【AIOT】Haptics Contributes To Contactless HCI
在未来,随着可穿戴和智能手机的发展,力触觉设备小型化和与智能手机、可穿戴设备集成,将为时不远。彼时,或许我们真的可以借助力触觉安慰远在它乡哭泣的恋人,思念的抚摸,可爱的儿女。
1、介绍
力触觉(Haptics)的感知是一种无所不在的对环境的感知能力。原始的力触觉是现代生物的感知: 视觉,听觉,嗅觉,痛觉和其他一切感知之母。
-
人类感知(生物神经)
-
机器感知(各类传感器)
-
计算机虚拟感知(数学建模)
随着技术的不断突破,我们将从影视时代进入虚拟现实时代,机器人(或者说人工智能)最终会成为这颗美丽星球的主流。而力反馈技术,将在这个进化中,起到不可磨灭的作用。
1.1. 可穿戴式
- EXOS 触觉控制器
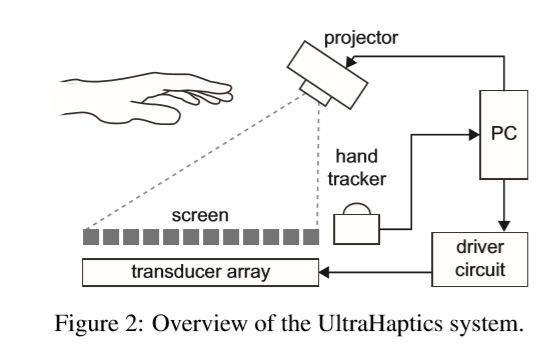
1.2. 超声波技术触觉反馈
- Ultrahaptics
- video
Focal Point: the place where all the ultrasound waves coincide. where the focal point is positioned in 3D space is programmable in real time. It can change position from instant to instant. Using a hand tracking device to track the exact position of your hand and position the focal point at a spot on it.
Pressure Point: the combined ultrasound waves have enough force to create a tiny dent in your skin, use this pressure point to create a vibration that touch sensors in you hands can detect.
Tactile effects in mid-air: use the pressure points to create a wide range of tactile effects–from sculpting virtual lines and shapes to froming 3D controls in mid-air.
1、VALUATION PROGRAM(评估项目)
这个项目协助一些还没有尝试过Ultrahaptics技术的,但可能有类似需求的用户确定是否要使用这项技术。
2、TOUCH DEVELOPMENT KIT(TOUCH 开发套件)Ultrahaptics提供给你这个开发套件,让你能迅速开发属于自己的超声波触觉反馈应用
3、ACADEMIC PROGRAM (学术项目)
与学校和非营利机构合作,采用Ultrahaptics做一些科研项目,探索更多的可能性。
focused ultrasound is capable of inducing tactile, thermal, tickling, itching and pain sensations [13].
2. 超声成像技术
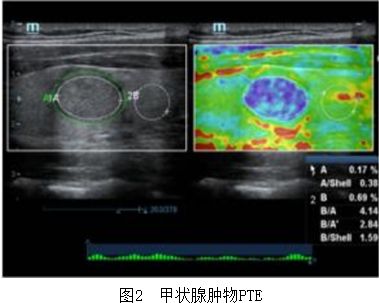
弹性成像技术通过获取有关组织弹性信息进行成像。弹性即可压缩性,指外力作用下组织发生变形的难易程度。组织的弹性值反映组织硬度,与其分子组成及病理组织结构有关[1-2]。弹性与组织的硬度呈反比,组织越硬,可压缩性越小,弹性越小;组织越软,可压缩性越大,弹性越大。超声弹性成像的基本原理为:外力对组织施加一定压力,依组织内部发生变形程度的不同,导致收集回波信号分布产生一定差异,回波信号经计算机处理在示波屏上以黑白/彩色的形式表示,得到组织弹性分布图。
2.1. 实时组织弹性成像
检查者需手动施加一定压力并保持一定振动频率,比较感兴趣区病变组织与周围正常组织在加压过程中的弹性差异[3-4]。根据组织弹性应力不同估计其内部不同位置的位移变化,计算出组织变形率,再通过灰阶或彩色编码成像。蓝色到红色表示感兴趣区组织从“硬”到“软”的变化。RTE主要应用于可压缩的表浅器官,如乳腺、甲状腺等,见图1、2。RTE能有效地分辨不同硬度的物体,但反映的是与周围组织的相对硬度值而非其绝对硬度[5-6]。近些年,RTE在评价慢性肌肉神经疼痛性病变中应用,RTE能够评价冈上肌较小的撕裂伤,并对之后旋转套修复术有预后监测作用[7]。但是,RTE技术无法从体外对深部组织有效施压,因此不适合深部脏器病变的检测。由于弹性成像图色彩的多样性及复杂性,难以对病灶及观察部位进行定量测量;操作者施加压力大小及频率成为RTE的主要影响因素[8]。
