快速模式第二包: quick_inI1_ouR1()
文章目录
- 1. 序言
- 2. quick_inI1_outR1()流程图
- 3. 快速模式消息②数据包格式
- 4. 源码分析
- 4.1 quick_inI1_outR1()
- 4.2 quick_inI1_outR1_authtail()
- 4.3 quick_inI1_outR1_cryptocontinue1()
- 4.4 quick_inI1_outR1_cryptotail()
- 5. 其他接口源码分析
- 5.1 decode_net_id()
- 5.2 emit_subnet_id()
- 6. 小结
1. 序言
在介绍第②包quick_inI1_outR1()函数之前,先说明下处理流程中的主要的功能:
- 协商第二阶段的SA算法信息,包括AH协议、ESP协议、封装模式等重要参数。
- 密钥材料交换,包括Nonce、KE(可选)。
- 使用ID载荷来协商两端的保护子网范围。
- 建立IPSec SA结构。
- 报文的认证和加密。
从上述作用可以看出,quick_inI1_outR1()及后续函数几乎实现了第一阶段的所有基本交换(第一阶段里的重要载荷在此流程中基本都有实现),因此第二包处理流程算是IKEv1协商流程里最为复杂的流程了。这里只是做一个简单的笔记说明核心流程,无法涉及到完整的交换流程。此外响应端通过此次交换后会建立一个inbound sa,这部分流程尚未看明白处理逻辑(可能在于涉及到内核路由表等内容,目前还没有get到)。因此如果需要深入了解此流程,请参考源码实现。
2. quick_inI1_outR1()流程图
刚才已经说明第二个报文的处理流程比较复杂,实现的功能也较其他接口复杂了很多,从流程图上便可以看出:
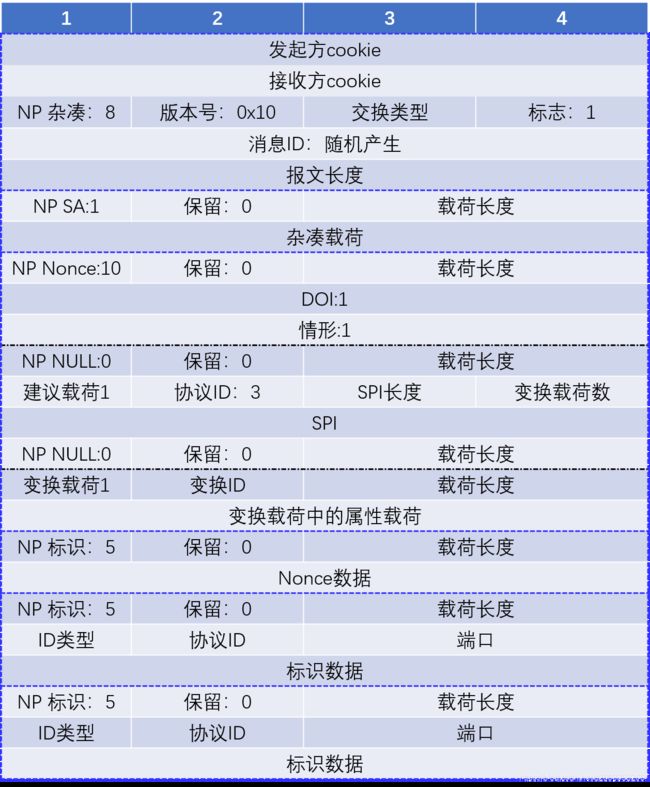
3. 快速模式消息②数据包格式
下表中的报文格式有部分字段应该为变长类型,但是并未标出,这一点请注意。
4. 源码分析
4.1 quick_inI1_outR1()
quick_inI1_outR1()接口的作用包括:
-
检验报文的完整性
- HASH载荷(杂凑载荷)既可以用来检验报文的完整性,也可以用来实现源认证功能,两者实际上是一致的。它计算范围是除了ISAKMP头部以外的完整报文进行杂凑运算。计算方式为:
H A S H = P R F ( S K E Y I D − a , M s g I D ∣ N i ∣ S A ∣ N r [ ∣ I D i ∣ I D r ] ) HASH = PRF(SKEYID-a, MsgID | Ni | SA | Nr [ | IDi | IDr ] ) HASH=PRF(SKEYID−a,MsgID∣Ni∣SA∣Nr[∣IDi∣IDr])
还需要注意的是快速模式的三个报文的HASH载荷的运算模式并不相同。
- HASH载荷(杂凑载荷)既可以用来检验报文的完整性,也可以用来实现源认证功能,两者实际上是一致的。它计算范围是除了ISAKMP头部以外的完整报文进行杂凑运算。计算方式为:
-
解析报文中的ID载荷
- 快速模式中,身份标识ID载荷缺省定义为ISAKMP双方的协商地址。如果双方需要指定身份ID载荷,则需要按照一定的顺序进行传输:IDi + IDr。还需要注意的是协商隧道时配置的保护子网(感兴趣流)是通过ID载荷来传输并完成协商的。ID载荷可以传输IPv4和IPv6的主机地址、子网地址、地址范围。因此使用ID载荷来协商感兴趣流完全满足需求。使用
emit_subnet_id()来将保护子网填充到ID载荷,使用decode_net_id()将ID载荷解析为保护子网地址.
