Java集合框架学习笔记及完整源码案例浅析
一、集合的应用场景
- 无法预测存储数据的数量
- 需要进行数据的增删改查
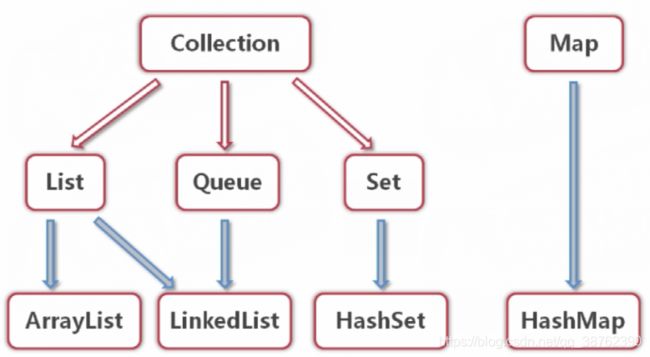
二、集合框架的体系结构
- 接口Collection有三个子接口List(实现类为ArrayList、LinkedList)、Queue(实现接口为LinkedList)、Set(HashSet);
- 接口Map的实现类为HashMap
三、List(列表)
- List是元素有序并且可以重复的集合,称为序列
- List的两个主要实现类是ArrayList和LinkedList
1、ArrayList实现类
- ArrayList底层是由数组实现的
- ArrayList中的元素可以为null
案例:公告管理
· 需求
- 公告的添加和显示
- 在指定位置处插入公告
- 删除公告
- 修改公告
Notice类(javaBean设计思想):
import java.util.Date;
public class Notice {
private int id;
private String title;
private String creator;
private Date createTime;
public Notice(int id, String title, String creator, Date createTime) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.title = title;
this.creator = creator;
this.createTime = createTime;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getCreator() {
return creator;
}
public void setCreator(String creator) {
this.creator = creator;
}
public Date getCreateTime() {
return createTime;
}
public void setCreateTime(Date createTime) {
this.createTime = createTime;
}
}
NoticeTest类(测试类):
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
public class NoticeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建3条公告
Notice notice1 = new Notice(1001, "关于做好2019年上半年普通话水平测试报名工作的通知", "系统管理员", new Date());
Notice notice2 = new Notice(1002, "关于参加第九届全国大学生电子商务“创新、创意和创业”挑战赛参赛通知", "信息管理员", new Date());
Notice notice4 = new Notice(1004, "关于2018级学生转专业考试工作安排的通知", "信息管理员", new Date());
//将公告对象添加到序列
// List list = new ArrayList();
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(notice1);
list.add(notice2);
list.add(notice4);
//循环打印输出
for(int i=0; i 2、LinkedList
四、Set集
- Set是元素无序且不可重复的集合,被称为集
- HashSet:Set的实现类,称为哈希集
- HashSet中只允许一个null元素
- 具有良好的存取和查找性能
案例:狗狗信息管理
· 需求
- 添加和显示狗狗信息
- 查找某只狗狗的信息并输出
- 修改狗狗的信息
- 删除狗狗信息
Dog类(javaBean设计思想):
public class Dog {
private String name;
private int month; //狗龄
private String speces; //品种
public Dog(String name, int month, String speces) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.month = month;
this.speces = speces;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(int month) {
this.month = month;
}
public String getSpeces() {
return speces;
}
public void setSpeces(String speces) {
this.speces = speces;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "[名字=" + name + ", 狗龄=" + month + ", 品种=" + speces + "]";
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + month;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((speces == null) ? 0 : speces.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
//判断obj是否与当前对象相等
if(this == obj) {
return true;
}
//判断obj是否是Dog类的对象
if(obj.getClass() == Dog.class) {
Dog dog = (Dog)obj;
return dog.getName().equals(name) && dog.getMonth()==month && dog.getSpeces().equals(speces);
}
return true;
}
}
DogTest类(测试类):
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class DogTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog maomao = new Dog("毛毛", 5, "金毛");
Dog qiqi = new Dog("奇奇", 16, "哈士奇");
//将狗狗对象添加入集合
Set set = new HashSet();
set.add(maomao);
set.add(qiqi);
//显示狗狗信息
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
System.out.println();
//添加相同狗狗信息
Dog qiqiRe = new Dog("奇奇", 16, "哈士奇");
set.add(qiqiRe);
iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
System.out.println();
Dog doudou = new Dog("豆豆", 18, "秋田犬");
set.add(doudou);
//查找doudou对象
if(set.contains(doudou)) {
System.out.println("找到了:"+doudou);
}
else {
System.out.println("没找到");
}
System.out.println();
//按名字查找狗狗信息
boolean flag = false;
iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
if("奇奇".equals(iterator.next().getName())){
flag = true;
break;
}
}
if(flag) {
System.out.println("奇奇找到了");
}
else {
System.out.println("奇奇没找到");
}
System.out.println();
//修改狗狗信息
maomao.setMonth(20);
//删除指定狗狗信息
// set.remove(maomao); //删除一条
//删除一类
// Set set2 = new HashSet();
// iterator = set.iterator();
// while(iterator.hasNext()) {
// Dog dog = iterator.next();
// if(dog.getMonth() < 18){
// set2.add(dog);
// }
// }
// set.removeAll(set2);
// for(Dog dog:set) {
// System.out.println(dog);
// }
// System.out.println();
//删除全部
Boolean flag1 = set.removeAll(set);
if (flag1) {
System.out.println("狗狗都没了");
}
else {
System.out.println("狗狗还在");
}
}
} 五、Map
- Map中的数据是以键值对(Key-value)的形式存储的
- key-value以Entry类型的对象实例存在
- 可以通过key值快速地查找value
- HashMap类是基于哈希表的Map接口的实现
- key值不允许重复
- HashMap中的Entry对象是无序排列的
案例1:类似字典功能的程序
- 将单词以及单词的注释存储到HashMap中
- 显示HashMap中的内容
- 查找某个单词的注释并显示
DinctionaryDemo类:
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
public class DictionaryDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map animal = new HashMap();
System.out.println("请输入三组单词对应的注释,并存放到HashMap中");
Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in);
//添加数据
int i=0;
while(i<3) {
System.out.println("请输入Key值(单词):");
String key = console.next();
System.out.println("请输入value值(注释):");
String value = console.next();
animal.put(key, value);
i++;
}
System.out.println();
//打印输出value值(直接使用迭代器)
System.out.println("使用迭代器输出所有的value:");
Iterator iterator = animal.values().iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iterator.next()+" ");
}
System.out.println();
//打印输出key和value值
//通过entrySet()
System.out.println("通过entrySet方法得到key、value:");
Set> entrySet = animal.entrySet();
for(Entry entry:entrySet) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"-"+ entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println();
//通过单词找到注释并输出
//使用keySet方法
System.out.println("请输入要查找的单词:");
String strSearch = console.next();
//1、取得keySet
Set keySet = animal.keySet();
//2、遍历keySet
for(String key:keySet) {
if(strSearch.equals(key)) {
System.out.println("找到了! " + key+"-" + animal.get(key));
break;
}
else {
System.out.println("没找到!");
}
}
}
} 案例2:商品信息管理(练习)
- 使用HashMap对商品进行管理(其中key为商品编号,value为商品对象)
- 对HashMap中的商品信息进行增、删、改、查操作
Goods类(javaBean设计思想):
public class Goods {
private String id;
private String name;
private double price;
public Goods(String id, String name, double price) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String toString() {
return "商品编号:" + id + ",商品名称:" + name + ",商品价格:" + price;
}
}GoodsTest类(测试类):
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class GoodsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in);
//定义HashMap对象
Map goodsMap = new HashMap();
System.out.println("****请输入2条商品信息****");
int i=0;
while(i<2) {
System.out.println("请输入第"+(i+1)+"条信息");
System.out.print("-商品编号:");
String goodsId = console.next();
//判断商品编号是否已经存在
if(goodsMap.containsKey(goodsId)) {
System.out.println("该商品编号已经存在,请重新输入:");
continue; //i++在语句后,循环变量并不会改变
}
System.out.print("-商品名称:");
String goodsName = console.next();
System.out.print("-商品价格:");
double goodPrice = 0;
try {
goodPrice = console.nextDouble();
} catch (InputMismatchException e) {
System.out.println("商品价格的格式不正确,请输入数值型数据!");
console.next();
continue; //继续执行
}
Goods goods = new Goods(goodsId, goodsName, goodPrice);
//将商品信息添加到HashMap中
goodsMap.put(goodsId, goods);
i++;
}
//遍历Map,输出商品信息
System.out.println("商品的全部信息为:");
Iterator iteratorGoods = goodsMap.values().iterator();
while(iteratorGoods.hasNext())
{
System.out.println(iteratorGoods.next());
}
//增删改查操作
}
}
六、总结
- ArrayList
- HashSet
- HashMap
以上三类的基本操作,具体更多可以查阅参考Java API文档。