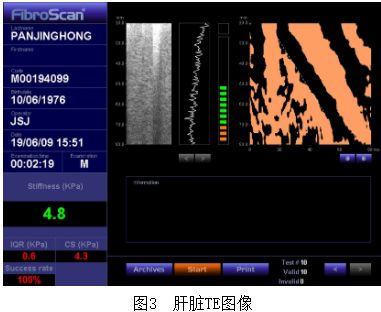
2.2. 瞬时弹性成像技术
TE是一种利用外振动器振动法测量组织弹性的方法。组织硬度越高,外力作用下发生变形能力小,弹性小,剪切波传播速度越快。基于一维TE,可进行肝脏硬度测值,为肝纤维化程度及肝硬化的无创诊断提供了非常有效的方法。
但TE仍存在本身的不足,因其为独立于传统超声成像系统的测量仪器,无法进行常规超声成像,不具有定位引导功能;对操作者经验依赖性高,若不能准确定位,会因不能避开血管及胆道对结果产生较大影响;取样范围较局限,测量采集来源于肝脏内1 cm×2 cm×5 cm的区域,测值为检测区域的平均弹性值;目前对肝纤维化的分期数据有较大的重叠,对Cut off值的划分仍不一样;肥胖、肋间隙狭小、腹水、肝实质和大血管结构的改变、坏死炎症及脂肪肝等因素对弹性结果的测值存在影响。
2.3. 实时剪切波弹性成像
SWE/SWEI是采用探头发射脉冲刺激产生声辐射力,在组织不同深度上连续聚焦,产生Mach Cone效应,组织粒子高效振动引起位移变化产生剪切波,剪切波为传播速度约1~10 m/s的横波,波速较慢,可利用达20 000帧/s的超快速成像系统捕获、追踪剪切波得到实时的组织应变分布图,即弹性成像图[1, 3-4, 12-14]。SWE较TE、声辐射力弹性成像(acoustic radiation force impulse,ARFI)等弹性成像技术影响因素较少,可用于腹腔积液患者,且不受气体干扰影响[15-16]。
2.4. ARFI技术
第一代ARFI技术,具有声辐射力定量技术 (virtual touch tissue quantification,VTQ)一种成像模式,仅能用于腹部,器官弹性值定量测量;
第二代 ARFI 技术可用于腹部及浅表器官,具有VTQ和声辐射力成像技术(virtual touch tissue imaging,VTI )两种成像模式,但仅能对病灶内部某一点弹性参数进行定量测量,对于内部弹性参数分布不均的病灶测量存在困难,且重复性较差。
第三代ARFI技术被称为VTIQ“鹰眼”技术,能进行单幅图像多次测量,重复性更佳;将定性及定量剪切波测量合为一体,更能直观对感兴趣区进行显示;取样框大小最小为1 mm×1 mm,对小病灶进行更精准的测值。目前只能应用于表浅器官。
3. Paper
level:
author: Tom Carter( Department of Computer Science and Mechanical Engineering)
date: 2013
keyword:
- UltraHaptics; Interactive; Haptic feedback; touch screens;
Carter, Tom, et al. “UltraHaptics: multi-point mid-air haptic feedback for touch surfaces.” Proceedings of the 26th annual ACM symposium on User interface software and technology. 2013.
Paper: UltraHaptics
UltraHaptics: Multi-Point Mid-Air Haptic Feedback for Touch Surfaces
Summary
- outline the principle, design and implementation of an ultrasonic, mid-air haptic feedback system for touch surfaces.
- investigate the desirable properties of an acoustically transparent display surface that allows the haptic feedback to be projected through the display from below.