- 快速模式中,身份标识ID载荷缺省定义为ISAKMP双方的协商地址。如果双方需要指定身份ID载荷,则需要按照一定的顺序进行传输:IDi + IDr。还需要注意的是协商隧道时配置的保护子网(感兴趣流)是通过ID载荷来传输并完成协商的。ID载荷可以传输IPv4和IPv6的主机地址、子网地址、地址范围。因此使用ID载荷来协商感兴趣流完全满足需求。使用
-
保存IV值,并调用后续处理
quick_inI1_outR1()函数并没有协商保护子网信息,而是在后续接口中进行的协商。(NAT-T相关略)
stf_status
quick_inI1_outR1(struct msg_digest *md)
{
const struct state *const p1st = md->st;
struct connection *c = p1st->st_connection;
struct payload_digest *const id_pd = md->chain[ISAKMP_NEXT_ID];
struct verify_oppo_bundle b;
/* HASH(1) in *//*使用第一阶段的算法、计算并检验报文的hash载荷*/
CHECK_QUICK_HASH(md
, quick_mode_hash12(hash_val, hash_pbs->roof, md->message_pbs.roof
, p1st, &md->hdr.isa_msgid, FALSE)
, "HASH(1)", "Quick I1");
/* [ IDci, IDcr ] in
* We do this now (probably out of physical order) because
* we wish to select the correct connection before we consult
* it for policy.
*/
if (id_pd != NULL)/*如果ID载荷存在*/
{
struct payload_digest *IDci = id_pd->next;
/* ??? we are assuming IPSEC_DOI */
/* IDci (initiator is peer) */
if (!decode_net_id(&id_pd->payload.ipsec_id, &id_pd->pbs
, &b.his.net, "peer client"))/*获取到对端的网段*/
return STF_FAIL + INVALID_ID_INFORMATION;
/* Hack for MS 818043 NAT-T Update */
if (id_pd->payload.ipsec_id.isaiid_idtype == ID_FQDN) {/*将单个地址转换为子网地址*/
loglog(RC_LOG_SERIOUS, "Applying workaround for MS-818043 NAT-T bug");
memset(&b.his.net, 0, sizeof(ip_subnet));
happy(addrtosubnet(&c->spd.that.host_addr, &b.his.net));
}
/* End Hack for MS 818043 NAT-T Update */
b.his.proto = id_pd->payload.ipsec_id.isaiid_protoid;
b.his.port = id_pd->payload.ipsec_id.isaiid_port;
b.his.net.addr.u.v4.sin_port = htons(b.his.port);
/* IDcr (we are responder) */
if (!decode_net_id(&IDci->payload.ipsec_id, &IDci->pbs
, &b.my.net, "our client"))
return STF_FAIL + INVALID_ID_INFORMATION;
b.my.proto = IDci->payload.ipsec_id.isaiid_protoid;
b.my.port = IDci->payload.ipsec_id.isaiid_port;
b.my.net.addr.u.v4.sin_port = htons(b.my.port);
#ifdef NAT_TRAVERSAL
/*
* 略
*/
#endif
}
else
{ /*载荷中不存在ID载荷,如果两端的地址类型不一致的化则返回错误
*
*如果不存在ID载荷,则使用协商地址作为保护子网
*/
/* implicit IDci and IDcr: peer and self */
if (!sameaddrtype(&c->spd.this.host_addr, &c->spd.that.host_addr))
return STF_FAIL;
/*默认使用IP地址当作ID*/
happy(addrtosubnet(&c->spd.this.host_addr, &b.my.net));
happy(addrtosubnet(&c->spd.that.host_addr, &b.his.net));
b.his.proto = b.my.proto = 0;
b.his.port = b.my.port = 0;
}
b.step = vos_start;
b.md = md;
b.new_iv_len = p1st->st_new_iv_len;
save_new_iv(p1st, b.new_iv);
/*
* FIXME - DAVIDM
* "b" is on the stack, for OPPO tunnels this will be bad, in
* quick_inI1_outR1_start_query it saves a pointer to it before
* a crypto (async op).
