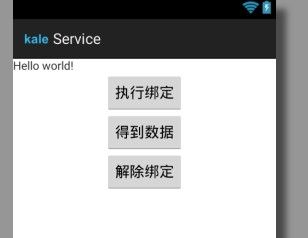
- 鸿蒙API14开发【@ohos.account.distributedAccount (分布式账号管理)】短距通信服务
移动开发技术栈
鸿蒙开发harmonyos分布式华为鸿蒙系统鸿蒙通信
本模块提供管理分布式账号的一些基础功能,主要包括查询和更新账号登录状态。说明本模块首批接口从APIversion7开始支持。后续版本的新增接口,采用上角标单独标记接口的起始版本。导入模块import{distributedAccount}from'@kit.BasicServicesKit';distributedAccount.getDistributedAccountAbilitygetDis
- Java调本地接口重定向
唯他命
javajson开发语言
/***通用接口*/@PostMapping("/deviceToService/up")@ApiOperationSupport(order=1)@ApiOperation(value="通用接口",notes="传入requestDTO")publicObjectdetail(@RequestBodyRequestDTOrequestDTO){Instructionsdetail=instru
- kubectl describe pod 命令以及输出详情讲解
Moshow郑锴
CloudDockerKuberneteskubernetes云原生kubectlpoddocker
kubectldescribepod命令格式kubectldescribepod-n:Pod的名称。-n:指定命名空间,默认是当前命名空间。controlplane~✖kubectldescribepodnewpods-dzmkgName:newpods-dzmkgNamespace:defaultPriority:0ServiceAccount:defaultNode:controlplane/
- MyBatisPlus 代码生成器如何使用?一篇文章学会它!!!
程序猿ZhangSir
Java数据库#MyBatisjavaspring数据库
目录一.MP代码生成器简介二.准备工作2.1建立数据库和表2.1创建项目三.编写工具类3.1创建类3.2定义数据库连接变量3.3定义单表代码生成函数3.4扩展为任意表自动生成代码四.测试代码生成器4.1测试单表生成model方法一.MP代码生成器简介代码生成器是MyBatis-Plus提供的一个非常实用的功能,可以快速生成Entity、Mapper、MapperXML、Service、Contro
- Docker 部署RabbitMQ
逢生博客
dockerrabbitmq容器springboot
文章目录镜像docker-compose.yml访问控制台SpringBoot批量声明队列镜像https://hub.docker.com/_/rabbitmqdockerpullrabbitmq:managementdockerpullrabbitmq:4.0.7-managementdocker-compose.ymlservices:rabbitmq:image:rabbitmq:3.9.5
- MybatisPlus+Spring Boot3 分页查询实现
新停浊酒杯
springbootmybatis后端
目录导入依赖本文的house表直接复制粘贴运行即可MybatisConfig配置文件创建数据库对应的实体类创建mapper层接口在service包下创建xxxService接口controller层创建XXXController类完成分页查询导入依赖com.baomidoumybatis-plus-spring-boot3-starter3.5.5本文的house表直接复制粘贴运行即可/*Navi
- pyspark 遇到**Py4JJavaError** Traceback (most recent call last) ~\AppData\
2pi
sparkpython
Py4JJavaErrorTraceback(mostrecentcalllast)~\AppData\Local\Temp/ipykernel_22732/1401292359.pyin---->1feat_df.show(5,vertical=True)D:\Anaconda3\envs\recall-service-cp4\lib\site-packages\pyspark\sql\data
- 高级java每日一道面试题-2025年3月06日-微服务篇[Eureka篇]-Eureka服务注册与发现是什么?
