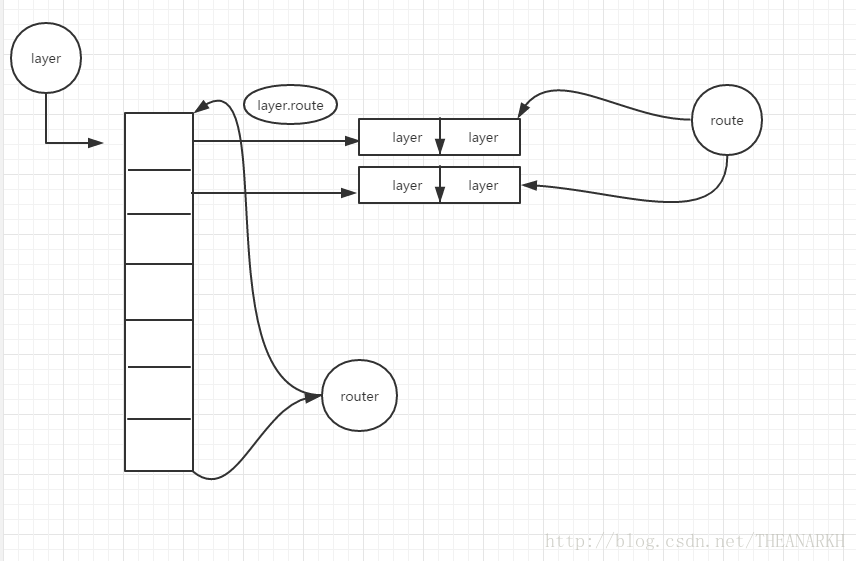
express的router.js源码分析
router.js的代码其实是router/index.js,里面的代码是express的路由的核心和入口。下面我们看一下重要的代码。
proto.handle = function handle(req, res, out) {
var self = this;
debug('dispatching %s %s', req.method, req.url);
var search = 1 + req.url.indexOf('?');//搜索参数的位置
var pathlength = search ? search - 1 : req.url.length;//url路径的长度
var fqdn = req.url[0] !== '/' && 1 + req.url.substr(0, pathlength).indexOf('://');
//如果url不以/开头,则找出://的位置
var protohost = fqdn ? req.url.substr(0, req.url.indexOf('/', 2 + fqdn)) : '';
//找出协议和主机的值
var idx = 0;
var removed = '';
var slashAdded = false;
var paramcalled = {};
// store options for OPTIONS request
// only used if OPTIONS request
var options = [];
// middleware and routes
var stack = self.stack;
// manage inter-router variables
var parentParams = req.params;
var parentUrl = req.baseUrl || '';
var done = restore(out, req, 'baseUrl', 'next', 'params');
// setup next layer
req.next = next;
// for options requests, respond with a default if nothing else responds
if (req.method === 'OPTIONS') {
done = wrap(done, function(old, err) {
if (err || options.length === 0) return old(err);
sendOptionsResponse(res, options, old);
});
}
// setup basic req values
req.baseUrl = parentUrl;
req.originalUrl = req.originalUrl || req.url;
next();
function next(err) {
var layerError = err === 'route'
? null
: err;
// remove added slash
if (slashAdded) {
req.url = req.url.substr(1);
slashAdded = false;
}
// restore altered req.url
if (removed.length !== 0) {
req.baseUrl = parentUrl;
req.url = protohost + removed + req.url.substr(protohost.length);
removed = '';
}
// no more matching layers
if (idx >= stack.length) {
setImmediate(done, layerError);
return;
}
// get pathname of request
var path = getPathname(req);
if (path == null) {
return done(layerError);
}
// find next matching layer
var layer;
var match;
var route;
while (match !== true && idx < stack.length) {//idx在是递增的变量,不需要置0,while的逻辑为在路由栈中找到每个匹配path的layer并且一个个执行
layer = stack[idx++];
match = matchLayer(layer, path);
route = layer.route;
if (typeof match !== 'boolean') {
// hold on to layerError
layerError = layerError || match;
}
if (match !== true) {//没有匹配
continue;
}
if (!route) {//
// process non-route handlers normally
continue;
}
if (layerError) {
// routes do not match with a pending error
match = false;
continue;
}
var method = req.method;
var has_method = route._handles_method(method);//因为是使用use方法增加的,所以不需要去判断是否匹配了请求方法
// build up automatic options response
if (!has_method && method === 'OPTIONS') {
appendMethods(options, route._options());
}
// don't even bother matching route
if (!has_method && method !== 'HEAD') {
match = false;
continue;
}
}
// no match
if (match !== true) {//找不到匹配的路由,执行执行done
return done(layerError);
}
// store route for dispatch on change
if (route) {
req.route = route;
}
// Capture one-time layer values
req.params = self.mergeParams
