Flowable 快速入门教程:任务驳回与回退
Flowable 快速入门教程:任务驳回与回退
- 前言
- 支持场景
- 功能描述
- 驳回
- 退回
- 脏数据
- 什么是脏数据
- 串行样例
- 并行样例
- 会签样例
- 脏数据清洗效果图
- 完整代码
- 效果图
前言
本文的代码中没有对流程做任何特殊处理,用的都是流程本身的数据,因此可以通用,直接复制粘贴即可
方法不支持多对多跳转
回退不能够直接回退到子流程上,我这里按照只能回退到用户任务节点处理的
驳回可以直接驳回到子流程开始
可根据自己需要对代码进行调整
支持场景
并行网关,高级网关,包容网关,会签,子流程
功能描述
驳回
参数:当前任务ID,驳回原因
直接根据历史数据,获取上个用户任务节点,进行跳转
退回
参数:当前任务ID,驳回的节点Key
脏数据
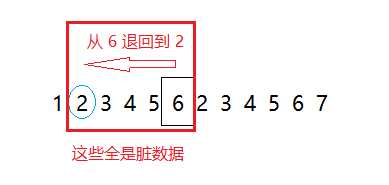
什么是脏数据
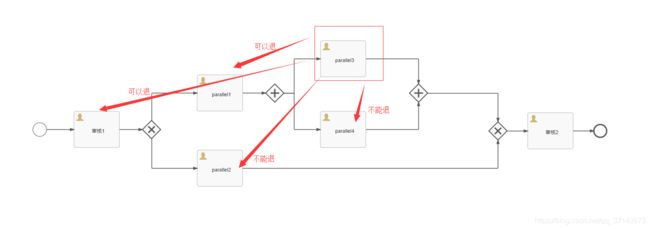
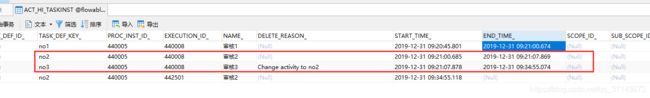
如图,假如我从节点6回退到节点2,这时红框中的数据对于我们来说是一个历史记录,但是对于流程来说,这些数据是无意义的废弃数据
串行样例
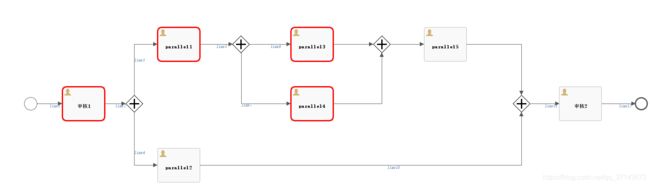
并行样例
会签样例
脏数据清洗效果图
流程图

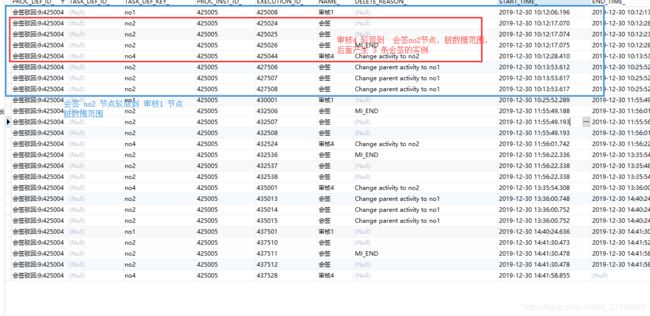
对应数据
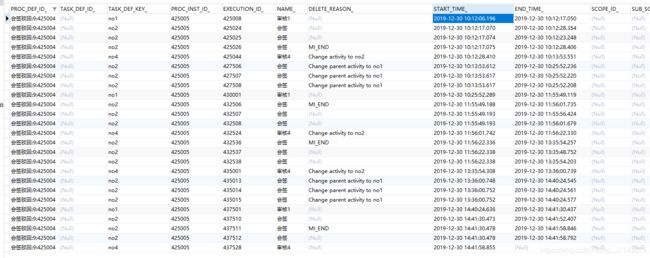
清洗效果截图,由于没有循环,可以看到除了会签对应 3 条实例数据,其他节点清洗后都只有一个
sid-4FE193FF-E1E2-4F87-8424-2F00BCA9AFC5 是网关,没给它命名

完整代码
FlowableApiController.java
/**
* 流程收回/驳回
* @param taskId 当前任务ID
* @param comment 审核意见
* @return
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/flowTackback/{taskId}")
public String flowTackback(@PathVariable(value = "taskId") String taskId, @RequestParam(value = "comment", defaultValue = "") String comment) {
if (taskService.createTaskQuery().taskId(taskId).singleResult().isSuspended()) {
return JsonUtil.toJSON(ErrorMsg.ERROR.setNewErrorMsg("任务处于挂起状态"));
}
// 当前任务 task
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery().taskId(taskId).singleResult();
// 获取流程定义信息
ProcessDefinition processDefinition = repositoryService.createProcessDefinitionQuery().processDefinitionId(task.getProcessDefinitionId()).singleResult();
// 获取所有节点信息
Process process = repositoryService.getBpmnModel(processDefinition.getId()).getProcesses().get(0);
// 获取全部节点列表,包含子节点
Collection<FlowElement> allElements = FlowableUtils.getAllElements(process.getFlowElements(), null);
// 获取当前任务节点元素
FlowElement source = null;
if (allElements != null) {
for (FlowElement flowElement : allElements) {
// 类型为用户节点
if (flowElement.getId().equals(task.getTaskDefinitionKey())) {
// 获取节点信息
source = flowElement;
}
}
}
// 目的获取所有跳转到的节点 targetIds
// 获取当前节点的所有父级用户任务节点
// 深度优先算法思想:延边迭代深入
List<UserTask> parentUserTaskList = FlowableUtils.iteratorFindParentUserTasks(source, null, null);
if (parentUserTaskList == null || parentUserTaskList.size() == 0) {
return JsonUtil.toJSON(ErrorMsg.ERROR.setNewErrorMsg("当前节点为初始任务节点,不能驳回"));
}
// 获取活动 ID 即节点 Key
List<String> parentUserTaskKeyList = new ArrayList<>();
parentUserTaskList.forEach(item -> parentUserTaskKeyList.add(item.getId()));
// 获取全部历史节点活动实例,即已经走过的节点历史,数据采用开始时间升序
List<HistoricTaskInstance> historicTaskInstanceList = historyService.createHistoricTaskInstanceQuery().processInstanceId(task.getProcessInstanceId()).orderByHistoricTaskInstanceStartTime().asc().list();
// 数据清洗,将回滚导致的脏数据清洗掉
List<String> lastHistoricTaskInstanceList = FlowableUtils.historicTaskInstanceClean(allElements, historicTaskInstanceList);
// 此时历史任务实例为倒序,获取最后走的节点
List<String> targetIds = new ArrayList<>();
// 循环结束标识,遇到当前目标节点的次数
int number = 0;
StringBuilder parentHistoricTaskKey = new StringBuilder();
for (String historicTaskInstanceKey : lastHistoricTaskInstanceList) {
// 当会签时候会出现特殊的,连续都是同一个节点历史数据的情况,这种时候跳过
if (parentHistoricTaskKey.toString().equals(historicTaskInstanceKey)) {
continue;
}
parentHistoricTaskKey = new StringBuilder(historicTaskInstanceKey);
if (historicTaskInstanceKey.equals(task.getTaskDefinitionKey())) {
number ++;
}
// 在数据清洗后,历史节点就是唯一一条从起始到当前节点的历史记录,理论上每个点只会出现一次
// 在流程中如果出现循环,那么每次循环中间的点也只会出现一次,再出现就是下次循环
// number == 1,第一次遇到当前节点
// number == 2,第二次遇到,代表最后一次的循环范围
if (number == 2) {
break;
}
// 如果当前历史节点,属于父级的节点,说明最后一次经过了这个点,需要退回这个点
if (parentUserTaskKeyList.contains(historicTaskInstanceKey)) {
targetIds.add(historicTaskInstanceKey);
}
}
// 目的获取所有需要被跳转的节点 currentIds
// 取其中一个父级任务,因为后续要么存在公共网关,要么就是串行公共线路
UserTask oneUserTask = parentUserTaskList.get(0);
// 获取所有正常进行的任务节点 Key,这些任务不能直接使用,需要找出其中需要撤回的任务