java我跟你拼了
java每日一道面试题java微服务eureka
如果有遗漏,评论区告诉我进行补充面试官:Eureka服务注册与发现是什么我回答:根据你提供的详细解析,结合之前的回答,我们可以更加全面地理解Eureka服务注册与发现机制,并补充一些关键点,特别是针对面试准备的内容。一、服务注册(ServiceRegistration)核心机制:当服务提供者启动时,它会通过EurekaClient向EurekaServer发送元数据。这些元数据包括但不限于IP地址
- 安装(python 版)
C-haidragon
mysql
安装安装sudoapt-getinstallmysql-servermysql-client然后按照提示输入管理服务启动servicemysqlstart停止servicemysqlstop重启servicemysqlrestart允许远程连接找到mysql配置文件并修改sudovi/etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf将bind-address=127.0.0.1注
- [ARM+Codesys Customer Case] Application Case of RK3568/A40i/STM32+Codesys in Intelligent Manufacturi
ARM+FPGA+AI工业主板定制专家
stm32codesysrk3568A40I
Vegetablesareessentialfoodsinpeople'sdailylives,andtherearevariouswaystoconsumethem.Sinceenteringamoderatelyprosperoussociety,people'spaceoflifehasbecomeincreasinglyfast,andmanytraditionalservicescann
- Infura 简介
倒霉男孩
区块链知识区块链web3
文章目录Infura简介Infura的主要功能Infura的替代方案(类似服务)AlchemyQuickNodeAnkrMoralisPocketNetwork什么时候选择Infura?Infura简介Infura是一个区块链基础设施即服务(BaaS,BlockchainasaService),提供高可用性的以太坊(Ethereum)节点和IPFS存储访问,让开发者可以轻松连接区块链网络,而无需自
- goldengate sqlserver mysql_Oracle GoldenGate 之 SqlServer数据同步到Mysql数据库
Huawei_Germany
goldengatesqlservermysql
C:\OGG>INSTALLADDSERVICEService'GGSMGR'created.Installprogramterminatednormally.C:\OGG>配置ODBC数据源MicrosoftSQLServerODBC驱动程序版本06.01.7601数据源名称:oa_test数据源描述:服务器:WIN-UGCMTTOTKE7数据库:(Default)语言:(Default)翻译字
- Java、Spring、SpringBoot
陈陈爱java
springbootjavaspring
JAVA与Spring不使用Spring的程序UserService.javapublicclassUserService{publicStringgetUserName(){return"JohnDoe";}}Main.javapublicclassMain{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){//手动创建UserService实例UserServiceuser
- 高级java每日一道面试题-2025年3月05日-微服务篇[Eureka篇]-Eureka在微服务架构中的角色?
java我跟你拼了
java每日一道面试题架构java微服务架构服务发现健康检查服务注册
如果有遗漏,评论区告诉我进行补充面试官:Eureka在微服务架构中的角色?我回答:在微服务架构中,Eureka作为Netflix开源的服务发现组件,在解决服务间通信的寻址问题方面扮演着至关重要的角色。以下是结合提供的内容对Eureka在微服务架构中的角色进行的详细解析和综合概述:1.服务注册(ServiceRegistration)功能:服务提供者(Provider)启动时向EurekaServe
- 使用mockMVC对controller层进行接口调试
无一郎的技术圈
工作经验积累java后端mvc
文章目录背景一、controller层构建二、controller层测试1.先尝试本地postman测试2.使用mockMVC进行调试3.使用mockMVC和本地不同总结背景后端新增了一个对算法badCase排查功能,通过用户传入的内容按照节点成功或者失败走不同分支流程处理,流程结构如图所示。判定流程的底层功能通过service层以RPC接口形式提供服务,结构定义如下:publicResponse
- 鸿蒙Next开发与未来发展的变革:全场景操作系统的全新纪元
北辰alk
鸿蒙harmonyos华为
文章目录引言:从兼容到自主的跨越式进化一、鸿蒙Next技术架构解析1.1系统架构全景图1.1.1微内核架构优势1.2与OpenHarmony的关系二、开发范式革命2.1应用开发模式对比2.1.1元服务(MetaService)定义2.2开发工具链升级(DevEcoStudio4.0)2.2.1核心功能增强2.2.2工程结构变革三、关键技术突破3.1方舟编译器深度优化3.2分布式能力增强3.2.1设
- 天地图WMTS GetTile(地图API)请求参数深度解析
喆星时瑜
#天地图arcgis
以下针对天地图API影像底图瓦片请求URL进行逐项参数拆解,结合OGCWMTS1.0.0标准与天地图技术规范进行专业解读:http://t0.tianditu.gov.cn/img_w/wmts?SERVICE=WMTS&REQUEST=GetTile&VERSION=1.0.0&LAYER=img&STYLE=default&TILEMATRIXSET=w&FORMAT=tiles&TILEMA
- python 如何引入同一个文件夹下py方法
m0_68335176
eclipse
前言毕业快三年了,前后也待过几家公司,碰到各种各样的同事。见识过各种各样的代码,优秀的、垃圾的、不堪入目的、看了想跑路的等等,所以这篇文章记录一下一个优秀的后端Java开发应该有哪些好的开发习惯。拆分合理的目录结构受传统的MVC模式影响,传统做法大多是几个固定的文件夹controller、service、mapper、entity,然后无限制添加,到最后你就会发现一个service文件夹下面有几十
- 【spring-boot-starter-data-neo4j】创建结点和查找结点操作
阿梦Anmory
neo4jneo4j
配置连接neo4j#application.propertiesspring.neo4j.uri=bolt://localhost:7687spring.neo4j.authentication.username=neo4jspring.neo4j.authentication.password=你的密码定义实体类packagecom.anmory.platform.GraphService.Da
- ActivityManagerService是什么?有什么作用?以及内部原理——概要!!!!!!