*/
return quick_inI1_outR1_authtail(&b, NULL);
}
4.2 quick_inI1_outR1_authtail()
quick_inI1_outR1_authtail()函数作用包括如下几个:
-
根据子网信息查询连接
这部分代码没有看懂。
.assets%5C80DF1671.gif) 。按常理来说,接收此报文时已经确定了连接和状态信息,直接比较连接上的保护子网信息和SA载荷中的保护子网信息,确定是否匹配即可。但是openswan源码中的逻辑负责了很多,没有看明白这部分代码,先留一个疑问吧。
。按常理来说,接收此报文时已经确定了连接和状态信息,直接比较连接上的保护子网信息和SA载荷中的保护子网信息,确定是否匹配即可。但是openswan源码中的逻辑负责了很多,没有看明白这部分代码,先留一个疑问吧。 -
根据连接创建新的状态
-
解析IPSec SA建议载荷
-
解析SA载荷:
parse_ipsec_sa_body()这个接口是快速模式协商IPSec策略的核心接口,包括封装协议 (ESP | AH | IPCOM)、加密算法、认证算法(完整性算法)、隧道模式or传输模式等等,都是在此接口中进行协商的。此外,该函数也可以完成应答报文的SA载荷的封装。
近700行的代码,不再另行说明了。
-
-
解析Nonce载荷
-
如果支持PFS,则解析KE载荷
- 启动PFS功能(完美向前加密),则第二阶段需要再进行一次DH交换,因此需要重新计算生成KE载荷。PFS简单的说如果第一阶段的秘钥被破解(无论采用何种方式),由第一阶段密钥衍生的第二阶段密钥则不受影响。这就要求在第二阶段再次进行DH交换。
-
构建密钥交换材料申请结构信息,包括:
- 本端的KE载荷
- 本端的Nonce载荷
static stf_status
quick_inI1_outR1_authtail(struct verify_oppo_bundle *b
, struct adns_continuation *ac)
{
struct msg_digest *md = b->md;
struct state *const p1st = md->st;
struct connection *c = p1st->st_connection;
ip_subnet *our_net = &b->my.net
, *his_net = &b->his.net;
struct end our, peer;
struct hidden_variables hv;
zero(&our); zero(&peer);
our.host_type = KH_IPADDR;
our.client = b->my.net;
our.port = b->my.port;
our.protocol = b->my.proto;
our.has_client = TRUE;
peer.host_type = KH_IPADDR;
peer.client = b->his.net;
peer.port = b->his.port;
peer.protocol = b->his.proto;
peer.has_client = TRUE;
/*log信息*/
/* Now that we have identities of client subnets, we must look for
* a suitable connection (our current one only matches for hosts).
*/
struct connection *p = find_client_connection(c, &our, &peer);/*根据两端的保护子网来查询连接*/
... ...
/* now that we are sure of our connection, create our new state */
{
struct state *const st = duplicate_state(p1st);
/* first: fill in missing bits of our new state object
* note: we don't copy over st_peer_pubkey, the public key
* that authenticated the ISAKMP SA. We only need it in this
* routine, so we can "reach back" to p1st to get it.
*/
if (st->st_connection != c)
{
struct connection *t = st->st_connection;
st->st_connection = c;
set_cur_connection(c);
connection_discard(t);
}
st->st_try = 0; /* not our job to try again from start */
st->st_msgid = md->hdr.isa_msgid;
st->st_new_iv_len = b->new_iv_len;
set_new_iv(st, b->new_iv);
set_cur_state(st); /* (caller will reset) */
md->st = st; /* feed back new state */
st->st_peeruserprotoid = b->his.proto;
st->st_peeruserport = b->his.port;
st->st_myuserprotoid = b->my.proto;
st->st_myuserport = b->my.port;
change_state(st, STATE_QUICK_R0);
insert_state(st); /* needs cookies, connection, and msgid */
/* copy hidden variables (possibly with changes) */
st->hidden_variables = hv;
/* copy the connection's
* IPSEC policy into our state. The ISAKMP policy is water under
* the bridge, I think. It will reflect the ISAKMP SA that we
* are using.
