()*map_length
rand()*map_length rand()*map_length rand()*map_length rand()*map_length rand()*map_length rand()*map_length rand()*map_length rand()*map_length rand()*map_length rand()*map_length rand()*map_length rand()*map_length];
control_noise = 5; %控制机器人运动的噪声
sensor_noise = 10; %传感器对地图的测量噪声
robot_v = 20; %机器人在20m内随机运动
robot_w = 0;%0.1*pi;
T = 20;%进行T次迭代
particle_num = 1000;%使用1000个粒子
particle = zeros([3,particle_num]);%粒子的位置
temp_particle = zeros([3,particle_num]);%更新粒子时的临时变量
weight = zeros([1,particle_num]);%粒子的权重
%% 粒子滤波步骤
% 随机生成初始机器人的位置
robot_pos = [rand()*map_length,rand()*map_length,rand()*2*pi]';
% 随机生成初始粒子分布的位置
for i = 1:particle_num
particle(:,i) = [rand()*map_length,rand()*map_length,rand()*2*pi]';
end
%% plot
plot(robot_pos(1),robot_pos(2),'b*');
xlim([0 200])
ylim([0 200])
hold on;
for i=1:landMarkNum
plot(landMark(1,i),landMark(2,i),'go');
hold on;
end
for i=1:particle_num
plot(particle(1,i),particle(2,i),'y.');
hold on;
end
for t = 1:T
% 假设机器人一直在随机运动
set_v = rand()*robot_v;
set_w = rand()*robot_w;
% 将命令给实际的机器人,但是会有一定的误差
robot_pos = move(robot_pos,set_w,set_v,control_noise/10);
% 在当前位置测量,测量同样会有一定误差
Z = getDistance(robot_pos,landMark,sensor_noise);
% 粒子滤波:根据上一次的分布和当前指令得到预测分布,并计算权重
for i = 1:particle_num
particle(:,i) = move(particle(:,i),set_w,set_v,control_noise);
weight(i) = get_probability(particle(:,i),Z,landMark,sensor_noise);
end
% 粒子滤波:根据权重进行重采样
sum_weight = sum(weight);
weight = weight./sum_weight;%归一化权重
max_weight = max(weight);
index = ceil(rand()*particle_num);%开始时随机选取一个位置
for i = 1:particle_num %随机采样的过程
beta = rand() * 2 * max_weight;%随机生成前进距离,避免太远处或太近,设置为最大值的两倍内
while beta > weight(index+1)%重采样过程
beta = beta - weight(index+1);
index = mod(index + 1,particle_num-1);
end
temp_particle(:,i) = particle(:,index+1);
end
particle = temp_particle;
%% update plot
clf;
for i=1:particle_num
plot(particle(1,i),particle(2,i),'r.');
hold on;
end
plot(robot_pos(1),robot_pos(2),'b*');
xlim([0 200])
ylim([0 200])
hold on;
pause(0.1);
end
%% function define
% 获取机器人在当前位置观测到对应数据的概率
function weight = get_probability(P,Z,landMark,sensor_noise)
particle_Z = getDistance(P,landMark,sensor_noise);%根据地图获取理论上最有可能的观测结果
distance = particle_Z - Z;%计算和真实值之间的差值
noise = zeros([1,12]) + sensor_noise*sensor_noise;%根据设定观测噪声,构建协方差
sigma = diag(noise);
%带入多维高斯分布的公式中,这里去掉了归一化常数项
weight = exp(-1/2 * (distance)' / (sigma) * (distance));
end
%计算当前机器人位置观测到地图中的地标位置的距离
function distance = getDistance(position,landMark,sensor_noise)
dis = [0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]';
for j=1:length(landMark) %遍历所有地标
% 计算和当前机器人的距离
l = sqrt((position(1) - landMark(1,j))^2 + (position(2) - landMark(2,j))^2);
dis(j) = l + sensor_noise*rand();% 加上随机生成的噪声项
end
% 返回各距离数据
distance = dis;
end
%控制机器人前进
function pos = move(robot_pos,set_w,set_v,control_noise)
% 先进行旋转,加上噪声,并归一化到0~pi*2
pos(3) = mod(robot_pos(3) + set_w + control_noise*rand(),2*pi);
% 前进距离+噪声
V = set_v + control_noise*rand();
% 坐标变换,因为前进距离是车体坐标系而要求的是世界坐标系下的
pos(1) = mod(robot_pos(1) - V*sin(pos(3)),200);
pos(2) = mod(robot_pos(2) + V*cos(pos(3)),200);
end