脚踏实地,坚持不懈!
android
下面有关于ActivityManagerService的一些理解的资料,可以参考加深理解ActivityManagerService是什么?有什么作用?https://zhaokaiqiang.gitbook.io/the-analysis-of-android-key-point/android_system/activitymanagerserviceActivityManagerServic
- 前端缓存接口数据
jjjjjjjjj¢
笔记前端
在前端缓存接口数据时,可以结合浏览器缓存策略、前端存储(localStorage、sessionStorage、IndexedDB)、内存缓存(变量存储)、ServiceWorker等方式,选择适合的方案。使用浏览器HTTP缓存(推荐,依赖后端支持)如果接口数据不会频繁变化,可以使用HTTP缓存策略(强缓存+协商缓存),减少不必要的请求。后端设置Cache-Control在接口响应头中,服务器可以
- 【第一天】并发编程的10个坑 (万字血泪经验教训)
程序猿小假
Java开发日记java
1、SimpleDateFormat线程不安全在Java8之前,对时间的格式化处理,一般都是用的SimpleDateFormat类实现的。例如:@ServicepublicclassSimpleDateFormatService{publicDatetime(Stringtime)throwsParseException{SimpleDateFormatdateFormat=newSimpleDa
- Spring 核心注解深度解析教程
我不是少爷.
Java基础springpythonjava
(涵盖@Component/@Repository/@Service/@Controller/@Autowired/@Qualifier/@Resource/@Value)一、组件扫描与分层注解1.@Component基础组件标识@Component//通用组件标识publicclassBasicComponent{//会被Spring自动扫描并注册为Bean}特性:所有组件注解的基类默认Bean
- 微服务调试:多环境 env 组件详解
时雨h
算法JAVA面试javapython运维
微服务调试:多环境env组件详解一、多环境env组件(一)微服务调试的痛点在微服务架构下,开发人员在调试过程中常常会遇到各种挑战。其中一个常见的问题就是在多人协作的开发环境中,如何确保自己的调试请求能够准确地到达自己本地的服务实例,而不是被其他开发者的实例所拦截。例如,假设团队中有两位开发人员A和B,他们都在本地启动了名为"user-service"的微服务实例。当A发起一个针对"user-ser
- 微服务架构: SpringCloud实战经验总结
苹果酱0567
面试题汇总与解析课程设计springbootvue.jsjavamysql
微服务架构:SpringCloud实战经验总结一、微服务架构简介什么是微服务架构微服务架构(MicroservicesArchitecture)是一种以业务功能组织的松散耦合、高内聚的服务架构。它将传统的单体应用拆分成一组小型服务,每个服务都可以独立开发、部署、扩展和替换。微服务架构通过服务之间的松耦合和互相隔离,使得开发团队能够更快速地迭代和交付应用,同时提高了整体系统的可扩展性和灵活性。二、S
- linux下使用curl访问多参数url
耘田
Linuxcurllinuxurl多参数
curl-ihttp://marsoffset.goforandroid.com/GoSmsMarService/abc?a=116.397428&b=39.90923[1]8741[jb-xccheng@usa-ip-12~]$HTTP/1.1500InternalServerErrorServer:nginx/1.2.0Date:Wed,20Jun201204:16:21GMTContent-
- javaweb中@Component和@Mapper和@Service和@RestController这几个注解要加在哪?为什么?