*/
st->st_policy = (p1st->st_policy & POLICY_ID_AUTH_MASK)
| (c->policy & ~POLICY_ID_AUTH_MASK);
#ifdef NAT_TRAVERSAL
...
#endif
passert(st->st_connection != NULL);
passert(st->st_connection == c);
/* process SA in */
{
struct payload_digest *const sapd = md->chain[ISAKMP_NEXT_SA];
pb_stream in_pbs = sapd->pbs;
/* parse and accept body, setting variables, but not forming
* our reply. We'll make up the reply later on.
*
* note that we process the copy of the pbs, so that
* we can process it again in the cryptotail().
*/
st->st_pfs_group = &unset_group;
RETURN_STF_FAILURE(parse_ipsec_sa_body(&in_pbs
, &sapd->payload.sa
, NULL
, FALSE, st));
}
/* Ni in *//*Nonce载荷存储在state上*/
RETURN_STF_FAILURE(accept_v1_nonce(md, &st->st_ni, "Ni"));
/* [ KE ] in (for PFS) *//*KE载荷存储在state上*/
RETURN_STF_FAILURE(accept_PFS_KE(md, &st->st_gi
, "Gi", "Quick Mode I1"));
/*本端的KE和NONCE载荷哪里进行的填充???*/
passert(st->st_pfs_group != &unset_group);
passert(st->st_connection != NULL);
{/*根据发起端的KE和Nonce载荷,生成本端的ke和Nonce材料*/
struct qke_continuation *qke = alloc_thing(struct qke_continuation
, "quick_outI1 KE");
stf_status e;
enum crypto_importance ci;
ci = pcim_ongoing_crypto;
if(ci < st->st_import) ci = st->st_import;
qke->md = md;
pcrc_init(&qke->qke_pcrc);
qke->qke_pcrc.pcrc_func = quick_inI1_outR1_cryptocontinue1;
if (st->st_pfs_group != NULL) {/*支持PFS???*/
e = build_ke(&qke->qke_pcrc, st, st->st_pfs_group, ci);
} else {
e = build_nonce(&qke->qke_pcrc, st, ci);
}
passert(st->st_connection != NULL);
return e;
}
}
}
4.3 quick_inI1_outR1_cryptocontinue1()
quick_inI1_outR1_cryptocontinue1()函数的作用如下:
- 提取计算得到的Nonce载荷
- 如果启动PFS功能,则计算DH密钥信息
- 如果未启动PFS功能,则进行应答报文封装操作
static void
quick_inI1_outR1_cryptocontinue1(struct pluto_crypto_req_cont *pcrc
, struct pluto_crypto_req *r
, err_t ugh)
{
struct qke_continuation *qke = (struct qke_continuation *)pcrc;
struct msg_digest *md = qke->md;
struct state *const st = state_with_serialno(qke->qke_pcrc.pcrc_serialno);/*根据序号查找状态*/
stf_status e;
set_cur_state(st); /* we must reset before exit */
st->st_calculating=FALSE;
set_suspended(st, NULL);
/* we always calcualte a nonce */
unpack_nonce(&st->st_nr, r);/*提取Nonce值*/
if (st->st_pfs_group != NULL) {/*如果支持PFS,则需要进行第二次DH协商*/
struct dh_continuation *dh = alloc_thing(struct dh_continuation
, "quick outR1 DH");
unpack_KE(st, r, &st->st_gr);
/* set up second calculation */
dh->md = md;
set_suspended(st, md);
pcrc_init(&dh->dh_pcrc);
dh->dh_pcrc.pcrc_func = quick_inI1_outR1_cryptocontinue2;
e = start_dh_secret(&dh->dh_pcrc, st
, st->st_import
, RESPONDER
, st->st_pfs_group->group);
/* In the STF_INLINE, quick_inI1_outR1_cryptocontinue1 has already
* called complete_v1_state_transition and it has freed *dh. It
* called quick_inI1_outR1_cryptocontinue2 which did the release_md too.
*/
if(e != STF_SUSPEND && e != STF_INLINE) {
if(dh->md != NULL) {
complete_v1_state_transition(&qke->md, e);
if(dh->md) release_md(qke->md);
}
}
} else {/*无需第二次DH协商*/
/* but if PFS is off, we don't do a second DH, so
* just call the continuation after making something up.