List<Task> runTaskList = taskService.createTaskQuery().processInstanceId(task.getProcessInstanceId()).list();
List<String> runTaskKeyList = new ArrayList<>();
runTaskList.forEach(item -> runTaskKeyList.add(item.getTaskDefinitionKey()));
// 需驳回任务列表
List<String> currentIds = new ArrayList<>();
// 通过父级网关的出口连线,结合 runTaskList 比对,获取需要撤回的任务
List<UserTask> currentUserTaskList = FlowableUtils.iteratorFindChildUserTasks(oneUserTask, runTaskKeyList, null, null);
currentUserTaskList.forEach(item -> currentIds.add(item.getId()));
// 规定:并行网关之前节点必须需存在唯一用户任务节点,如果出现多个任务节点,则并行网关节点默认为结束节点,原因为不考虑多对多情况
if (targetIds.size() > 1 && currentIds.size() > 1) {
return JsonUtil.toJSON(ErrorMsg.ERROR.setNewErrorMsg("任务出现多对多情况,无法撤回"));
}
// 循环获取那些需要被撤回的节点的ID,用来设置驳回原因
List<String> currentTaskIds = new ArrayList<>();
currentIds.forEach(currentId -> runTaskList.forEach(runTask -> {
if (currentId.equals(runTask.getTaskDefinitionKey())) {
currentTaskIds.add(runTask.getId());
}
}));
// 设置驳回信息
currentTaskIds.forEach(item -> {
taskService.addComment(item, task.getProcessInstanceId(), "taskStatus", "reject");
taskService.addComment(item, task.getProcessInstanceId(), "taskMessage", "已驳回");
taskService.addComment(item, task.getProcessInstanceId(), "taskComment", comment);
});
try {
// 如果父级任务多于 1 个,说明当前节点不是并行节点,原因为不考虑多对多情况
if (targetIds.size() > 1) {
// 1 对 多任务跳转,currentIds 当前节点(1),targetIds 跳转到的节点(多)
runtimeService.createChangeActivityStateBuilder().processInstanceId(task.getProcessInstanceId()).moveSingleActivityIdToActivityIds(currentIds.get(0), targetIds).changeState();
}
// 如果父级任务只有一个,因此当前任务可能为网关中的任务
if (targetIds.size() == 1) {
// 1 对 1 或 多 对 1 情况,currentIds 当前要跳转的节点列表(1或多),targetIds.get(0) 跳转到的节点(1)
runtimeService.createChangeActivityStateBuilder().processInstanceId(task.getProcessInstanceId()).moveActivityIdsToSingleActivityId(currentIds, targetIds.get(0)).changeState();
}
} catch (FlowableObjectNotFoundException e) {
return JsonUtil.toJSON(ErrorMsg.ERROR.setNewErrorMsg("未找到流程实例,流程可能已发生变化"));
} catch (FlowableException e) {
return JsonUtil.toJSON(ErrorMsg.ERROR.setNewErrorMsg("无法取消或开始活动"));
}
return JsonUtil.toJSON(ErrorMsg.SUCCESS);
}
/**
* 流程回退
* @param taskId 当前任务ID
* @param targetKey 要回退的任务 Key
* @return
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/flowReturn/{taskId}/{targetKey}")
public String flowReturn(@PathVariable(value = "taskId") String taskId, @PathVariable(value = "targetKey") String targetKey) {
if (taskService.createTaskQuery().taskId(taskId).singleResult().isSuspended()) {
return JsonUtil.toJSON(ErrorMsg.ERROR.setNewErrorMsg("任务处于挂起状态"));
}
// 当前任务 task
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery().taskId(taskId).singleResult();
// 获取流程定义信息
ProcessDefinition processDefinition = repositoryService.createProcessDefinitionQuery().processDefinitionId(task.getProcessDefinitionId()).singleResult();
// 获取所有节点信息
Process process = repositoryService.getBpmnModel(processDefinition.getId()).getProcesses().get(0);
// 获取全部节点列表,包含子节点
Collection<FlowElement> allElements = FlowableUtils.getAllElements(process.getFlowElements(), null);
// 获取当前任务节点元素
FlowElement source = null;
// 获取跳转的节点元素
FlowElement target = null;
if (allElements != null) {
for (FlowElement flowElement : allElements) {
// 当前任务节点元素
if (flowElement.getId().equals(task.getTaskDefinitionKey())) {
source = flowElement;
}
// 跳转的节点元素
if (flowElement.getId().equals(targetKey)) {
target = flowElement;
}
}
}
// 从当前节点向前扫描
// 如果存在路线上不存在目标节点,说明目标节点是在网关上或非同一路线上,不可跳转
// 否则目标节点相对于当前节点,属于串行
Boolean isSequential = FlowableUtils.iteratorCheckSequentialReferTarget(source, targetKey, null, null);
if (!isSequential) {
return JsonUtil.toJSON(ErrorMsg.ERROR.setNewErrorMsg("当前节点相对于目标节点,不属于串行关系,无法回退"));
}
// 获取所有正常进行的任务节点 Key,这些任务不能直接使用,需要找出其中需要撤回的任务
List<Task> runTaskList = taskService.createTaskQuery().processInstanceId(task.getProcessInstanceId()).list();