瑞金彭于晏
mavenjavaspringbootspring
在JavaWeb开发中特别是在使用Spring框架(包括SpringBoot)时,@Component、@Mapper、@Service、@RestController这些注解扮演着非常重要的角色,它们用于定义组件的类型,并帮助Spring框架进行自动装配和依赖注入。下面分别解释这些注解应该加在哪里以及为什么:1.@Component加在哪里:@Component可以加在任何类上,表示这个类是一个
- Java开发-面试题-0014-@Component, @Controller, @Repository,@Mapper,@Service有何区别
CodeZeng1998
面试题java开发语言springboot
更多内容欢迎关注我(持续更新中,欢迎Star✨)Github:CodeZeng1998/Java-Developer-Work-Note技术公众号:CodeZeng1998(纯纯技术文)生活公众号:好锅(Lifeismorethancode)其他平台:CodeZeng1998、好锅@Component,@Controller,@Repository,@Mapper,@Service有何区别:@Co
- 学习SpringBoot过程中常见问题汇总及多工程项目使用 IntelliJ IDEA 打开
KunQian_smile
springBoot
一:SpringBoot:redisClientine.test.serviceImpl.RedisServiceImplrequiredabeanoftype‘com.examp1:没有自动注入导致。service类上面没有@service注解或者mapper上没有@Repository注解,但是这种情况比较少见,一般不会忘记。2:配置了mybatis,但没有指定扫描的包。(1)直接在生成出来的
- SpringBoot中Server层以及Mapper层常用注解
π大星的日常
javajava-rabbitmq
最近看了一下SpringBoot2的课程,发现好多的注解并不是很了解,只是简单的会用,但是真是发生的作用却不知道,最近花了一些时间把这些注解进行了一下整理,针对不同的层级进行了细致的划分,最近几天会依次给大家更新关于注解的内容,对大家有帮助的话点赞支持一下哦!4.Service层注解@Service注解一般写在业务层的接口实现类上,而不是接口上。4.1@Service@Service:@Servi
- LeetCode[位运算] - #137 Single Number II
Cwind
javaAlgorithmLeetCode题解位运算
原题链接:#137 Single Number II
要求:
给定一个整型数组,其中除了一个元素之外,每个元素都出现三次。找出这个元素
注意:算法的时间复杂度应为O(n),最好不使用额外的内存空间
难度:中等
分析:
与#136类似,都是考察位运算。不过出现两次的可以使用异或运算的特性 n XOR n = 0, n XOR 0 = n,即某一
- 《JavaScript语言精粹》笔记
aijuans
JavaScript
0、JavaScript的简单数据类型包括数字、字符创、布尔值(true/false)、null和undefined值,其它值都是对象。
1、JavaScript只有一个数字类型,它在内部被表示为64位的浮点数。没有分离出整数,所以1和1.0的值相同。
2、NaN是一个数值,表示一个不能产生正常结果的运算结果。NaN不等于任何值,包括它本身。可以用函数isNaN(number)检测NaN,但是
- 你应该更新的Java知识之常用程序库
Kai_Ge
java
在很多人眼中,Java 已经是一门垂垂老矣的语言,但并不妨碍 Java 世界依然在前进。如果你曾离开 Java,云游于其它世界,或是每日只在遗留代码中挣扎,或许是时候抬起头,看看老 Java 中的新东西。
Guava
Guava[gwɑ:və],一句话,只要你做Java项目,就应该用Guava(Github)。
guava 是 Google 出品的一套 Java 核心库,在我看来,它甚至应该
- HttpClient
120153216
httpclient
/**
* 可以传对象的请求转发,对象已流形式放入HTTP中
*/
public static Object doPost(Map<String,Object> parmMap,String url)
{
Object object = null;
HttpClient hc = new HttpClient();
String fullURL
- Django model字段类型清单
2002wmj
django
Django 通过 models 实现数据库的创建、修改、删除等操作,本文为模型中一般常用的类型的清单,便于查询和使用: AutoField:一个自动递增的整型字段,添加记录时它会自动增长。你通常不需要直接使用这个字段;如果你不指定主键的话,系统会自动添加一个主键字段到你的model。(参阅自动主键字段) BooleanField:布尔字段,管理工具里会自动将其描述为checkbox。 Cha
- 在SQLSERVER中查找消耗CPU最多的SQL
357029540
SQL Server
返回消耗CPU数目最多的10条语句
SELECT TOP 10
total_worker_time/execution_count AS avg_cpu_cost, plan_handle,
execution_count,
(SELECT SUBSTRING(text, statement_start_of
- Myeclipse项目无法部署,Undefined exploded archive location
7454103
eclipseMyEclipse
做个备忘!