*/
struct dh_continuation dh;
dh.md=md;
e = quick_inI1_outR1_cryptotail(&dh, NULL);
if(e == STF_OK) {
if(dh.md != NULL) {
/* note: use qke-> pointer */
complete_v1_state_transition(&qke->md, e);
if(dh.md)
release_md(qke->md);
}
}
}
reset_cur_state();
}
4.4 quick_inI1_outR1_cryptotail()
quick_inI1_outR1_cryptotail()函数的作用如下:
-
构建应答报文
- ISAKMP头部
- HASH载荷
- SA载荷
- Nonce载荷
- KE载荷
- ID载荷
-
计算报文的哈希值
-
生成密钥材料:
compute_keymats-
不同协议生成不同的keymats, 如AH、ESP分别生成不同的keymats。
-
计算公式:
K E Y M A T = P R F ( S K E Y I D — d , p r o t o c o l ∣ S P I ∣ N i − b ∣ N r − b ) KEYMAT = PRF(SKEYID—d, protocol | SPI | Ni-b | Nr-b) KEYMAT=PRF(SKEYID—d,protocol∣SPI∣Ni−b∣Nr−b) -
实现中将所有算法需要的密钥长度全部相加,通过反馈连接方法从而生成所需长度的密钥材料。
-
-
建立入ipsec sa:
install_inbound_ipsec_sa- 最最关键的部分没看懂…
-
加密报文
static stf_status
quick_inI1_outR1_cryptotail(struct dh_continuation *dh
, struct pluto_crypto_req *r)
{
struct msg_digest *md = dh->md;
struct state *st = md->st;
struct payload_digest *const id_pd = md->chain[ISAKMP_NEXT_ID];
struct payload_digest *const sapd = md->chain[ISAKMP_NEXT_SA];
struct isakmp_sa sa = sapd->payload.sa;
pb_stream r_sa_pbs;
u_char /* set by START_HASH_PAYLOAD: */
*r_hashval, /* where in reply to jam hash value */
*r_hash_start; /* from where to start hashing */
/* Start the output packet.
*
* proccess_packet() would automatically generate the HDR*
* payload if smc->first_out_payload is not ISAKMP_NEXT_NONE.
* We don't do this because we wish there to be no partially
* built output packet if we need to suspend for asynch DNS.
*
* We build the reply packet as we parse the message since
* the parse_ipsec_sa_body emits the reply SA
*/
/* HDR* out */
echo_hdr(md, TRUE, ISAKMP_NEXT_HASH);
/* HASH(2) out -- first pass *//*填充HASH载荷并清零hash数据部分*/
START_HASH_PAYLOAD(md->rbody, ISAKMP_NEXT_SA);
passert(st->st_connection != NULL);
/* sa header is unchanged -- except for np *//*SA载荷头部未发生改变,直接填充即可*/
sa.isasa_np = ISAKMP_NEXT_NONCE;
if (!out_struct(&sa, &isakmp_sa_desc, &md->rbody, &r_sa_pbs))
return STF_INTERNAL_ERROR;
/* parse and accept body, this time recording our reply *//*再次匹配SA载荷,然后将
* 匹配的SA载荷填充到r_sa_pbs中*/
RETURN_STF_FAILURE(parse_ipsec_sa_body(&sapd->pbs
, &sapd->payload.sa
, &r_sa_pbs
, FALSE, st));
/**** packet payload: HDR SA Nr [, KE ] [, IDci, IDcr ] ****/
passert(st->st_pfs_group != &unset_group);
if ((st->st_policy & POLICY_PFS) && st->st_pfs_group == NULL) {
loglog(RC_LOG_SERIOUS, "we require PFS but Quick I1 SA specifies no GROUP_DESCRIPTION");
return STF_FAIL + NO_PROPOSAL_CHOSEN; /* ??? */
}
openswan_log("responding to Quick Mode proposal {msgid:%08x}", st->st_msgid);
{
char instbuf[END_BUF];
struct connection *c = st->st_connection;
struct spd_route *sr = &c->spd;
format_end(instbuf, sizeof(instbuf),&sr->this,&sr->that,TRUE, LEMPTY);
openswan_log(" us: %s", instbuf);
format_end(instbuf, sizeof(instbuf),&sr->that,&sr->this,FALSE, LEMPTY); openswan_log(" them: %s", instbuf);
}
/**** finish reply packet: Nr [, KE ] [, IDci, IDcr ] ****/
{
int np;
#ifdef IMPAIR_UNALIGNED_R1_MSG
char *padstr=getenv("PLUTO_UNALIGNED_R1_MSG");
if(padstr) {
np = ISAKMP_NEXT_VID;
} else
#endif
if(st->st_pfs_group != NULL) {
