Web安全之机器学习 | 决策树与随机森林算法
决策树算法
1、决策树算法概述
决策树表现了对象属性与对象值之间的一种映射关系。决策树中每个节点表示某个对象,而每个分叉路径则代表某个可能的属性值,每个叶节点则对应从根节点到该叶节点所经历的路径所表示的对象值。决策树可以用于数据分类也可以用于预测。
例如:
from sklearn import tree
X = [[0, 0], [1, 1]]
Y = [0, 1]
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier()
# 训练样本
clf = clf.fit(X, Y)
# 结果预测
print(clf.predict([[2., 2.]]))打印结果:
[1]2、示例:决策树应用
通过导入Scikit-Learn自带的iris数据集合,使用决策树算法训练,并生成可视化决策树图:
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn import tree
import pydotplus
# 加载iris数据集
iris = load_iris()
#使用决策树算法进行训练,并将训练得到的决策树保存成pdf文件
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier()
clf = clf.fit(iris.data, iris.target)
dot_data = tree.export_graphviz(clf, out_file=None)
graph = pydotplus.graph_from_dot_data(dot_data)
graph.write_pdf("photo/iris.pdf")
打开iris.pdf:
如果遇到报错:pydotplus.graphviz.InvocationException: GraphViz's executables not found
解决方式:(1)先使用pip安装graphviz:
pip install graphviz(2)下载GraphViz软件安装,下载地址:https://graphviz.gitlab.io/_pages/Download/Download_windows.html
(3)然后将GraphViz的安装目录的bin目录添加到环境变量Path中。
(4)重启编译器
3、示例:使用决策树算法检测POP3暴力破解
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn import tree
import pydotplus
# 加载KDD 99数据集中的数据
def load_kdd99(filename):
x=[]
with open(filename) as f:
for line in f:
line=line.strip('\n')
line=line.split(',')
x.append(line)
return x
def get_guess_passwdandNormal(x):
v=[]
w=[]
y=[]
# 筛选标记为guess_passwd和normal且是pop3协议的数据
for x1 in x:
if ( x1[41] in ['guess_passwd.','normal.'] ) and ( x1[2] == 'pop_3' ):
if x1[41] == 'guess_passwd.':
y.append(1)
else:
y.append(0)
# 挑选与POP3密码破解相关的网络特征以及TCP协议内容的特征作为样本特征
x1 = [x1[0]] + x1[4:8]+x1[22:30]
v.append(x1)
for x1 in v :
v1=[]
for x2 in x1:
v1.append(float(x2))
w.append(v1)
return w,y
if __name__ == '__main__':
v=load_kdd99("../data/kddcup99/corrected")
x,y=get_guess_passwdandNormal(v)
# 实例化决策树算法
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier()
# 使用十折交叉验证
print(cross_val_score(clf, x, y, n_jobs=-1, cv=10))
clf = clf.fit(x, y)
# 可视化训练得到的决策树
dot_data = tree.export_graphviz(clf, out_file=None)
graph = pydotplus.graph_from_dot_data(dot_data)
graph.write_pdf("photo/iris-dt.pdf")
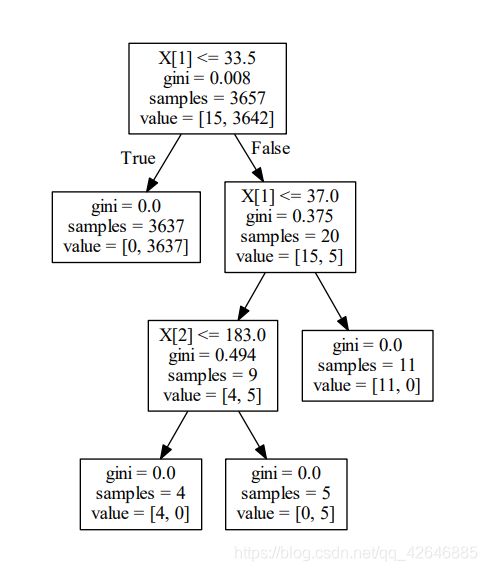
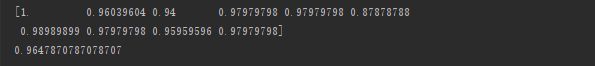
测试结果准确率约为99%:
可视化决策树iris-dt.pdf:
4、示例:使用决策树算法检测FTP暴力破解
使用ADFA-LD数据集中FTP暴力破解的相关数据,ADFA-LD系统调用可抽象成向量。
import re
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
import os
from sklearn import tree
import pydotplus
import numpy as np
def load_one_flle(filename):
x=[]
with open(filename) as f:
line=f.readline()
line=line.strip('\n')
return line
# 加载ADFA-LD中的正常样本数据
def load_adfa_training_files(rootdir):
x=[]
y=[]
list = os.listdir(rootdir)
for i in range(0, len(list)):
path = os.path.join(rootdir, list[i])
if os.path.isfile(path):
x.append(load_one_flle(path))
y.append(0)
return x,y
# 变量目录下的文件
def dirlist(path, allfile):
filelist = os.listdir(path)
for filename in filelist:
filepath = os.path.join(path, filename)
if os.path.isdir(filepath):
dirlist(filepath, allfile)
else:
allfile.append(filepath)
return allfile
def load_adfa_hydra_ftp_files(rootdir):
x=[]
y=[]
allfile=dirlist(rootdir,[])
# 从攻击数据集中筛选和FTP暴力破解相关的数据
for file in allfile:
if re.match(r"ADFA-LD/Attack_Data_Master/Hydra_FTP_\d",file):
x.append(load_one_flle(file))
y.append(1)
return x,y
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 特征化
x1,y1=load_adfa_training_files("ADFA-LD/Training_Data_Master/")
x2,y2=load_adfa_hydra_ftp_files("ADFA-LD/Attack_Data_Master/")
x=x1+x2
y=y1+y2
#print x
vectorizer = CountVectorizer(min_df=1)
x=vectorizer.fit_transform(x)
x=x.toarray()
#print y
# 训练样本
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier()
# 十折交叉验证
scores = cross_val_score(clf, x, y, n_jobs=-1, cv=10)
print(scores)
# 准确率
print(np.mean(scores))
# 可视化训练得到的决策树
clf = clf.fit(x, y)
dot_data = tree.export_graphviz(clf, out_file=None)
graph = pydotplus.graph_from_dot_data(dot_data)
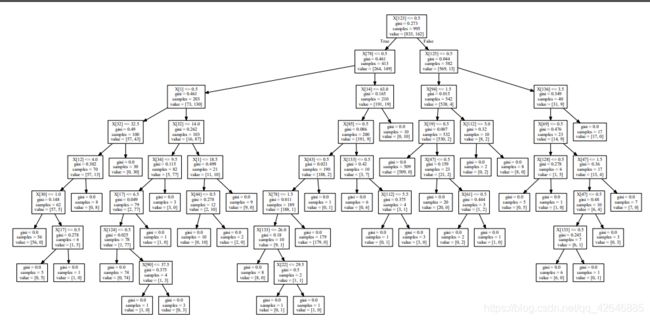
graph.write_pdf("photo/ftp.pdf")测试结果准确率约为96%:
可视化决策树:
随机森林算法概述:
1、随机森林算法概述:
随机森林指的是利用多棵树对样本进行训练并预测的一种分类器。随机森林是用随机的方式建立一个森林,森林由很多的决策树组成,随机森林的每棵树决策树之间是没有关联的。在得到森林之后,当有一个新的输入样本进入的时候,就让森林中的每棵决策树分别进行判断,看看这个样本属于哪一类,然后看哪一类被选最多,则预测这个样本为那一类。
2、示例:随机森林应用(一)
使用同样的数据集合测试来对比决策树和随机森林:
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
# 随机生成测试样本集合
X, y = make_blobs(n_samples=10000, n_features=10, centers=100, random_state=0)
# 使用决策树训练,获取训练结果
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=None, min_samples_split=2, random_state=0)
scores = cross_val_score(clf, X, y)
print(scores.mean())
# 使用随机森林训练,获取训练结果
clf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=10, max_depth=None, min_samples_split=2, random_state=0)
scores = cross_val_score(clf, X, y)
print(scores.mean())
打印结果:
0.9794087938205586
0.9996078431372549可大概看出,一般情况下,随机森林的判决性能优于决策树。
3、示例:使用随机森林算法检测FTP暴力破解
继续使用ADFA-LD数据集中FTP暴力破解的相关数据。
关键代码:
if __name__ == '__main__':
x1,y1=load_adfa_training_files("ADFA-LD/Training_Data_Master/")
x2,y2=load_adfa_hydra_ftp_files("ADFA-LD/Attack_Data_Master/")
x=x1+x2
y=y1+y2
#print x
vectorizer = CountVectorizer(min_df=1)
x=vectorizer.fit_transform(x)
x=x.toarray()
# 实例化决策树
clf1 = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier()
score=cross_val_score(clf1, x, y, n_jobs=-1, cv=10)
print(np.mean(score))
# 实例化随机森林
clf2 = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=10, max_depth=None,min_samples_split=2, random_state=0)
score=cross_val_score(clf2, x, y, n_jobs=-1, cv=10)
print(np.mean(score))测试结果显示,决策树准确率约为96%,随机森林准确率约为98%: