最新Pyecharts-基本图表
Pyecharts是由Echarts而来,Echarts是百度开源的数据可视化的库,适合用来做图表设计开发,当使用Python与Echarts结合时就产生了Pyecharts。可使用pip安装,默认是最新版本的Pyecharts,查看安装的版本号可以使用pycharts.__version__查看。
安装
现在安装的v1版本与以前的0.5版本是不兼容的,使用方法上存在较大的差异,并且v0.5版本对Python的支持在Python2.7和3.4+的版本上,v1版本支持最新的Python版本。所以网上的很多关于Pyecharts的代码在新版本上并不适用,安装命令:pin install pyecharts
链式调用
可以使用链式调用的方法来创建一个图表
from pyecharts.charts import Bar
from pyecharts import options as opts
bar= (
Bar()
.add_xaxis(["裤子", "高跟鞋", "袜子"])
.add_yaxis(["销售额"],[300,509,300])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="主标题", subtitle="副标题"))
)
bar.render()上述代码中我们可以加入主题:from pyecharts.globals import ThemeTypeBar(init_opts.IninOpts(theme=ThemeType.LTGHT))
图形绘制
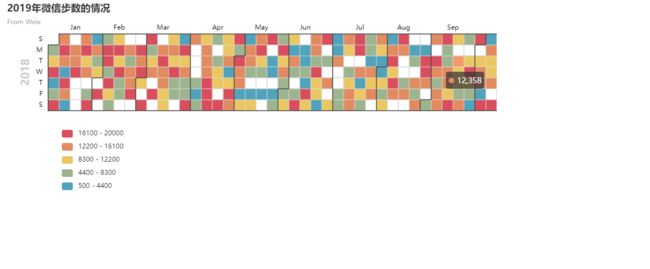
日历图
Calendar可以用来显示日历图,timedelta用来设置日期间的间隔。具体代码如下
import datetime
import random
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Calendar
def calendar_base() -> Calendar:
begin = datetime.date(2018, 1, 1) #设置起始日期
end = datetime.date(2019, 12, 31) #设置终止日期
data =[
[str(begin + datetime.timedelta(days=i)), random.randint(1000, 25000)] #设置日期间隔,步数范围
for i in range((end - begin).days + 1)
]
c = (
Calendar()
.add('', data, calendar_opts=opts.CalendarOpts(range_='2019')) #添加到日历图,指定显示2019年数据
.set_global_opts( #设置底部显示条,解释数据
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title='2019年微信步数的情况',subtitle='From Weix'),
visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(
max_=20000,
min_=500,
orient='vertical', #设置垂直显示
pos_top='230px',
pos_left='100px',
is_piecewise=True #是否连续
)
)
)
return c.render('charts1.html')
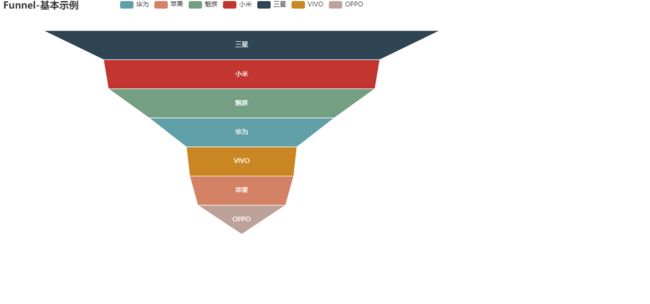
calendar_base()漏斗图
使用Funnel创建一个漏斗图
from pyecharts.faker import Faker
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Funnel, Page
def funnel_base() -> Funnel:
c = (
Funnel()
.add("商品", [list(z) for z in zip(Faker.choose(), Faker.values())], label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(position="inside"))
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Funnel-基本示例"))
)
return c.render('charts2.html')
funnel_base()这里使用的Faker,它是python的一个第三方模块,主要用来创建一些测试用的随机数据。
Faken使用文档地址:https://faker.readthedocs.io/en/master/index.html
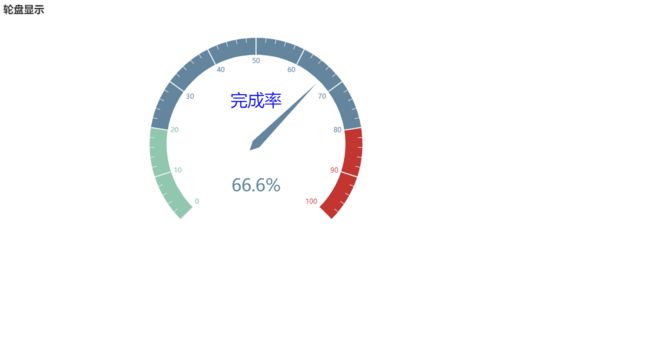
轮盘
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Gauge, Page
def gauge_label_title_setting() -> Gauge:
c = (
Gauge()
.add(
"",
[("完成率", 66.6)],
title_label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(
font_size=30, color="blue", font_family="Microsoft YaHei"
),
)
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="轮盘显示"))
)
return c.render('charts3.html')
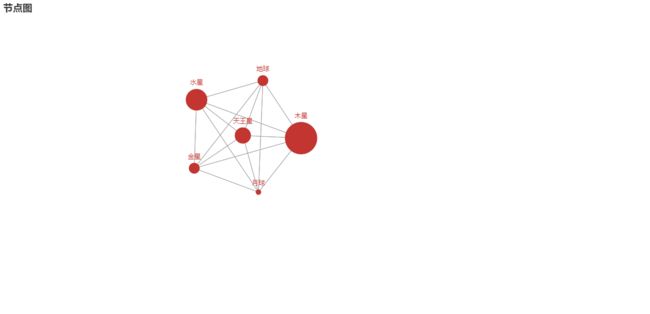
gauge_label_title_setting()节点图
import json
import os
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Graph, Page
def graph_base() -> Graph:
nodes = [
{'name': '天王星', 'symbolSize': 30},
{'name': '金星', 'symbolSize': 20},
{'name': '木星', 'symbolSize': 60},
{'name': '水星', 'symbolSize': 40},
{'name': '月球', 'symbolSize': 10},
{'name': '地球', 'symbolSize': 20}
]
links = []
for i in nodes:
for j in nodes:
links.append({'source': i.get('name'), 'target': j.get('name')})
c = (
Graph()
.add('', nodes, links, repulsion=8000)
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title='节点图'))
)
return c.render('charts4.html')
graph_base() opts.GraphLink(source="结点1", target="结点2"),
opts.GraphLink(source="结点2", target="结点3"),
opts.GraphLink(source="结点3", target="结点4"),
opts.GraphLink(source="结点4", target="结点5"),
opts.GraphLink(source="结点5", target="结点1"),水球图
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Liquid, Page
from pyecharts.globals import SymbolType
def liquid_base() -> Liquid:
c = (
Liquid()
.add("lq", [0.6, 0.7])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Liquid-基本示例"))
)
return c.render('charts5.html')
liquid_base()运行结果:
波浪颜色。color: Optional[Sequence[str]] = None
是否显示波浪动画。is_animation: bool = True
是否显示边框。is_outline_show: bool = True
饼状图
from pyecharts.faker import Faker
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Pie
def pie_base() -> Pie:
c = (
Pie()
.add("", [list(z) for z in zip(Faker.choose(), Faker.values())])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Pie-基本示例"),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(
type_="scroll", pos_left="80%", orient="vertical"
)
)
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter="{b}: {c}"))
)
return c.render('charts6.html')
pie_base()