错误信息为:
Undefined exploded archive location
原因:
在工程转移过程中,导致工程的配置文件出错;
解决方法:
- GMT时间格式转换
adminjun
GMT时间转换
普通的时间转换问题我这里就不再罗嗦了,我想大家应该都会那种低级的转换问题吧,现在我向大家总结一下如何转换GMT时间格式,这种格式的转换方法网上还不是很多,所以有必要总结一下,也算给有需要的朋友一个小小的帮助啦。
1、可以使用
SimpleDateFormat SimpleDateFormat
EEE-三位星期
d-天
MMM-月
yyyy-四位年
- Oracle数据库新装连接串问题
aijuans
oracle数据库
割接新装了数据库,客户端登陆无问题,apache/cgi-bin程序有问题,sqlnet.log日志如下:
Fatal NI connect error 12170.
VERSION INFORMATION: TNS for Linux: Version 10.2.0.4.0 - Product
- 回顾java数组复制
ayaoxinchao
java数组
在写这篇文章之前,也看了一些别人写的,基本上都是大同小异。文章是对java数组复制基础知识的回顾,算是作为学习笔记,供以后自己翻阅。首先,简单想一下这个问题:为什么要复制数组?我的个人理解:在我们在利用一个数组时,在每一次使用,我们都希望它的值是初始值。这时我们就要对数组进行复制,以达到原始数组值的安全性。java数组复制大致分为3种方式:①for循环方式 ②clone方式 ③arrayCopy方
- java web会话监听并使用spring注入
bewithme
Java Web
在java web应用中,当你想在建立会话或移除会话时,让系统做某些事情,比如说,统计在线用户,每当有用户登录时,或退出时,那么可以用下面这个监听器来监听。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.ut
- NoSQL数据库之Redis数据库管理(Redis的常用命令及高级应用)
bijian1013
redis数据库NoSQL
一 .Redis常用命令
Redis提供了丰富的命令对数据库和各种数据库类型进行操作,这些命令可以在Linux终端使用。
a.键值相关命令
b.服务器相关命令
1.键值相关命令
&
- java枚举序列化问题
bingyingao
java枚举序列化
对象在网络中传输离不开序列化和反序列化。而如果序列化的对象中有枚举值就要特别注意一些发布兼容问题:
1.加一个枚举值
新机器代码读分布式缓存中老对象,没有问题,不会抛异常。
老机器代码读分布式缓存中新对像,反序列化会中断,所以在所有机器发布完成之前要避免出现新对象,或者提前让老机器拥有新增枚举的jar。
2.删一个枚举值
新机器代码读分布式缓存中老对象,反序列
- 【Spark七十八】Spark Kyro序列化
bit1129
spark
当使用SparkContext的saveAsObjectFile方法将对象序列化到文件,以及通过objectFile方法将对象从文件反序列出来的时候,Spark默认使用Java的序列化以及反序列化机制,通常情况下,这种序列化机制是很低效的,Spark支持使用Kyro作为对象的序列化和反序列化机制,序列化的速度比java更快,但是使用Kyro时要注意,Kyro目前还是有些bug。
Spark
- Hybridizing OO and Functional Design
bookjovi
erlanghaskell
推荐博文:
Tell Above, and Ask Below - Hybridizing OO and Functional Design
文章中把OO和FP讲的深入透彻,里面把smalltalk和haskell作为典型的两种编程范式代表语言,此点本人极为同意,smalltalk可以说是最能体现OO设计的面向对象语言,smalltalk的作者Alan kay也是OO的最早先驱,
- Java-Collections Framework学习与总结-HashMap
BrokenDreams
Collections
开发中常常会用到这样一种数据结构,根据一个关键字,找到所需的信息。这个过程有点像查字典,拿到一个key,去字典表中查找对应的value。Java1.0版本提供了这样的类java.util.Dictionary(抽象类),基本上支持字典表的操作。后来引入了Map接口,更好的描述的这种数据结构。
&nb
- 读《研磨设计模式》-代码笔记-职责链模式-Chain Of Responsibility
bylijinnan
java设计模式
声明: 本文只为方便我个人查阅和理解,详细的分析以及源代码请移步 原作者的博客http://chjavach.iteye.com/
/**
* 业务逻辑:项目经理只能处理500以下的费用申请,部门经理是1000,总经理不设限。简单起见,只同意“Tom”的申请
* bylijinnan
*/
abstract class Handler {
/*
- Android中启动外部程序
cherishLC
android
1、启动外部程序
引用自:
http://blog.csdn.net/linxcool/article/details/7692374
//方法一
Intent intent=new Intent();
//包名 包名+类名(全路径)
intent.setClassName("com.linxcool", "com.linxcool.PlaneActi
- summary_keep_rate
coollyj
SUM
BEGIN
/*DECLARE minDate varchar(20) ;
DECLARE maxDate varchar(20) ;*/
DECLARE stkDate varchar(20) ;
DECLARE done int default -1;
/* 游标中 注册服务器地址 */
DE
- hadoop hdfs 添加数据目录出错
daizj
hadoophdfs扩容
由于原来配置的hadoop data目录快要用满了,故准备修改配置文件增加数据目录,以便扩容,但由于疏忽,把core-site.xml, hdfs-site.xml配置文件dfs.datanode.data.dir 配置项增加了配置目录,但未创建实际目录,重启datanode服务时,报如下错误:
2014-11-18 08:51:39,128 WARN org.apache.hadoop.h
- grep 目录级联查找
dongwei_6688
grep
在Mac或者Linux下使用grep进行文件内容查找时,如果给定的目标搜索路径是当前目录,那么它默认只搜索当前目录下的文件,而不会搜索其下面子目录中的文件内容,如果想级联搜索下级目录,需要使用一个“-r”参数:
grep -n -r "GET" .