List<String> runTaskKeyList = new ArrayList<>();
runTaskList.forEach(item -> runTaskKeyList.add(item.getTaskDefinitionKey()));
// 需退回任务列表
List<String> currentIds = new ArrayList<>();
// 通过父级网关的出口连线,结合 runTaskList 比对,获取需要撤回的任务
List<UserTask> currentUserTaskList = FlowableUtils.iteratorFindChildUserTasks(target, runTaskKeyList, null, null);
currentUserTaskList.forEach(item -> currentIds.add(item.getId()));
// 循环获取那些需要被撤回的节点的ID,用来设置驳回原因
List<String> currentTaskIds = new ArrayList<>();
currentIds.forEach(currentId -> runTaskList.forEach(runTask -> {
if (currentId.equals(runTask.getTaskDefinitionKey())) {
currentTaskIds.add(runTask.getId());
}
}));
// 设置回退信息
for (String currentTaskId: currentTaskIds) {
taskService.addComment(currentTaskId, task.getProcessInstanceId(), "taskStatus", "return");
taskService.addComment(currentTaskId, task.getProcessInstanceId(), "taskMessage", "已退回");
taskService.addComment(currentTaskId, task.getProcessInstanceId(), "taskComment", "流程回退到" + target.getName() + "节点");
}
try {
// 1 对 1 或 多 对 1 情况,currentIds 当前要跳转的节点列表(1或多),targetKey 跳转到的节点(1)
runtimeService.createChangeActivityStateBuilder().processInstanceId(task.getProcessInstanceId()).moveActivityIdsToSingleActivityId(currentIds, targetKey).changeState();
} catch (FlowableObjectNotFoundException e) {
return JsonUtil.toJSON(ErrorMsg.ERROR.setNewErrorMsg("未找到流程实例,流程可能已发生变化"));
} catch (FlowableException e) {
return JsonUtil.toJSON(ErrorMsg.ERROR.setNewErrorMsg("无法取消或开始活动"));
}
return JsonUtil.toJSON(ErrorMsg.SUCCESS);
}
/**
* 获取所有可回退的节点
* @param taskId
* @return
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/findReturnUserTask/{taskId}")
public String findReturnUserTask(@PathVariable(value = "taskId") String taskId) {
// 当前任务 task
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery().taskId(taskId).singleResult();
// 获取流程定义信息
ProcessDefinition processDefinition = repositoryService.createProcessDefinitionQuery().processDefinitionId(task.getProcessDefinitionId()).singleResult();
// 获取所有节点信息,暂不考虑子流程情况
Process process = repositoryService.getBpmnModel(processDefinition.getId()).getProcesses().get(0);
Collection<FlowElement> flowElements = process.getFlowElements();
// 获取当前任务节点元素
UserTask source = null;
if (flowElements != null) {
for (FlowElement flowElement : flowElements) {
// 类型为用户节点
if (flowElement.getId().equals(task.getTaskDefinitionKey())) {
source = (UserTask) flowElement;
}
}
}
// 获取节点的所有路线
List<List<UserTask>> roads = FlowableUtils.findRoad(source, null, null, null);
// 可回退的节点列表
List<UserTask> userTaskList = new ArrayList<>();
for (List<UserTask> road : roads) {
if (userTaskList.size() == 0) {
// 还没有可回退节点直接添加
userTaskList = road;
} else {
// 如果已有回退节点,则比对取交集部分
userTaskList.retainAll(road);
}
}
return JsonUtil.toJSON(ErrorMsg.SUCCESS.setNewData(userTaskList));
}
FlowableUtils.java
/**
* 流程引擎工具类封装
* @author: linjinp
* @create: 2019-12-24 13:51
**/
public class FlowableUtils {
public static final Logger logger = LogManager.getLogger(FlowableUtils.class);
/**
* 根据节点,获取入口连线
* @param source
* @return
*/
public static List<SequenceFlow> getElementIncomingFlows(FlowElement source) {
List<SequenceFlow> sequenceFlows = null;
if (source instanceof Task) {
sequenceFlows = ((Task) source).getIncomingFlows();
} else if (source instanceof Gateway) {
sequenceFlows = ((Gateway) source).getIncomingFlows();
} else if (source instanceof SubProcess) {
sequenceFlows = ((SubProcess) source).getIncomingFlows();
} else if (source instanceof StartEvent) {
sequenceFlows = ((StartEvent) source).getIncomingFlows();
} else if (source instanceof EndEvent) {
sequenceFlows = ((EndEvent) source).getIncomingFlows();
}
return sequenceFlows;
}
/**
* 根据节点,获取出口连线
* @param source
* @return
*/
public static List<SequenceFlow> getElementOutgoingFlows(FlowElement source) {