np = ISAKMP_NEXT_KE;
} else if(id_pd != NULL) {
np = ISAKMP_NEXT_ID;
} else {
np = ISAKMP_NEXT_NONE;
}
/* Nr out */
if (!justship_nonce(&st->st_nr, &md->rbody, np, "Nr"))
return STF_INTERNAL_ERROR;
#ifdef IMPAIR_UNALIGNED_R1_MSG
if(padstr) {
pb_stream vid_pbs;
int padsize;
padsize = strtoul(padstr, NULL, 0);
openswan_log("inserting fake VID payload of %u size", padsize);
if(st->st_pfs_group != NULL) {
np = ISAKMP_NEXT_KE;
} else if(id_pd != NULL) {
np = ISAKMP_NEXT_ID;
} else {
np = ISAKMP_NEXT_NONE;
}
if (!out_generic(np,
&isakmp_vendor_id_desc, &md->rbody, &vid_pbs))
return STF_INTERNAL_ERROR;
if (!out_zero(padsize, &vid_pbs, "Filler VID"))
return STF_INTERNAL_ERROR;
close_output_pbs(&vid_pbs);
}
#endif
}
/* [ KE ] out (for PFS) */
if (st->st_pfs_group != NULL && r!=NULL) {
if (!justship_KE(&st->st_gr
, &md->rbody
, id_pd != NULL? ISAKMP_NEXT_ID : ISAKMP_NEXT_NONE))
return STF_INTERNAL_ERROR;
finish_dh_secret(st, r);
if(!r->pcr_success) {
return STF_FAIL + INVALID_KEY_INFORMATION;
}
}
/* [ IDci, IDcr ] out */
if (id_pd != NULL) {
struct isakmp_ipsec_id *p = (void *)md->rbody.cur; /* UGH! */
if (!out_raw(id_pd->pbs.start, pbs_room(&id_pd->pbs), &md->rbody, "IDci"))
return STF_INTERNAL_ERROR;
p->isaiid_np = ISAKMP_NEXT_ID;
p = (void *)md->rbody.cur; /* UGH! */
if (!out_raw(id_pd->next->pbs.start, pbs_room(&id_pd->next->pbs), &md->rbody, "IDcr"))
return STF_INTERNAL_ERROR;
p->isaiid_np = ISAKMP_NEXT_NONE;
}
#ifdef TPM
{
pb_stream *pbs = &md->rbody;
size_t enc_len = pbs_offset(pbs) - sizeof(struct isakmp_hdr);
TCLCALLOUT_crypt("preHash", st,pbs,sizeof(struct isakmp_hdr),enc_len);
r_hashval = tpm_relocateHash(pbs);
}
#endif
/* Compute reply HASH(2) and insert in output */
(void)quick_mode_hash12(r_hashval, r_hash_start, md->rbody.cur
, st, &st->st_msgid, TRUE);
/* Derive new keying material */
compute_keymats(st);
/* Tell the kernel to establish the new inbound SA
* (unless the commit bit is set -- which we don't support).
* We do this before any state updating so that
* failure won't look like success.
*/
if (!install_inbound_ipsec_sa(md->pst, st))
return STF_INTERNAL_ERROR; /* ??? we may be partly committed */
/* encrypt message, except for fixed part of header */
if (!encrypt_message(&md->rbody, st))
{
delete_ipsec_sa(st, TRUE);
return STF_INTERNAL_ERROR; /* ??? we may be partly committed */
}
DBG(DBG_CONTROLMORE, DBG_log("finished processing quick inI1"));
return STF_OK;
}
5. 其他接口源码分析
5.1 decode_net_id()
decode_net_id()函数的作用:
-
解析报文中的ID载荷,并将主机地址、子网地址、地址范围转换为子网信息。
这里解析的子网信息用于协商感兴趣流(保护子网)参数
- 如果类型为“ID_IPV4_ADDR”或者“ID_IPV6_ADDR”,则说明为单个主机地址,解析后转换为子网地址,掩码长度为32位;
- 如果类型为"ID_IPV4_ADDR_SUBNET"或者“ID_IPV6_ADDR_RANGE”,则表明ID载荷数据部分是子网信息,包含两部分:网络地址和子网掩码。通过网络地址和子网掩码共同确定保护子网信息。
- 如果类型为“ID_IPV4_ADDR_RANGE”或者“ID_IPV6_ADDR_RANGE”,则同样表明ID载荷数据是一个地址范围,包含两部分内容:起始地址和终止地址。需要注意的时,这里目前仅支持标准的子网范围,而非任意子网范围,这点需要注意(详情参见
rangetosubnet())。
static bool
decode_net_id(struct isakmp_ipsec_id *id
, pb_stream *id_pbs
, ip_subnet *net
, const char *which)
{
const struct af_info *afi = NULL;
/* Note: the following may be a pointer into static memory
* that may be recycled, but only if the type is not known.