上面的命令将会找出当前目录“.”及当前目录中所有下级目录
- yii 修改模块使用的布局文件
dcj3sjt126com
yiilayouts
方法一:yii模块默认使用系统当前的主题布局文件,如果在主配置文件中配置了主题比如: 'theme'=>'mythm', 那么yii的模块就使用 protected/themes/mythm/views/layouts 下的布局文件; 如果未配置主题,那么 yii的模块就使用 protected/views/layouts 下的布局文件, 总之默认不是使用自身目录 pr
- 设计模式之单例模式
come_for_dream
设计模式单例模式懒汉式饿汉式双重检验锁失败无序写入
今天该来的面试还没来,这个店估计不会来电话了,安静下来写写博客也不错,没事翻了翻小易哥的博客甚至与大牛们之间的差距,基础知识不扎实建起来的楼再高也只能是危楼罢了,陈下心回归基础把以前学过的东西总结一下。
*********************************
- 8、数组
豆豆咖啡
二维数组数组一维数组
一、概念
数组是同一种类型数据的集合。其实数组就是一个容器。
二、好处
可以自动给数组中的元素从0开始编号,方便操作这些元素
三、格式
//一维数组
1,元素类型[] 变量名 = new 元素类型[元素的个数]
int[] arr =
- Decode Ways
hcx2013
decode
A message containing letters from A-Z is being encoded to numbers using the following mapping:
'A' -> 1
'B' -> 2
...
'Z' -> 26
Given an encoded message containing digits, det
- Spring4.1新特性——异步调度和事件机制的异常处理
jinnianshilongnian
spring 4.1
目录
Spring4.1新特性——综述
Spring4.1新特性——Spring核心部分及其他
Spring4.1新特性——Spring缓存框架增强
Spring4.1新特性——异步调用和事件机制的异常处理
Spring4.1新特性——数据库集成测试脚本初始化
Spring4.1新特性——Spring MVC增强
Spring4.1新特性——页面自动化测试框架Spring MVC T
- squid3(高命中率)缓存服务器配置
liyonghui160com
系统:centos 5.x
需要的软件:squid-3.0.STABLE25.tar.gz
1.下载squid
wget http://www.squid-cache.org/Versions/v3/3.0/squid-3.0.STABLE25.tar.gz
tar zxf squid-3.0.STABLE25.tar.gz &&
- 避免Java应用中NullPointerException的技巧和最佳实践
pda158
java
1) 从已知的String对象中调用equals()和equalsIgnoreCase()方法,而非未知对象。 总是从已知的非空String对象中调用equals()方法。因为equals()方法是对称的,调用a.equals(b)和调用b.equals(a)是完全相同的,这也是为什么程序员对于对象a和b这么不上心。如果调用者是空指针,这种调用可能导致一个空指针异常
Object unk
- 如何在Swift语言中创建http请求
shoothao
httpswift
概述:本文通过实例从同步和异步两种方式上回答了”如何在Swift语言中创建http请求“的问题。
如果你对Objective-C比较了解的话,对于如何创建http请求你一定驾轻就熟了,而新语言Swift与其相比只有语法上的区别。但是,对才接触到这个崭新平台的初学者来说,他们仍然想知道“如何在Swift语言中创建http请求?”。
在这里,我将作出一些建议来回答上述问题。常见的
- Spring事务的传播方式
uule
spring事务
传播方式:
新建事务
required
required_new - 挂起当前
非事务方式运行
supports
&nbs