List<SequenceFlow> sequenceFlows = null;
if (source instanceof Task) {
sequenceFlows = ((Task) source).getOutgoingFlows();
} else if (source instanceof Gateway) {
sequenceFlows = ((Gateway) source).getOutgoingFlows();
} else if (source instanceof SubProcess) {
sequenceFlows = ((SubProcess) source).getOutgoingFlows();
} else if (source instanceof StartEvent) {
sequenceFlows = ((StartEvent) source).getOutgoingFlows();
} else if (source instanceof EndEvent) {
sequenceFlows = ((EndEvent) source).getOutgoingFlows();
}
return sequenceFlows;
}
/**
* 获取全部节点列表,包含子流程节点
* @param flowElements
* @param allElements
* @return
*/
public static Collection<FlowElement> getAllElements(Collection<FlowElement> flowElements, Collection<FlowElement> allElements) {
allElements = allElements == null ? new ArrayList<>() : allElements;
for (FlowElement flowElement : flowElements) {
allElements.add(flowElement);
if (flowElement instanceof SubProcess) {
// 继续深入子流程,进一步获取子流程
allElements = FlowableUtils.getAllElements(((SubProcess) flowElement).getFlowElements(), allElements);
}
}
return allElements;
}
/**
* 迭代获取父级任务节点列表,向前找
* @param source 起始节点
* @param hasSequenceFlow 已经经过的连线的 ID,用于判断线路是否重复
* @param userTaskList 已找到的用户任务节点
* @return
*/
public static List<UserTask> iteratorFindParentUserTasks(FlowElement source, Set<String> hasSequenceFlow, List<UserTask> userTaskList) {
userTaskList = userTaskList == null ? new ArrayList<>() : userTaskList;
hasSequenceFlow = hasSequenceFlow == null ? new HashSet<>() : hasSequenceFlow;
// 如果该节点为开始节点,且存在上级子节点,则顺着上级子节点继续迭代
if (source instanceof StartEvent && source.getSubProcess() != null) {
userTaskList = iteratorFindParentUserTasks(source.getSubProcess(), hasSequenceFlow, userTaskList);
}
// 根据类型,获取入口连线
List<SequenceFlow> sequenceFlows = getElementIncomingFlows(source);
if (sequenceFlows != null) {
// 循环找到目标元素
for (SequenceFlow sequenceFlow: sequenceFlows) {
// 如果发现连线重复,说明循环了,跳过这个循环
if (hasSequenceFlow.contains(sequenceFlow.getId())) {
continue;
}
// 添加已经走过的连线
hasSequenceFlow.add(sequenceFlow.getId());
// 类型为用户节点,则新增父级节点
if (sequenceFlow.getSourceFlowElement() instanceof UserTask) {
userTaskList.add((UserTask) sequenceFlow.getSourceFlowElement());
continue;
}
// 类型为子流程,则添加子流程开始节点出口处相连的节点
if (sequenceFlow.getSourceFlowElement() instanceof SubProcess) {
// 获取子流程用户任务节点
List<UserTask> childUserTaskList = findChildProcessUserTasks((StartEvent) ((SubProcess) sequenceFlow.getSourceFlowElement()).getFlowElements().toArray()[0], null, null);
// 如果找到节点,则说明该线路找到节点,不继续向下找,反之继续
if (childUserTaskList != null && childUserTaskList.size() > 0) {
userTaskList.addAll(childUserTaskList);
continue;
}
}
// 继续迭代
userTaskList = iteratorFindParentUserTasks(sequenceFlow.getSourceFlowElement(), hasSequenceFlow, userTaskList);
}
}
return userTaskList;
}
/**
* 根据正在运行的任务节点,迭代获取子级任务节点列表,向后找
* @param source 起始节点
* @param runTaskKeyList 正在运行的任务 Key,用于校验任务节点是否是正在运行的节点
* @param hasSequenceFlow 已经经过的连线的 ID,用于判断线路是否重复
* @param userTaskList 需要撤回的用户任务列表
* @return
*/
public static List<UserTask> iteratorFindChildUserTasks(FlowElement source, List<String> runTaskKeyList, Set<String> hasSequenceFlow, List<UserTask> userTaskList) {
hasSequenceFlow = hasSequenceFlow == null ? new HashSet<>() : hasSequenceFlow;
userTaskList = userTaskList == null ? new ArrayList<>() : userTaskList;
// 如果该节点为开始节点,且存在上级子节点,则顺着上级子节点继续迭代
if (source instanceof EndEvent && source.getSubProcess() != null) {
userTaskList = iteratorFindChildUserTasks(source.getSubProcess(), runTaskKeyList, hasSequenceFlow, userTaskList);
}
// 根据类型,获取出口连线
List<SequenceFlow> sequenceFlows = getElementOutgoingFlows(source);
if (sequenceFlows != null) {
// 循环找到目标元素
for (SequenceFlow sequenceFlow: sequenceFlows) {
// 如果发现连线重复,说明循环了,跳过这个循环
if (hasSequenceFlow.contains(sequenceFlow.getId())) {
continue;
}
// 添加已经走过的连线