* That case is disposed of very early -- in the first switch.
*/
const char *idtypename = enum_show(&ident_names, id->isaiid_idtype);
/*
* 子网ID可能为单个地址、子网、子网范围
*
*/
switch (id->isaiid_idtype)
{
case ID_IPV4_ADDR:
case ID_IPV4_ADDR_SUBNET:
case ID_IPV4_ADDR_RANGE:
afi = &af_inet4_info;
break;
case ID_IPV6_ADDR:
case ID_IPV6_ADDR_SUBNET:
case ID_IPV6_ADDR_RANGE:
afi = &af_inet6_info;
break;
case ID_FQDN:
loglog(RC_COMMENT, "%s type is FQDN", which);
return TRUE;
default:
/* XXX support more */
loglog(RC_LOG_SERIOUS, "unsupported ID type %s"
, idtypename);
/* XXX Could send notification back */
return FALSE;
}
switch (id->isaiid_idtype)
{
case ID_IPV4_ADDR:/*ID载荷为单个地址*/
case ID_IPV6_ADDR:
{
ip_address temp_address;
err_t ughmsg;
ughmsg = initaddr(id_pbs->cur, pbs_left(id_pbs), afi->af, &temp_address);
if (ughmsg != NULL)
{
loglog(RC_LOG_SERIOUS, "%s ID payload %s has wrong length in Quick I1 (%s)"
, which, idtypename, ughmsg);
/* XXX Could send notification back */
return FALSE;
}
if (isanyaddr(&temp_address))
{
loglog(RC_LOG_SERIOUS, "%s ID payload %s is invalid (%s) in Quick I1"
, which, idtypename, ip_str(&temp_address));
/* XXX Could send notification back */
return FALSE;
}
happy(addrtosubnet(&temp_address, net));/*将单个地址解析为保护子网地址*/
DBG(DBG_PARSING | DBG_CONTROL
, DBG_log("%s is %s", which, ip_str(&temp_address)));
break;
}
case ID_IPV4_ADDR_SUBNET:/*如果ID为子网信息*/
case ID_IPV6_ADDR_SUBNET:
{
ip_address temp_address, temp_mask;
err_t ughmsg;
if (pbs_left(id_pbs) != 2 * afi->ia_sz)/*子网信息包括IP和掩码,因此长度*2 */
{
loglog(RC_LOG_SERIOUS, "%s ID payload %s wrong length in Quick I1"
, which, idtypename);
/* XXX Could send notification back */
return FALSE;
}
ughmsg = initaddr(id_pbs->cur
, afi->ia_sz, afi->af, &temp_address);/*解析子网地址*/
if (ughmsg == NULL)
ughmsg = initaddr(id_pbs->cur + afi->ia_sz
, afi->ia_sz, afi->af, &temp_mask);/*解析子网掩码*/
if (ughmsg == NULL)
ughmsg = initsubnet(&temp_address, masktocount(&temp_mask)
, '0', net);
if (ughmsg == NULL && subnetisnone(net))
ughmsg = "contains only anyaddr";
if (ughmsg != NULL)
{
loglog(RC_LOG_SERIOUS, "%s ID payload %s bad subnet in Quick I1 (%s)"
, which, idtypename, ughmsg);
/* XXX Could send notification back */
return FALSE;
}
DBG(DBG_PARSING | DBG_CONTROL,
{
char temp_buff[SUBNETTOT_BUF];
subnettot(net, 0, temp_buff, sizeof(temp_buff));
DBG_log("%s is subnet %s", which, temp_buff);
});
break;
}
case ID_IPV4_ADDR_RANGE:
case ID_IPV6_ADDR_RANGE:
{
ip_address temp_address_from, temp_address_to;
err_t ughmsg;
if (pbs_left(id_pbs) != 2 * afi->ia_sz)
{
loglog(RC_LOG_SERIOUS, "%s ID payload %s wrong length in Quick I1"
, which, idtypename);
/* XXX Could send notification back */
return FALSE;
}/*解析子网地址*/
ughmsg = initaddr(id_pbs->cur, afi->ia_sz, afi->af, &temp_address_from);
if (ughmsg == NULL)/*解析子网掩码*/
ughmsg = initaddr(id_pbs->cur + afi->ia_sz
, afi->ia_sz, afi->af, &temp_address_to);
if (ughmsg != NULL)
{
loglog(RC_LOG_SERIOUS, "%s ID payload %s malformed (%s) in Quick I1"
, which, idtypename, ughmsg);
/* XXX Could send notification back */
return FALSE;
}
ughmsg = rangetosubnet(&temp_address_from, &temp_address_to, net);
if (ughmsg == NULL && subnetisnone(net))
ughmsg = "contains only anyaddr";
if (ughmsg != NULL)
{
char temp_buff1[ADDRTOT_BUF], temp_buff2[ADDRTOT_BUF];
addrtot(&temp_address_from, 0, temp_buff1, sizeof(temp_buff1));
addrtot(&temp_address_to, 0, temp_buff2, sizeof(temp_buff2));
loglog(RC_LOG_SERIOUS, "%s ID payload in Quick I1, %s"
" %s - %s unacceptable: %s"
, which, idtypename, temp_buff1, temp_buff2, ughmsg);
return FALSE;
}
DBG(DBG_PARSING | DBG_CONTROL,
{
char temp_buff[SUBNETTOT_BUF];
subnettot(net, 0, temp_buff, sizeof(temp_buff));
DBG_log("%s is subnet %s (received as range)"
, which, temp_buff);
});
break;
}
}
/* set the port selector */
setportof(htons(id->isaiid_port), &net->addr);
DBG(DBG_PARSING | DBG_CONTROL,
DBG_log("%s protocol/port is %d/%d", which, id->isaiid_protoid, id->isaiid_port)
)
return TRUE;
}
5.2 emit_subnet_id()
emit_subnet_id()函数的作用:
- 将隧道的保护子网地址转换为ID载荷内容,然后封装到报文中。
这个函数默认使用保护子网地址填充ID载荷(usehost===FALSE)。此函数与decode_net_id()共同完成保护子网地址的转换工作。
*填充的是隧道端口IP还是子网的信息?
*保护子网是如何协商的???
*/
static bool
emit_subnet_id(struct end *e
, u_int8_t np
, ip_address endpoint
, u_int8_t protoid
, u_int16_t port
, pb_stream *outs)
{
struct isakmp_ipsec_id id;
pb_stream id_pbs;
ip_address ta;
unsigned char *tbp;
size_t tal;
const struct af_info *ai;
bool usehost = FALSE;
ip_subnet clientnet;
clientnet = e->client;
if(!e->has_client) {
/* we propose the IP address of the interface that we are using. */
/*
* we could instead propose 0.0.0.0->255.255.255.255 and let the other
* end narrow the TS, but if one wants that, it is easy to just specify
* in the configuration file: rightsubnet=0.0.0.0/0.
*
* When there is NAT involved, we may really want a tunnel to the
* address that this end point thinks it is. That works only when
* virtual_ip includes the IP involved.
*
*/
addrtosubnet(&endpoint, &clientnet);
}
ai = aftoinfo(subnettypeof(&clientnet));
passert(ai != NULL);
id.isaiid_np = np;
id.isaiid_idtype = (usehost ? ai->id_addr : ai->id_subnet);/*确定使用主机ID还是子网ID*/
id.isaiid_protoid = protoid;
id.isaiid_port = port;
if (!out_struct(&id, &isakmp_ipsec_identification_desc, outs, &id_pbs))
return FALSE;
networkof(&clientnet, &ta);/*获取保护子网*/
tal = addrbytesptr(&ta, &tbp);
if (!out_raw(tbp, tal, &id_pbs, "client network"))/*填充保护子网信息*/
return FALSE;
if(!usehost)
{
maskof(&clientnet, &ta);/*获取保护子网掩码*/
tal = addrbytesptr(&ta, &tbp);
if (!out_raw(tbp, tal, &id_pbs, "client mask"))/*填充保护子网掩码信息*/
return FALSE;
}
close_output_pbs(&id_pbs);
return TRUE;
}
6. 小结
快速模式的第二个报文流程相对其他报文复杂了很多,尚有很多关键部分没有完全没有理解。每有会意,再做更新,如果有get到的,请分享下共同进步。