requests+re模块,爬取《和平精英》武器信息
requests+re模块,爬取《和平精英》武器信息
- 1.分析网页
- 2.获取数据
- 3.分析数据
- 4.下载图片
- 5.格式化输出数据
- 6.主函数
1.分析网页
【1】首先,我们找到《和平精英》的游戏资料https://gp.qq.com/cp/a20190522gamedata/pc_list.shtml,在这里我们发现有游戏中的武器、配件、物资、载具和地图等信息,本文以武器的基本信息为例进行爬取,其他信息方法类似,咱不赘述。
【2】接下来,我们检查页面,点击Network,选择XHR,然后选择第2条数据。在这里,我们发现网页中的数据都是通过json数据加载来的,而不是静态页面。
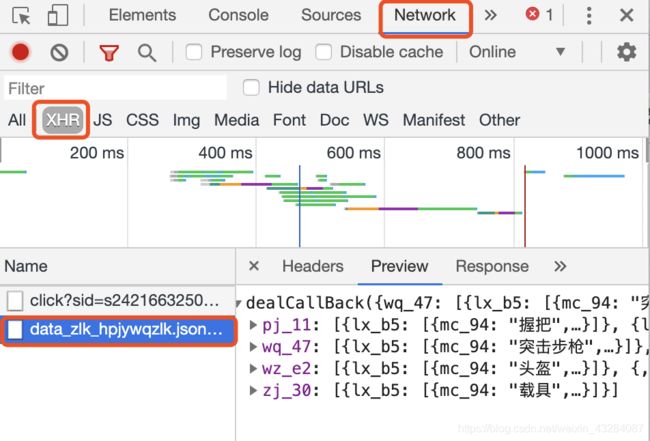
【3】我们再来分析json数据,这里可以直接看到json数据的URL,这正是我们想要的东西,同时我们也知道了该URL的Request Method是get方法,通过这些我们便可以获取武器、配件、物资、载具这些数据。

【4】但是在爬取的过程中发现,这样并不能爬取成功,于是我们再看Headers这里有没有其他需要的参数来获取json数据。在最下方找到了我们需要的parmas值,这样就可以把这里的参数添加到程序中,从而成功爬取数据。

2.获取数据
直接上代码
def get_html_text(url):
"""
获取页面json数据
:param url:
:return:
"""
headers = {'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_14_4) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/76.0.3809.100 Safari/537.36'}
parmas = {
'callback': 'dealCallBack',
'_': 1566815094736
}
try:
r = requests.get(url, headers=headers, params=parmas, timeout=30)
r.raise_for_status()
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
result = r.text
result = result.replace('dealCallBack(', '').replace(')', '') # 只留下"dealCallBack(……)"中间……这一部分
result = json.loads(result)
return result
except:
return ''
其中,url = ‘https://gp.qq.com/zlkdatasys/data_zlk_hpjywqzlk.json’。这样我们就得到了该网页的json数据了。
3.分析数据
分析时发现,源网页的json数据列表+字典套的层数比较多,这里使用正则表达式直接分析,找到每一个属性对应的key,然后再分析得到属性值。
def parse_page(ilt, html):
"""
使用re模块,利用正则表达式分析json数据,ilt列表中存储需要的数据
:param ilt:
:param html:
:return:
"""
try:
# 将数据转成字符串
html = str(html)
# 找到所有的武器名称
name = []
namelt = re.findall(r"'mc_94': '.*?'", html)
for i in range(len(namelt)):
name_temp = namelt[i].split(': ')[1].strip("'")
if len(name) < 43 and name_temp not in ['突击步枪', '射手步枪', '狙击枪', '冲锋枪', '霰弹枪', '机枪', '手枪', '近战武器', '其他']:
if name_temp not in name:
name.append(name_temp)
# 找到武器对应的属性
lt = re.findall(r"'ldtw_f2': \[.*?\]", html)
lt = str(lt)
weililt = re.findall(r"'wl_45': '\d+'", lt)
shechenglt = re.findall(r"'sc_54': '\d+'", lt)
shesult = re.findall(r"'ss_d0': '\d+'", lt)
zidanlt = re.findall(r"'zds_62': '\d+'", lt)
wendinglt = re.findall(r"'wdx_a7': '\d+'", lt)
imagelt = re.findall(r"'tp_93': '//.*?'", html)
# 获取武器的属性值和图片的url
for i in range(len(name)):
weili = eval(weililt[i].split(':')[1])
shecheng = eval(shechenglt[i].split(':')[1])
shesu = eval(shesult[i].split(':')[1])
zidan = eval(zidanlt[i].split(':')[1])
wending = eval(wendinglt[i].split(':')[1])
image = 'http://' + imagelt[i].split('//')[1].replace("'", "")
ilt.append([name[i], weili, shecheng, shesu, zidan, wending, image])
except:
print('')
4.下载图片
在上一步中,我们同时得到了所有武器图片的url,接下来,我们来下载所有武器的图片。这里使用了上一步中ilt列表中保存的武器名称和图片url数据。
def get_image(ilt):
"""
下载所有武器的图片
:param ilt:
:return:
"""
save_dir = './jingying_img/'
if not os.path.exists(save_dir):
os.mkdir(save_dir)
for lt in ilt:
name = lt[0]
url_img = lt[-1]
r = requests.get(url_img)
f = open('jingying_img/' + name + '.jpg', 'wb')
f.write(r.content)
f.close()
5.格式化输出数据
这里为了加入一些数据格式化的相关知识点,因而只在控制台进行输出,而没有将数据保存到文件中。
def print_weapon_list(ilt):
tplt = '{:^12}\t{:5}\t{:5}\t{:5}\t{:5}\t{:5}\t{:5}'
print(tplt.format('名称', '威力', '射程', '射速', '子弹数', '稳定性', '图片'))
for i in range(len(ilt)):
lt = ilt[i]
print(tplt.format(lt[0], lt[1], lt[2], lt[3], lt[4], lt[5], lt[6]))
6.主函数
其实就是依次调用上面的几个函数,一步一步进行就可以啦!
if __name__ == '__main__':
info_list = [] # 存储武器数据的列表
url = 'https://gp.qq.com/zlkdatasys/data_zlk_hpjywqzlk.json'
html = get_html_text(url)
parse_page(info_list, html)
get_image(info_list)
print_weapon_list(info_list)
以上~