ADXL345 三轴加速度角度传感器
@[topic]ADXL345 三轴加速度角度传感器目录
ADXL345 三轴加速度角度传感器
简介
这款ADXL345三轴加速度采用ADXL345芯片,具有体积小,功耗低的特点,13位数字精度分辨能够测量超过±16g的加速度变换。信号输出为16位数字输出,可以通过SPI与I2C接口实现信号采集。ADXL345适用于倾斜角度测量,能够进行静态重力加速度检测。同时也适用于运动状态的追踪,测量运动或冲击过程造成的瞬时加速度。其高分辨率(4mg/LSB)使之能够感应变化小于1°的倾斜角度。
DFrobot的ADXL345三轴加速度计还内置一款LDO模块让你的加速度计能够工作于3.3~6v的工作电压之下。同时传感器提供了几个特殊的功能。能够在静态或动态情况下检测是否有运动或停止出现,另外能够感知单轴的加速度值是否超出用户的设定值。检测单击/双击。如果该设备正在下降,能进行自由落体感应检测。这些功能能够被映射到两个中断输出引脚上。在低功耗模式是用户能够基于ADXL345动作感应,进行电源管理,同时只损耗极低的功耗。
另外,我们提供了一些常用的三轴加速度传感器数据处理的方法:How to Use a Three-Axis Accelerometer for Tilt Sensing.
技术规格
工作电压:3.3~6v
超低功耗:测量模式下40uA电流损耗,待机模式下[email protected]
通讯接口:I2C、SPI(3线or4线)
接口类型:0.1"插针孔
尺寸:20x15mm
应用
单击/双击检测
自由落体检测
倾角测量
切换横屏/竖屏模式
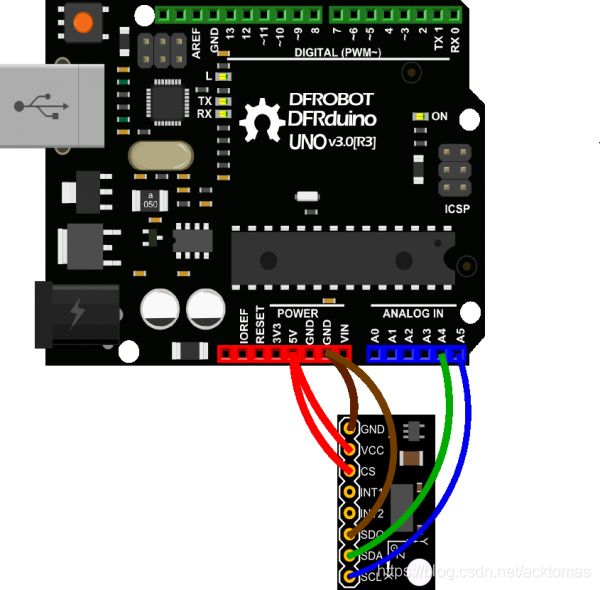
连线图
| ADXL345 | Arduino |
|---|---|
| VCC | 5V / 3V3 |
| GND | GND |
| CS | 5V / 3V3 |
| SDO | GND |
| SDA | A4 |
| SCL | A5 |
注:该连线方式适用于ADXL345的IIC通讯方式与Uno的通讯。如果您使用其他控制板,IIC管脚可能有所不同,请查阅对应管脚确保连线正确。如需使用ADXL345的SPI通讯模式,请查阅其数据手册。
样例代码
复制以下代码到您的Arduino IDE中并上传。该代码是用来收集传感器三轴加速度值,并计算Roll及Pitch角度信息。
#include Micropython示例
from machine import Pin,I2C
import ADXL345
import time
i2c = I2C(scl=Pin(22),sda=Pin(21), freq=10000)
adx = ADXL345.ADXL345(i2c)
while True:
x=adx.xValue
y=adx.yValue
z=adx.zValue
print('The acceleration info of x, y, z are:%d,%d,%d'%(x,y,z))
roll,pitch = adx.RP_calculate(x,y,z)
print('roll=',roll)
print('pitch=',pitch)
time.sleep_ms(50)
结果
打开串口监视窗口,可以看到类似下图的数据,分别为:三轴加速度的数据,按照R-xyz旋转顺序时的Roll及Pitch角。按各轴旋转可以观测到相应的数据变化。