hasSequenceFlow.add(sequenceFlow.getId());
// 如果为用户任务类型,且任务节点的 Key 正在运行的任务中存在,添加
if (sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement() instanceof UserTask && runTaskKeyList.contains((sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement()).getId())) {
userTaskList.add((UserTask) sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement());
continue;
}
// 如果节点为子流程节点情况,则从节点中的第一个节点开始获取
if (sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement() instanceof SubProcess) {
List<UserTask> childUserTaskList = iteratorFindChildUserTasks((FlowElement) (((SubProcess) sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement()).getFlowElements().toArray()[0]), runTaskKeyList, hasSequenceFlow, null);
// 如果找到节点,则说明该线路找到节点,不继续向下找,反之继续
if (childUserTaskList != null && childUserTaskList.size() > 0) {
userTaskList.addAll(childUserTaskList);
continue;
}
}
// 继续迭代
userTaskList = iteratorFindChildUserTasks(sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement(), runTaskKeyList, hasSequenceFlow, userTaskList);
}
}
return userTaskList;
}
/**
* 迭代获取子流程用户任务节点
* @param source 起始节点
* @param hasSequenceFlow 已经经过的连线的 ID,用于判断线路是否重复
* @param userTaskList 需要撤回的用户任务列表
* @return
*/
public static List<UserTask> findChildProcessUserTasks(FlowElement source, Set<String> hasSequenceFlow, List<UserTask> userTaskList) {
hasSequenceFlow = hasSequenceFlow == null ? new HashSet<>() : hasSequenceFlow;
userTaskList = userTaskList == null ? new ArrayList<>() : userTaskList;
// 根据类型,获取出口连线
List<SequenceFlow> sequenceFlows = getElementOutgoingFlows(source);
if (sequenceFlows != null) {
// 循环找到目标元素
for (SequenceFlow sequenceFlow: sequenceFlows) {
// 如果发现连线重复,说明循环了,跳过这个循环
if (hasSequenceFlow.contains(sequenceFlow.getId())) {
continue;
}
// 添加已经走过的连线
hasSequenceFlow.add(sequenceFlow.getId());
// 如果为用户任务类型,且任务节点的 Key 正在运行的任务中存在,添加
if (sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement() instanceof UserTask) {
userTaskList.add((UserTask) sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement());
continue;
}
// 如果节点为子流程节点情况,则从节点中的第一个节点开始获取
if (sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement() instanceof SubProcess) {
List<UserTask> childUserTaskList = findChildProcessUserTasks((FlowElement) (((SubProcess) sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement()).getFlowElements().toArray()[0]), hasSequenceFlow, null);
// 如果找到节点,则说明该线路找到节点,不继续向下找,反之继续
if (childUserTaskList != null && childUserTaskList.size() > 0) {
userTaskList.addAll(childUserTaskList);
continue;
}
}
// 继续迭代
userTaskList = findChildProcessUserTasks(sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement(), hasSequenceFlow, userTaskList);
}
}
return userTaskList;
}
/**
* 从后向前寻路,获取所有脏线路上的点
* @param source 起始节点
* @param passRoads 已经经过的点集合
* @param hasSequenceFlow 已经经过的连线的 ID,用于判断线路是否重复
* @param targets 目标脏线路终点
* @param dirtyRoads 确定为脏数据的点,因为不需要重复,因此使用 set 存储
* @return
*/
public static Set<String> iteratorFindDirtyRoads(FlowElement source, List<String> passRoads, Set<String> hasSequenceFlow, List<String> targets, Set<String> dirtyRoads) {
passRoads = passRoads == null ? new ArrayList<>() : passRoads;
dirtyRoads = dirtyRoads == null ? new HashSet<>() : dirtyRoads;
hasSequenceFlow = hasSequenceFlow == null ? new HashSet<>() : hasSequenceFlow;
// 如果该节点为开始节点,且存在上级子节点,则顺着上级子节点继续迭代
if (source instanceof StartEvent && source.getSubProcess() != null) {
dirtyRoads = iteratorFindDirtyRoads(source.getSubProcess(), passRoads, hasSequenceFlow, targets, dirtyRoads);
}
// 根据类型,获取入口连线
List<SequenceFlow> sequenceFlows = getElementIncomingFlows(source);
if (sequenceFlows != null) {
// 循环找到目标元素
for (SequenceFlow sequenceFlow: sequenceFlows) {
// 如果发现连线重复,说明循环了,跳过这个循环
if (hasSequenceFlow.contains(sequenceFlow.getId())) {
continue;
}
// 添加已经走过的连线
hasSequenceFlow.add(sequenceFlow.getId());
// 新增经过的路线