? mergeParams(layer.params, parentParams)
: layer.params;
var layerPath = layer.path;
// this should be done for the layer
self.process_params(layer, paramcalled, req, res, function (err) {
if (err) {
return next(layerError || err);
}
if (route) {
return layer.handle_request(req, res, next);
}
trim_prefix(layer, layerError, layerPath, path);
});
}
function trim_prefix(layer, layerError, layerPath, path) {
var c = path[layerPath.length];
if (c && '/' !== c && '.' !== c) return next(layerError);
// Trim off the part of the url that matches the route
// middleware (.use stuff) needs to have the path stripped
if (layerPath.length !== 0) {
debug('trim prefix (%s) from url %s', layerPath, req.url);
removed = layerPath;
req.url = protohost + req.url.substr(protohost.length + removed.length);
// Ensure leading slash
if (!fqdn && req.url[0] !== '/') {
req.url = '/' + req.url;
slashAdded = true;
}
// Setup base URL (no trailing slash)
req.baseUrl = parentUrl + (removed[removed.length - 1] === '/'
? removed.substring(0, removed.length - 1)
: removed);
}
debug('%s %s : %s', layer.name, layerPath, req.originalUrl);
if (layerError) {
layer.handle_error(layerError, req, res, next);
} else {
layer.handle_request(req, res, next);
}
}
};
proto.use = function use(fn) {
var offset = 0;
var path = '/';
// default path to '/'
// disambiguate router.use([fn])
if (typeof fn !== 'function') {
var arg = fn;
while (Array.isArray(arg) && arg.length !== 0) {
arg = arg[0];
}
// first arg is the path
if (typeof arg !== 'function') {
offset = 1;
path = fn;
}
}
var callbacks = flatten(slice.call(arguments, offset));
if (callbacks.length === 0) {
throw new TypeError('Router.use() requires middleware functions');
}
for (var i = 0; i < callbacks.length; i++) {
var fn = callbacks[i];
if (typeof fn !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError('Router.use() requires middleware function but got a ' + gettype(fn));
}
// add the middleware
debug('use %s %s', path, fn.name || '' );
var layer = new Layer(path, {
sensitive: this.caseSensitive,
strict: false,
end: false
}, fn);
layer.route = undefined;
this.stack.push(layer);
}
return this;
};
proto.route = function route(path) {
var route = new Route(path);
var layer = new Layer(path, {
sensitive: this.caseSensitive,
strict: this.strict,
end: true
}, route.dispatch.bind(route));
layer.route = route;
this.stack.push(layer);
return route;//返回该路由对象,让用户配置相关的路径和回调
};1.从use和route函数的代码中我们知道,这两个函数存储路由数据的方式是不一样的。虽然都是通过往router的stack里累加layer,但use是里的layer对应的回调是传进来的fn,而route里的layer对应的回调是route的dispatch,并且通过返回route对象,让用户配置相关的路径和回调。
2.handle函数是处理路由的入口,也是核心的代码,其中的逻辑比较多,我们主要关注一下next函数和里面的while逻辑,while的逻辑主要是在路由的二维数组中(见route分析那章)逐行查找匹配的路由,直到找到一个匹配的路由,如果找到了一个匹配的路由,则暂时停止查找,并且利于idx来记住当前的位置。然后把逻辑转到layer层中。
3.通过1的分析,我们知道,转到layer层的时候,可能只是执行一个fn,也可能是执行route对象的dispatch,不过对于router对象来说,这些都是透明的,执行完layer层后,layer层的函数会通过router传过去的next回到router的next函数逻辑中,然后基于idx位置继续查找匹配的路由,继续以上的过程,知道idx等于stack的长度。查找结束。