操作系统实验--spooling技术
实验四 假脱机技术
一、目的和要求
1、目的
假脱机(SPOOLING)技术是广泛应用于各种计算机系统的一种行之有效的输入输出手段。这种技术使用比较简单的方法,缓和了高速处理机与低速输入输出设备速度不匹配的矛盾,提高了设备的利用率。为了更好地掌握这种技术。本实习要求学生独立地用高级语言编写一个SPOOLING程序来模拟假脱机输入输出过程。
2、要求
可将SPOOLING输入输出程序编制成一个独立的进程,与其他要求输入输出的进程并发工作。
SPOOLING进程负责从键盘等设备读如信息送到磁盘输入井中,或是把磁盘输出井中的信息块送到打印机或CRT等设备输出。其余进程只要求编写输入输出部分的程序,可不考虑其他操作。
二、示例
1.题目
本实验编制一个SPOOLING输出进程,与另外两个要求输出的进程并发执行。要求输出进程每运行一次只输出一项信息到输出井,待输出到一个结束标志时,表示一批信息输出完成,在输出井中形成一输出信息块,再由SPOOLING进程把整个信息块实际输出到打印机或CRT。因此,进程运行必须考虑同步问题。
采用进程的随机调度法模拟SPOOLING输出是合适的,因为各进程的输出应该是随机的。
2、算法与框图
(1)进程调度采用随机调度法,假设两个要求输出进程的调度概率各为45%,SPOOLING进程的调度概率为10%。
(2)可为进程设置三种工作状态:可运行状态、不可运行状态和结束状态。为了区分要求输出的进程和SPOOLING进程处于不可运行状态的不同原因,又把不可运行状态分称不可运行状态1和2,分别叙述如下:
1)进程执行完毕后应设置成“结束状态”。
2)要求输出进程在输出信息时,如果发现输出井已满,应设置成“不可运行状态1”。
3)SPOOLING进程在输出井空时应设置成“不可运行状态2”。
4)SPOOLING进程输出一个信息块后,应释放该信息块所占的输出井位置,并将正在等待输出的进程置成“可运行状态”。
5)要求输出进程把信息输出到输出井并形成信息块后,应将SPOOLING进程置成“可运行状态”。
(3)程序中使用的数据结构有:
1)进程控制块(PCB)
其中,进程状态为:
0 可运行状态
1 不可运行状态1(输出井满)
2 不可运行状态2(无请求块)
3 结束状态
输出指针指向输出井的第一个空位置。
2)输出请求块:每构成一个输出信息块(即遇到结束标志)时,应形成一输出请求块,待SPOOLING进程运行时控制输出,结构如下:

3)输出井:要求输出的进程在输出井中应有自己的输出区域,不应与其他的输出进程混淆。
(4)程序框图
1)假脱机输出系统如图1,该进程由函数init和scheduler实现。
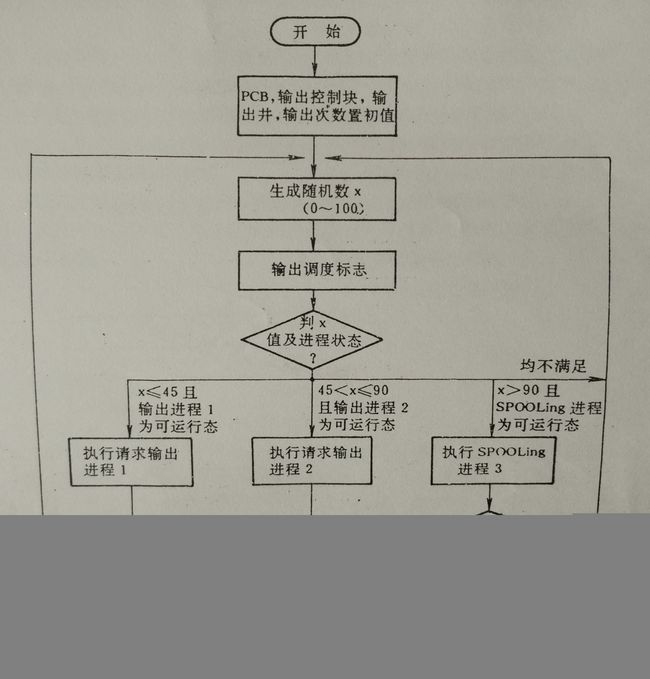
2)请求输出进程如图2,该进程由函数userproc实现。

3)SPOOLING进程,该进程由函数SPOOLING实现。

(5)程序说明
1)请求输出程序简单地设计成每运行一次,随机输出一个0~9之间的数字,为了方便,把“0”作为输出结束标志。当输出为“0”时,就可形成一个信息块输出。
2)程序中有关变量说明:
freeioblknum:空闲输出请求块计数器。初值为10,即系统最多可设置10个输出信息块。
pcb.start:进程输出请求块链链首指针,初值为1。
pcb.point:空闲输出请求块链链首指针,初值为1。
freepoollen(2):两个输出井的计数器,初值为100,即每个井能存放100个信息项。
count(2):用来控制两个请求输出进程的输出文件数,避免系统无限制循环下去。
3)程序运行过程。
程序启动后,屏幕上显示“input the times of user1’s output file”和“input the times of user2’s output file”,要求用户先后打入两个输出进程所要求的输出文件数,控制程序的整个运行时间。随后,系统自行调度SPOOLING进程输出,并在打印机上打印两个进程的假脱机输出过程,待完成各自输出文件数后停止。
#include