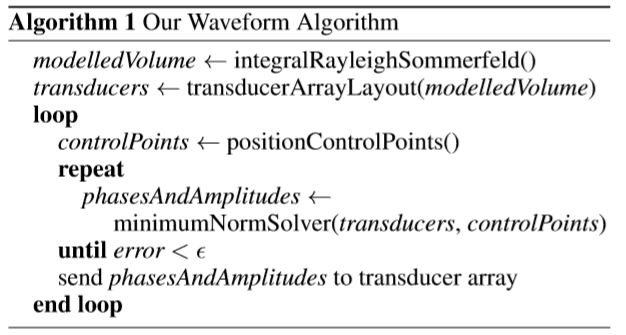
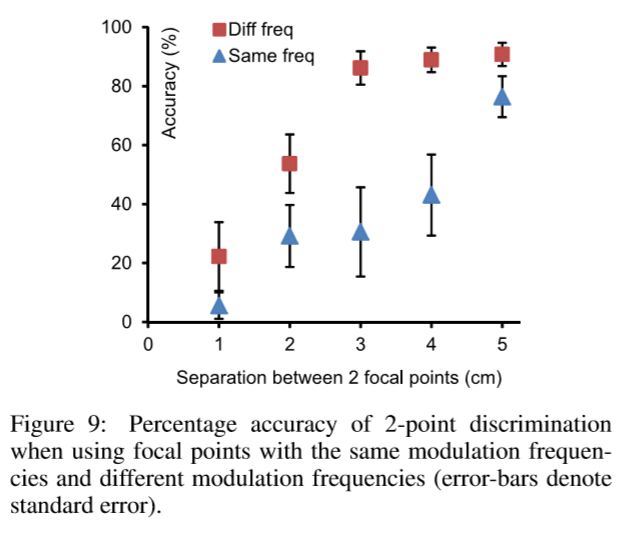
- present a series of psychophysical studies that demonstrate feedback points with different tactile properties can be distinguished at smaller separations and that users can identify different tactile properties with training.
Research Objective
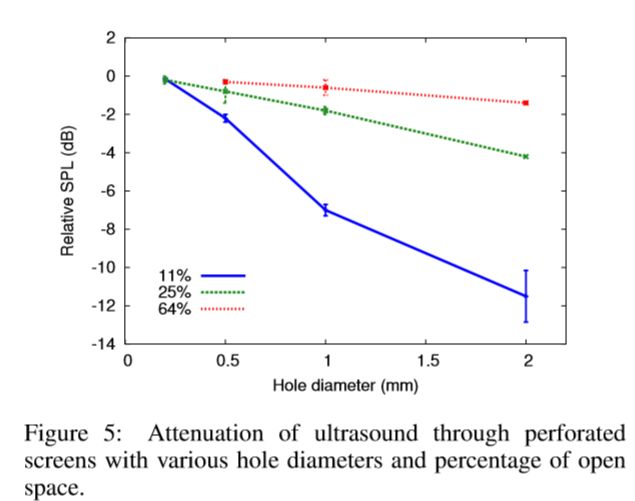
- Physical Phenomenon: surfaces with 0.5mm holes sizes and 25% open space reduce the impact on any foucusing algorithm while still creating a high performance projection surface.
- Application Area: hotel lobbies, shopping malls, and other high foot traffic areas.
- Purpose: walk-up and use ability to interaction and encourages spontaneous use.
- Scenario : when vision of the display is restricted, such as driving, and when the user doesn’t want to touch the device, such as when their hands are dirty.
Previous work:
-
recreating feedback on interactive surfaces, like vibration or by physically changing the shape of the surface.
-
Haptic Feedback Methods:
- vary the friction coefficient of the surface, either through vibrating the surface with ultrasound or through the use of electrovibraction, such as TeslaTouch. providing one haptic sensation at a time, and apply it across the entire surface
- physically change the shape of the touch surface, to contact with the surface
- Separating the visual and haptic displays, such as the haptic pen combines a pressure sensitive stylus with a physical actuator to provide a vibrotactile feedback.
- Wearable attachments: data gloves;
- SensableRays tranfers haptic feedback to an actuator on the user’s hand wirelessly through modulated light.
- FingerFlux alters a magnetic field to stimulate the user’s finger through an attached magnet.
-
Ultrasonic Haptic Feedback:
- acoustic radiation force: the ultrasound is focused onto the surface of the skin, where it induces a shear wave in the skin tissue.
- bypasses the receptors entirely and directly stimulates the nerve fibres, requires powerful acoustic fields that penetrate the skin.
By stimulating neuroreceptors within the skin,it has been demonstrated that focused ultrasound is capable of inducing tactile, thermal, tickling, itching and pain sensations [13].
Methods
- system overview:
【Aspect one】the array generating the acoustic field to also double as a projected diplay device.
【Aspect two】most existing approaches to generating acoustic fields suffer from secondary maxima that surround the central focus。
using a concept of control points to define a target for the algorithm by telling it to maximise and minimize the intensity selectively at these control points.
【Aspect three】there are no studies on users’ ability to disciminate different focal points generated using acoustic radiation force
focal points don’t have well defined edges we can not rely on the results of discrimination studies down with pins and vibrations.
Solution: feedback points with different tactile properties can be distinguished at smaller separations and that users can identify different tactile properties with training.
【Function one】Acoustically Transparent Display
the display surface must allow ultrasound to pass through without affecting the focusing and with minimal attenuation.
smaller and closer holes provide better transparency at higher frequencies
- relative sound pressure level( relative SPL(db)): where 0dB is the sound pressure level with no display surface present.
【Function Two】Independent Feedback Points
- adapt and extend an alternative focusing method so that each element of the transducer array can contribute to multiple focal points at the same time.
- correlate haptic and visual feedback, and attach meaning to noticeably different textures to transfer information.
- Perceptual Issures: the vibration is detected by mechanoreceptors within skin, which responsive to vibrations in the range 0.4Hz to 500 Hz.
【Implementation】constructing the hardware, computing amplitudes and phases for each transducer such that multiple points are formed, and modulating simultaneous focal points at different frequencies.
-
Haptic Feedback loog: when haptic feedback is required, a phase delay and amplitude is calculated for each transducer to create an acoustic field forming the desired focal points.
-
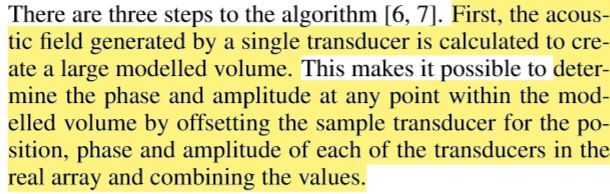
Computing Phase and Amplitudes:
-
Modulating Multiple Focal Points:
Modulating multiple focal points at different frequencies is achieved by time multiplexing scenes with different numbers of focal points.
Notes 去加强了解
-
遗留问题: 如何通过具体调节相位和信号强度的,下面三篇论文
- Multiple-focus ultrasound phased-array pattern synthesis: optimal driving-signal distributions for hyperthermia. IEEE T. Ultrason. Ferr. 36, 5 (1989), 540–548.
- Filonenko, E. A., Gavrilov, L. R., Khokhlova, V. A., and Hand, J. W. Heating of biological tissues by two-dimensional phased arrays with random and regular element distributions. Acoust. Phys. 50, 2 (2004), 222–231.
- TeslaTouch: Electrovibration for Touch Surfaces
level:
author: Marcello Giordano Orestis Georgiou Brygida Dzidek Loic Corenthy
date: 2018
keyword:
- HCI;
Paper: Mid-Air Haptics
Mid-Air Haptics for Control Interfaces
Summary
Proble Statement
- the immediateness provided by touch-less controllers has a significant draw-back: the lack of force or tactile feedback coming from the interaction with a physical device.
- mid-air focused ultrasonic haptic interfaces; air jets; air cannon; phemto-lasers
Challenges
- what kind of feedback can we generate effectively and which kind of mid-air haptic technology is more suitable for specific applications?
- hwo can we use perceptual effects, such as haptic illusion to generate better feedback in control applications?
- what’s the roadmap toward a miniaturized and portable mid-air haptic device?
- Do mid-air haptic control interfaces always require visual or audio feedback as well?
- what are the latency requirements in music robotics and tele-operation applications and hwo can mid-air haptic feedback be used in this space?