C++ STL常用算法-67-集合算法-交集/并集/差集
这篇是学习常用算法的最后一篇,来学习三个集合算法。主要和数学几个概念有关系,交集 并集 和差集。下面分别用代码来练习每一个集合算法。
算法简介:
set_intersection //求两个容器的交集
set_union //求两个容器的并集
set_difference //求两个容器的差集
1.set_intersection 交集
求两个容器的交集
函数原型:set_intersection()
返回数据存储在另一个容器,容器的大小建议取小容器的大小的值
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void Print01(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
void test01()
{
vector v1;
vector v2;
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i); // 范围0-9
v2.push_back(i+5); // 范围5-15
}
vector v3;
v3.resize(v1.size()); // 最特殊情况,v2全部包含v1里面的元素,这个时候v3大小建议取v1的大小
set_intersection(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());
cout << "交集:" << endl;
for_each(v3.begin(), v3.end(), Print01);
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
} 运行结果:
所以,这里建议选择一个容器大小最小用来当做交集后存储的容器,可以通过代码if比较两个容器的size。
vv3.resize(min(v1.size(), v2.size()));
2.set_union 并集
并集就是两个容器不重复的元素
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void Print01(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
void test01()
{
vector v1;
vector v2;
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i); // 范围0-9
v2.push_back(i+5); // 范围5-15
}
vector v3;
v3.resize(v1.size() + v2.size()); // 最特殊情况,v2全部包含v1里面的元素,这个时候v3大小建议取v1的大小
set_union(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());
cout << "并集:" << endl;
for_each(v3.begin(), v3.end(), Print01);
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
} 运行结果:
目标容器空间,后面有几个是0,除非,最特殊情况,两个容器都没有一个元素和对方相同。
3.set_difference 差集
差集分两种情况,容器1和容器2的差集,和反过来 容器2和容器1的差集 结果是不等价的
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void Print01(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
void test01()
{
vector v1;
vector v2;
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i); // 范围0-9
v2.push_back(i+5); // 范围5-15
}
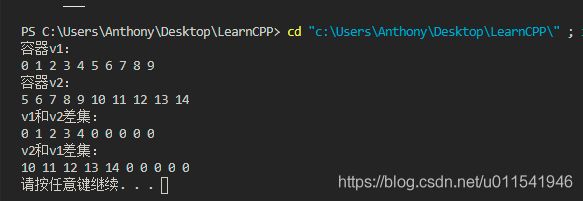
cout << "容器v1:" << endl;
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), Print01);
cout << endl;
cout << "容器v2:" << endl;
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), Print01);
cout << endl;
vector v3;
v3.resize(max(v1.size(),v2.size()));
set_difference(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());
cout << "v1和v2差集:" << endl;
for_each(v3.begin(), v3.end(), Print01);
cout << endl;
vector v4;
v4.resize(max(v1.size(),v2.size()));
set_difference(v2.begin(), v2.end(), v1.begin(), v1.end(), v4.begin());
cout << "v2和v1差集:" << endl;
for_each(v4.begin(), v4.end(), Print01);
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
} 运行结果
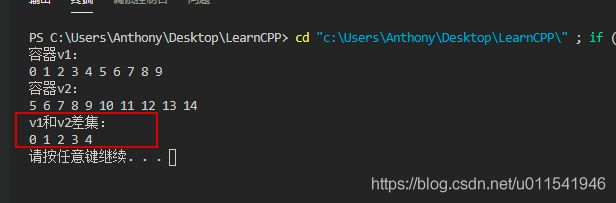
其实,注意到上面我们输出第三个容器的时候,后面会多一些0,如果不想要多余0输出,怎么办呢?
上面三个集合算法返回值都是迭代器,而且返回的都是结束迭代器
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void Print01(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
void test01()
{
vector v1;
vector v2;
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i); // 范围0-9
v2.push_back(i+5); // 范围5-15
}
cout << "容器v1:" << endl;
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), Print01);
cout << endl;
cout << "容器v2:" << endl;
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), Print01);
cout << endl;
vector v3;
v3.resize(max(v1.size(),v2.size()));
vector::iterator targetEnd = set_difference(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());
cout << "v1和v2差集:" << endl;
for_each(v3.begin(), targetEnd, Print01);
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
} 输出: