Freescale IMX6 Android (4): 基于TQIMX6 给Toolbox添加LED控制程序
本篇博文是为了后面的Android HAL层使用LED而做的准备,板子基于TQIMX6Q,Android 4.3,Android已经编译完成了,如果还没有可以参考前面我的博文:Freescale IMX6 Android: 使用HDMI作为Android显示输出的配置,以及TQ提供的开发者手册。
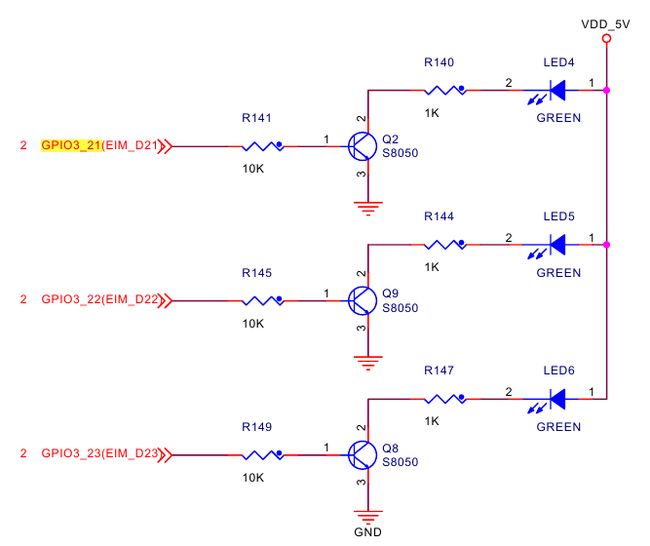
LED的硬件连接
LED4~6是给用户使用的,如下:
可以看到是GPIO3_21~23。而且是GPIO给高电平的时候接通。
LED软件方面的配置
直接导出使用
看到前面的原理图,在用户态直接将gpio导出来操作(gpiolib)是最容易的了,但是要在/sys/class/gpio中导出来需要知道各组gpio的base number,直接使用cat查看,结果如下:
#for i in gpiochip* ; do echo `cat $i/label`: `cat $i/base` ; done
gpio-0: 0
gpio-4: 128
gpio-5: 160
gpio-6: 192
gpio-1: 32
gpio-2: 64
gpio-3: 96可以知道gpio3是从64开始的,gpio3-21为64+21=85,于是直接操作:
#cd /sys/class/gpio
echo 85 > export
echo out > gpio85/direction
echo 0 > gpio85/value
但是发现不成功,因为gpio已经被使用了,无法导出来,尽管操作的时候没有出现问题log提示。
使用Gpio-led
内核使用的是3.0.35版本的内核,尽管也有dts,但是Freescale在最开始的Linuxkernel中并没有使用,因此都是hard code在board文件中的,例如这里的LED的配置就是在arch/arm/mach-mx6/board-mx6q_sabresd.c中:
#define SABRESD_GPIO_LED0 IMX_GPIO_NR(3, 21) //home
#define SABRESD_GPIO_LED1 IMX_GPIO_NR(3, 22) //enter
#define SABRESD_GPIO_LED2 IMX_GPIO_NR(3, 23) //esc
忽略注释,然后接下来定义了一个Platform device:
static struct gpio_led imx6q_gpio_leds[] =
{
GPIO_LED(SABRESD_GPIO_LED0, "led0", 0, 1, "charger-charging"),
GPIO_LED(SABRESD_GPIO_LED1, "led1", 0, 1, "charger-charging"),
GPIO_LED(SABRESD_GPIO_LED2, "led2", 0, 1, "charger-charging"),
/* For the latest B4 board, this GPIO_1 is connected to POR_B,
which will reset the whole board if this pin's level is changed,
so, for the latest board, we have to avoid using this pin as
GPIO.
GPIO_LED(SABRESD_CHARGE_DONE, "chg_done_led", 0, 1,
"charger-full"),
*/
};
static struct gpio_led_platform_data imx6q_gpio_leds_data =
{
.leds = imx6q_gpio_leds,
.num_leds = ARRAY_SIZE(imx6q_gpio_leds),
};
static struct platform_device imx6q_gpio_led_device =
{
.name = "leds-gpio",
.id = -1,
.num_resources = 0,
.dev = {
.platform_data = &imx6q_gpio_leds_data,
}
};
直接在代码中HardCode Device信息,这是老内核的通常做法。从上面的代码我们知道注册了leds-gpio设备,这个设备可以在/sys/class/leds中找到,启动的时候probe时候也会打印出设备信息:
Registered led device: led0
Registered led device: led1
Registered led device: led2从前面的imx6q_gpio_leds结构体以及最前面的定义中可以知道LED的对应关系为:
HW ------- SW
led4 led0
led5 led1
led6 led2在对应的目录中我们可以看到device设备信息:
root@sabresd_6dq:/sys/class/leds # ls -l
lrwxrwxrwx root root 1970-01-02 09:36 led0 -> ../../devices/platform/leds-gpio/leds/led0
lrwxrwxrwx root root 1970-01-02 09:36 led1 -> ../../devices/platform/leds-gpio/leds/led1
lrwxrwxrwx root root 1970-01-02 09:36 led2 -> ../../devices/platform/leds-gpio/leds/led2GPIO-LED设备的控制
gpio-led设备的子目录中有一个brightness文件,操作这个文件就可以操作led灯的亮灭,例如下面是点亮:
echo 255 > /class/gpio/leds/led0/brightness如果写入0,那么就是熄灭。
因为Android中基础小工具都是由Toolbox提供,因此我们可以往toolbox添加一个ledctrl工具来控制灯的亮灭:
#include
#ifndef lint
__COPYRIGHT("@(#) Copyright (c) 1989, 1993, 1994\
The Regents of the University of California. All rights reserved.");
#endif /* not lint */
#ifndef lint
#if 0
static char sccsid[] = "@(#)ledctrl.c 8.5 (Berkeley) 5/4/95";
#else
__RCSID("$NetBSD: ledctrl.c,v 1.33 2008/07/30 22:03:40 dsl Exp $");
#endif
#endif /* not lint */
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
void ledClose();
int ledctrl( int which, int status);
int ledOpen();
#define ALOGI printf
#define LED_NUM 3
int leds_fd[LED_NUM];
char path_buff[255];
int ledctrl( int which, int status)
{
int ret = -1;
if(status == 1) {
ret = write(leds_fd[which], "255", 3);
} else {
ret = write(leds_fd[which], "0", 1);
}
if(ret < 0){
return -1;
}
ALOGI("Native ctrl fd = [%d]\n", which);
return 0;
}
int ledOpen(void)
{
int i = 0;
for(i=0; i 我们在main函数中对每一个LED点亮1秒,然后就熄灭。将这个C代码保存为ledctrl.c,放在system/core/toolbox下面,然后更改toolbox目录下的Android.mk将其添加到toolbox中:
diff --git a/core/toolbox/Android.mk b/core/toolbox/Android.mk
index c764690..a19338e 100644
--- a/core/toolbox/Android.mk
+++ b/core/toolbox/Android.mk
@@ -57,6 +57,7 @@ TOOLS := \
touch \
lsof \
du \
+ ledctrl \
md5 \
clear \
getenforce \
直接在toolbox目录下面使用mm命令编译:
$ mm
============================================
PLATFORM_VERSION_CODENAME=REL
PLATFORM_VERSION=4.3
TARGET_PRODUCT=sabresd_6dq
TARGET_BUILD_VARIANT=eng
TARGET_BUILD_TYPE=release
TARGET_BUILD_APPS=
TARGET_ARCH=arm
TARGET_ARCH_VARIANT=armv7-a-neon
TARGET_CPU_VARIANT=cortex-a9
HOST_ARCH=x86
HOST_OS=linux
HOST_OS_EXTRA=Linux-3.13.0-39-generic-x86_64-with-Ubuntu-12.04-precise
HOST_BUILD_TYPE=release
BUILD_ID=1.1.0-rc4
OUT_DIR=out
============================================
PRODUCT_COPY_FILES device/fsl/common/input/HannStar_P1003_Touchscreen.idc:system/usr/idc/HannStar_P1003_Touchscreen.idc ignored.
PRODUCT_COPY_FILES device/fsl/common/input/Novatek_NT11003_Touch_Screen.idc:system/usr/idc/Novatek_NT11003_Touch_Screen.idc ignored.
PRODUCT_COPY_FILES device/fsl/common/input/qwerty.idc:system/usr/idc/qwerty.idc ignored.
PRODUCT_COPY_FILES device/fsl/common/input/qwerty2.idc:system/usr/idc/qwerty2.idc ignored.
No private recovery resources for TARGET_DEVICE sabresd_6dq
make: Entering directory `/home/hexiongjun/iMX6Q/TQIMX6_android-4.3'
target thumb C: toolbox <= system/core/toolbox/ledctrl.c
target Executable: toolbox (out/target/product/sabresd_6dq/obj/EXECUTABLES/toolbox_intermediates/LINKED/toolbox)
target Symbolic: toolbox (out/target/product/sabresd_6dq/symbols/system/bin/toolbox)
target Strip: toolbox (out/target/product/sabresd_6dq/obj/EXECUTABLES/toolbox_intermediates/toolbox)
Install: out/target/product/sabresd_6dq/system/bin/toolbox
make: Leaving directory `/home/hexiongjun/iMX6Q/TQIMX6_android-4.3'
编译完成后toolbox,我们可以重新将system目录的文件拷贝到SD开对应的system分区中,也可以直接将toolbox push到android机器中,在push之前需要先remount system为rw,因此在串口中,或者有root权限的adb shell中输入下面命令:
# mount -t ext4 -r -w -o remount /system
EXT4-fs (mmcblk1p2): re-mounted. Opts: (null)
$ adb push $OUT/system/bin/toolbox /system/bin/
1309 KB/s (139096 bytes in 0.103s)然后在机器的console中测试:
# toolbox ledctrl
path:/sys/class/leds/led0/brightness
led0: /sys/class/leds/led0/brightness, open success
path:/sys/class/leds/led1/brightness
led1: /sys/class/leds/led1/brightness, open success
path:/sys/class/leds/led2/brightness
led2: /sys/class/leds/led2/brightness, open success
Native ctrl fd = [0]
Native ctrl fd = [0]
Native ctrl fd = [1]
Native ctrl fd = [1]
Native ctrl fd = [2]
Native ctrl fd = [2]如果看到LED点亮1秒然后熄灭,那么说明代码无误。