passRoads.add(sequenceFlow.getSourceFlowElement().getId());
// 如果此点为目标点,确定经过的路线为脏线路,添加点到脏线路中,然后找下个连线
if (targets.contains(sequenceFlow.getSourceFlowElement().getId())) {
dirtyRoads.addAll(passRoads);
continue;
}
// 如果该节点为开始节点,且存在上级子节点,则顺着上级子节点继续迭代
if (sequenceFlow.getSourceFlowElement() instanceof SubProcess) {
dirtyRoads = findChildProcessAllDirtyRoad((StartEvent) ((SubProcess) sequenceFlow.getSourceFlowElement()).getFlowElements().toArray()[0], null, dirtyRoads);
// 是否存在子流程上,true 是,false 否
Boolean isInChildProcess = dirtyTargetInChildProcess((StartEvent) ((SubProcess) sequenceFlow.getSourceFlowElement()).getFlowElements().toArray()[0], null, targets, null);
if (isInChildProcess) {
// 已在子流程上找到,该路线结束
continue;
}
}
// 继续迭代
dirtyRoads = iteratorFindDirtyRoads(sequenceFlow.getSourceFlowElement(), passRoads, hasSequenceFlow, targets, dirtyRoads);
}
}
return dirtyRoads;
}
/**
* 迭代获取子流程脏路线
* 说明,假如回退的点就是子流程,那么也肯定会回退到子流程最初的用户任务节点,因此子流程中的节点全是脏路线
* @param source 起始节点
* @param hasSequenceFlow 已经经过的连线的 ID,用于判断线路是否重复
* @param dirtyRoads 确定为脏数据的点,因为不需要重复,因此使用 set 存储
* @return
*/
public static Set<String> findChildProcessAllDirtyRoad(FlowElement source, Set<String> hasSequenceFlow, Set<String> dirtyRoads) {
hasSequenceFlow = hasSequenceFlow == null ? new HashSet<>() : hasSequenceFlow;
dirtyRoads = dirtyRoads == null ? new HashSet<>() : dirtyRoads;
// 根据类型,获取出口连线
List<SequenceFlow> sequenceFlows = getElementOutgoingFlows(source);
if (sequenceFlows != null) {
// 循环找到目标元素
for (SequenceFlow sequenceFlow: sequenceFlows) {
// 如果发现连线重复,说明循环了,跳过这个循环
if (hasSequenceFlow.contains(sequenceFlow.getId())) {
continue;
}
// 添加已经走过的连线
hasSequenceFlow.add(sequenceFlow.getId());
// 添加脏路线
dirtyRoads.add(sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement().getId());
// 如果节点为子流程节点情况,则从节点中的第一个节点开始获取
if (sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement() instanceof SubProcess) {
dirtyRoads = findChildProcessAllDirtyRoad((FlowElement) (((SubProcess) sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement()).getFlowElements().toArray()[0]), hasSequenceFlow, dirtyRoads);
}
// 继续迭代
dirtyRoads = findChildProcessAllDirtyRoad(sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement(), hasSequenceFlow, dirtyRoads);
}
}
return dirtyRoads;
}
/**
* 判断脏路线结束节点是否在子流程上
* @param source 起始节点
* @param hasSequenceFlow 已经经过的连线的 ID,用于判断线路是否重复
* @param targets 判断脏路线节点是否存在子流程上,只要存在一个,说明脏路线只到子流程为止
* @param inChildProcess 是否存在子流程上,true 是,false 否
* @return
*/
public static Boolean dirtyTargetInChildProcess(FlowElement source, Set<String> hasSequenceFlow, List<String> targets, Boolean inChildProcess) {
hasSequenceFlow = hasSequenceFlow == null ? new HashSet<>() : hasSequenceFlow;
inChildProcess = inChildProcess == null ? false : inChildProcess;
// 根据类型,获取出口连线
List<SequenceFlow> sequenceFlows = getElementOutgoingFlows(source);
if (sequenceFlows != null && !inChildProcess) {
// 循环找到目标元素
for (SequenceFlow sequenceFlow: sequenceFlows) {
// 如果发现连线重复,说明循环了,跳过这个循环
if (hasSequenceFlow.contains(sequenceFlow.getId())) {
continue;
}
// 添加已经走过的连线
hasSequenceFlow.add(sequenceFlow.getId());
// 如果发现目标点在子流程上存在,说明只到子流程为止
if (targets.contains(sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement().getId())) {
inChildProcess = true;
break;
}
// 如果节点为子流程节点情况,则从节点中的第一个节点开始获取
if (sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement() instanceof SubProcess) {
inChildProcess = dirtyTargetInChildProcess((FlowElement) (((SubProcess) sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement()).getFlowElements().toArray()[0]), hasSequenceFlow, targets, inChildProcess);
}
// 继续迭代
inChildProcess = dirtyTargetInChildProcess(sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement(), hasSequenceFlow, targets, inChildProcess);
}
}
return inChildProcess;
}
/**
* 迭代从后向前扫描,判断目标节点相对于当前节点是否是串行
* 不存在直接回退到子流程中的情况,但存在从子流程出去到父流程情况
* @param source 起始节点
* @param isSequential 是否串行
* @param hasSequenceFlow 已经经过的连线的 ID,用于判断线路是否重复
* @param targetKsy 目标节点
* @return
*/
public static Boolean iteratorCheckSequentialReferTarget(FlowElement source, String targetKsy, Set<String> hasSequenceFlow, Boolean isSequential) {
isSequential = isSequential == null ? true : isSequential;
hasSequenceFlow = hasSequenceFlow == null ? new HashSet<>() : hasSequenceFlow;
// 如果该节点为开始节点,且存在上级子节点,则顺着上级子节点继续迭代
if (source instanceof StartEvent && source.getSubProcess() != null) {
isSequential = iteratorCheckSequentialReferTarget(source.getSubProcess(), targetKsy, hasSequenceFlow, isSequential);
}
// 根据类型,获取入口连线
List<SequenceFlow> sequenceFlows = getElementIncomingFlows(source);
if (sequenceFlows != null) {
// 循环找到目标元素
for (SequenceFlow sequenceFlow: sequenceFlows) {
// 如果发现连线重复,说明循环了,跳过这个循环
if (hasSequenceFlow.contains(sequenceFlow.getId())) {
continue;
}
// 添加已经走过的连线
hasSequenceFlow.add(sequenceFlow.getId());
// 如果目标节点已被判断为并行,后面都不需要执行,直接返回
if (isSequential == false) {
break;
}
// 这条线路存在目标节点,这条线路完成,进入下个线路
if (targetKsy.equals(sequenceFlow.getSourceFlowElement().getId())) {
continue;
}
if (sequenceFlow.getSourceFlowElement() instanceof StartEvent) {
isSequential = false;
break;
}
// 否则就继续迭代
isSequential = iteratorCheckSequentialReferTarget(sequenceFlow.getSourceFlowElement(), targetKsy, hasSequenceFlow, isSequential);
}
}
return isSequential;
}
/**
* 从后向前寻路,获取到达节点的所有路线
* 不存在直接回退到子流程,但是存在回退到父级流程的情况
* @param source 起始节点
* @param passRoads 已经经过的点集合
* @param roads 路线
* @return
*/
public static List<List<UserTask>> findRoad(FlowElement source, List<UserTask> passRoads, Set<String> hasSequenceFlow, List<List<UserTask>> roads) {
passRoads = passRoads == null ? new ArrayList<>() : passRoads;
roads = roads == null ? new ArrayList<>() : roads;
hasSequenceFlow = hasSequenceFlow == null ? new HashSet<>() : hasSequenceFlow;
// 如果该节点为开始节点,且存在上级子节点,则顺着上级子节点继续迭代
if (source instanceof StartEvent && source.getSubProcess() != null) {
roads = findRoad(source.getSubProcess(), passRoads, hasSequenceFlow, roads);
}
// 根据类型,获取入口连线
List<SequenceFlow> sequenceFlows = getElementIncomingFlows(source);
if (sequenceFlows != null && sequenceFlows.size() != 0) {
for (SequenceFlow sequenceFlow: sequenceFlows) {
// 如果发现连线重复,说明循环了,跳过这个循环
if (hasSequenceFlow.contains(sequenceFlow.getId())) {
continue;
}
// 添加已经走过的连线
hasSequenceFlow.add(sequenceFlow.getId());
// 添加经过路线
if (sequenceFlow.getSourceFlowElement() instanceof UserTask) {
passRoads.add((UserTask) sequenceFlow.getSourceFlowElement());
}
// 继续迭代
roads = findRoad(sequenceFlow.getSourceFlowElement(), passRoads, hasSequenceFlow, roads);
}
} else {
// 添加路线
roads.add(passRoads);
}
return roads;
}
/**
* 历史节点数据清洗,清洗掉又回滚导致的脏数据
* @param allElements 全部节点信息
* @param historicTaskInstanceList 历史任务实例信息,数据采用开始时间升序
* @return
*/
public static List<String> historicTaskInstanceClean(Collection<FlowElement> allElements, List<HistoricTaskInstance> historicTaskInstanceList) {
// 会签节点收集
List<String> multiTask = new ArrayList<>();
allElements.forEach(flowElement -> {
if (flowElement instanceof UserTask) {
// 如果该节点的行为为会签行为,说明该节点为会签节点
if (((UserTask) flowElement).getBehavior() instanceof ParallelMultiInstanceBehavior || ((UserTask) flowElement).getBehavior() instanceof SequentialMultiInstanceBehavior) {
multiTask.add(flowElement.getId());
}
}
});
// 循环放入栈,栈 LIFO:后进先出
Stack<HistoricTaskInstance> stack = new Stack<>();
historicTaskInstanceList.forEach(item -> stack.push(item));
// 清洗后的历史任务实例
List<String> lastHistoricTaskInstanceList = new ArrayList<>();
// 网关存在可能只走了部分分支情况,且还存在跳转废弃数据以及其他分支数据的干扰,因此需要对历史节点数据进行清洗
// 临时用户任务 key
StringBuilder userTaskKey = null;
// 临时被删掉的任务 key,存在并行情况
List<String> deleteKeyList = new ArrayList<>();
// 临时脏数据线路
List<Set<String>> dirtyDataLineList = new ArrayList<>();
// 由某个点跳到会签点,此时出现多个会签实例对应 1 个跳转情况,需要把这些连续脏数据都找到
// 会签特殊处理下标
int multiIndex = -1;
// 会签特殊处理 key
StringBuilder multiKey = null;
// 会签特殊处理操作标识
boolean multiOpera = false;
while (!stack.empty()) {
// 从这里开始 userTaskKey 都还是上个栈的 key
// 是否是脏数据线路上的点
final boolean[] isDirtyData = {false};
for (Set<String> oldDirtyDataLine : dirtyDataLineList) {
if (oldDirtyDataLine.contains(stack.peek().getTaskDefinitionKey())) {
isDirtyData[0] = true;
}
}
// 删除原因不为空,说明从这条数据开始回跳或者回退的
// MI_END:会签完成后,其他未签到节点的删除原因,不在处理范围内
if (stack.peek().getDeleteReason() != null && !stack.peek().getDeleteReason().equals("MI_END")) {
// 可以理解为脏线路起点
String dirtyPoint = "";
if (stack.peek().getDeleteReason().indexOf("Change activity to ") >= 0) {
dirtyPoint = stack.peek().getDeleteReason().replace("Change activity to ", "");
}
// 会签回退删除原因有点不同
if (stack.peek().getDeleteReason().indexOf("Change parent activity to ") >= 0) {
dirtyPoint = stack.peek().getDeleteReason().replace("Change parent activity to ", "");
}
FlowElement dirtyTask = null;
// 获取变更节点的对应的入口处连线
// 如果是网关并行回退情况,会变成两条脏数据路线,效果一样
for (FlowElement flowElement : allElements) {
if (flowElement.getId().equals(stack.peek().getTaskDefinitionKey())) {
dirtyTask = flowElement;
}
}
// 获取脏数据线路
Set<String> dirtyDataLine = FlowableUtils.iteratorFindDirtyRoads(dirtyTask, null, null, Arrays.asList(dirtyPoint.split(",")), null);
// 自己本身也是脏线路上的点,加进去
dirtyDataLine.add(stack.peek().getTaskDefinitionKey());
logger.info(stack.peek().getTaskDefinitionKey() + "点脏路线集合:" + dirtyDataLine);
// 是全新的需要添加的脏线路
boolean isNewDirtyData = true;
for (int i = 0; i < dirtyDataLineList.size(); i++) {
// 如果发现他的上个节点在脏线路内,说明这个点可能是并行的节点,或者连续驳回
// 这时,都以之前的脏线路节点为标准,只需合并脏线路即可,也就是路线补全
if (dirtyDataLineList.get(i).contains(userTaskKey.toString())) {
isNewDirtyData = false;
dirtyDataLineList.get(i).addAll(dirtyDataLine);
}
}
// 已确定时全新的脏线路
if (isNewDirtyData) {
// deleteKey 单一路线驳回到并行,这种同时生成多个新实例记录情况,这时 deleteKey 其实是由多个值组成
// 按照逻辑,回退后立刻生成的实例记录就是回退的记录
// 至于驳回所生成的 Key,直接从删除原因中获取,因为存在驳回到并行的情况
deleteKeyList.add(dirtyPoint + ",");
dirtyDataLineList.add(dirtyDataLine);
}
// 添加后,现在这个点变成脏线路上的点了
isDirtyData[0] = true;
}
// 如果不是脏线路上的点,说明是有效数据,添加历史实例 Key
if (!isDirtyData[0]) {
lastHistoricTaskInstanceList.add(stack.peek().getTaskDefinitionKey());
}
// 校验脏线路是否结束
for (int i = 0; i < deleteKeyList.size(); i ++) {
// 如果发现脏数据属于会签,记录下下标与对应 Key,以备后续比对,会签脏数据范畴开始
if (multiKey == null && multiTask.contains(stack.peek().getTaskDefinitionKey())
&& deleteKeyList.get(i).contains(stack.peek().getTaskDefinitionKey())) {
multiIndex = i;
multiKey = new StringBuilder(stack.peek().getTaskDefinitionKey());
}
// 会签脏数据处理,节点退回会签清空
// 如果在会签脏数据范畴中发现 Key改变,说明会签脏数据在上个节点就结束了,可以把会签脏数据删掉
if (multiKey != null && !multiKey.toString().equals(stack.peek().getTaskDefinitionKey())) {
deleteKeyList.set(multiIndex , deleteKeyList.get(multiIndex).replace(stack.peek().getTaskDefinitionKey() + ",", ""));
multiKey = null;
// 结束进行下校验删除
multiOpera = true;
}
// 其他脏数据处理
// 发现该路线最后一条脏数据,说明这条脏数据线路处理完了,删除脏数据信息
// 脏数据产生的新实例中是否包含这条数据
if (multiKey == null && deleteKeyList.get(i).contains(stack.peek().getTaskDefinitionKey())) {
// 删除匹配到的部分
deleteKeyList.set(i , deleteKeyList.get(i).replace(stack.peek().getTaskDefinitionKey() + ",", ""));
}
// 如果每组中的元素都以匹配过,说明脏数据结束
if ("".equals(deleteKeyList.get(i))) {
// 同时删除脏数据
deleteKeyList.remove(i);
dirtyDataLineList.remove(i);
break;
}
}
// 会签数据处理需要在循环外处理,否则可能导致溢出
// 会签的数据肯定是之前放进去的所以理论上不会溢出,但还是校验下
if (multiOpera && deleteKeyList.size() > multiIndex && "".equals(deleteKeyList.get(multiIndex))) {
// 同时删除脏数据
deleteKeyList.remove(multiIndex);
dirtyDataLineList.remove(multiIndex);
multiIndex = -1;
multiOpera = false;
}
// pop() 方法与 peek() 方法不同,在返回值的同时,会把值从栈中移除
// 保存新的 userTaskKey 在下个循环中使用
userTaskKey = new StringBuilder(stack.pop().getTaskDefinitionKey());
}
logger.info("清洗后的历史节点数据:" + lastHistoricTaskInstanceList);
return lastHistoricTaskInstanceList;
}
}