算法与数据结构【C++】:稀疏表
很多情境下,存储数据的最好方式就是表。
当数据较为稠密的聚集在某个坐标范围中时,采用数组是最好的选择。
比如,要存储一个班学生的成绩,该班级有30人,编号从1-30,有10门课,编号1-10
那么就可以用一个30x10的数组存储这张成绩表,经济实惠使用方便
但是有的时候数据非常稀疏,比如一个学校一共开设了1000门课,有的学生可以随意选课,现在需要一个数据结构存储每个学生每门课的成绩。
显然一个学生一学期只能上十几门课,所以表内的数据很稀疏,大部分结点都是空结点,没有数据。如果使用数组,那就需要提前分配好空间,不仅成绩表本身很大,也浪费了很多空间。
这个时候,就可以使用稀疏表。
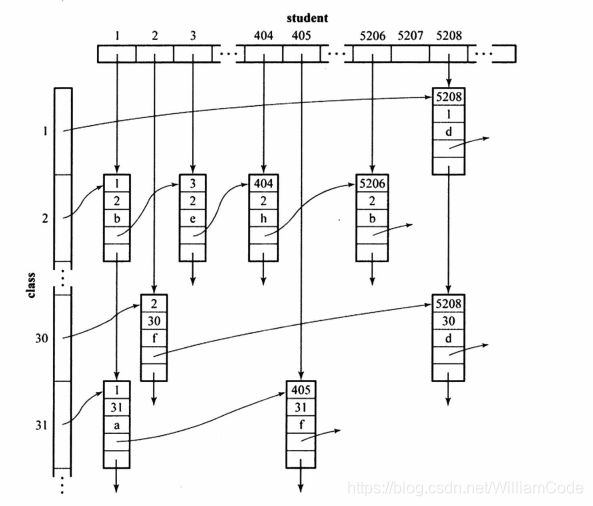
想象现在有一张记录3000名学生在1000门课的成绩。
现在把每个非空的表中元素抽象成一个结点,每一列串起来形成很多列,这些列一起放入一个数组;每一行串起来形成很多行,这些行一起放入一个数组,这样,整个稠密的数组被选出来的结点编织成一张稀疏的网。
维护与存储这张网即可
如下图:
稀疏表的属性如下:
int rowTotalNum; //总行数
int colTotalNum; //总列数
LinkedList[] row; //行链表的指针,大小需要与下方一致
LinkedList[] col; //列链表的指针,大小需要与下方一致
稀疏表提供的方法如下:
SparseTable():构造方法,初始化参数
void insert(int value ,int rowIndex, int colIndex):向稀疏表的某个点(rowIndex,colIndex)插入value值
void remove(int rowIndex, int colIndex):删除某个坐标(rowIndex,colIndex)的结点
int getValue(int rowIndex, int colIndex):获取指定坐标(rowIndex,colIndex)的值,如果没有该结点,返回-1;方法内部提供了两种方法,按列查找和按行查找
void printSelfByRow():通过行链表打印稀疏表
void printSelfByCol():通过列链表打印稀疏表
LinkedList getCol(int colIndex):获取某列的列链表
LinkedList getRow(int rowIndex):获取某行的行链表
下方是C++代码:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
//节点类,代表链表的结点
class Node{
public:
int row;
int col;
int value; //存储节点的值
Node* next; //存储下一个节点的指针
Node(int aValue, int aRow, int aCol, Node* aNext = NULL){ //构造函数,必须传入结点的值,下一个节点默认为NULL
this->value = aValue;
this->next = aNext;
this->row = aRow;
this->col = aCol;
}
};
class LinkedList{ //普通单向链表类
public:
int length; //链表长度,该属性不重要,下面的方法中也没有用到,但是维护了该属性
Node* head; //链表头节点的指针
Node* tail; //链表尾节点的指针
LinkedList(){
length = 0;
head = tail = 0;
}
//把链表当作一列的链表,在第row行插入结点,值为value
void insertToCol(int value, int row, int col){
//Search in col where nextCol > col
//在一列中查找坐标为row的结点,返回该结点的前一个结点的值
//返回结果有如下情况
//1、NULL:说明找到了该结点,且该结点是头结点,所以没有前驱结点;
//2、NULL:链表为空
//3、不为空,说明找到了前驱结点,寻找的依据是后继结点的坐标大于要插入的坐标
Node* aheadOfInsert = searchInCol(row);
//insertNode in that position
//如果链表为空,返回了NULL,说明需要在第一个位置插入结点,更新head和tail
if (aheadOfInsert == NULL && isEmpty()){
head = tail = new Node(value, row, col);
}
//如果返回NULL且链表不为空,说明要添加首结点,更新head
else if (aheadOfInsert == NULL && !isEmpty()){
head = new Node(value, row, col, head);
}
//否则,正常插入
else {
aheadOfInsert->next = new Node(value, row, col, aheadOfInsert->next);
}
length++;
}
//同理,向行链表的col坐标处,插入结点
void insertToRow(int value, int row, int col){
//Search in col where nextCol > col
Node* aheadOfInsert = searchInRow(col);
//insertNode in that position
if (aheadOfInsert == NULL && isEmpty()){
head = tail = new Node(value, row, col);
}
else if (aheadOfInsert == NULL && !isEmpty()){
head = new Node(value, row, col, head);
}
else {
aheadOfInsert->next = new Node(value, row, col, aheadOfInsert->next);
}
length++;
}
//把当前链表当作列链表,删除坐标为row的结点
void deleteByCol(int row, int col){
//Search in col where nextCol > col
//搜索得到要删除结点的前驱结点
//返回结果有如下情况
//1、NULL:说明找到了该结点,且该结点是头结点,所以没有前驱结点;
//2、NULL:链表为空
//3、NULL:没有找到该结点
//4、不为空,说明找到了前驱结点,寻找的依据是后继结点的坐标大于要插入的坐标,所以后继结点并不一定是要删除的结点
Node* aheadOfDelete = searchInCol(row);
Node* deletedNode=NULL;
//情况1:可能要删除头结点,对比坐标,如果的确要删除,删除头结点并更新head
if (aheadOfDelete == NULL && !isEmpty()
&& head->col==col && head->row==row){
deletedNode = head;
head = head->next;
length--;
}
//情况2、3:没有找到要删除的结点,返回
else if (aheadOfDelete==NULL)
return ;
//情况3:没有找到要删除的结点,返回
else if(aheadOfDelete->next == NULL)
return ;
//否则,正常删除结点
else if (aheadOfDelete->next->col==col && aheadOfDelete->next->row==row){
deletedNode = aheadOfDelete->next;
aheadOfDelete->next = aheadOfDelete->next->next;
length--;
}
//释放该结点的内存
delete deletedNode;
}
//把当前链表当作行链表,删除坐标为col的结点
//同理
void deleteByRow(int row, int col){
//Search in col where nextCol > col
Node* aheadOfDelete = searchInRow(col);
//cout<<"deleting by row"<col==col && head->row==row){
deletedNode = head;
head = head->next;
length--;
}
else if (aheadOfDelete==NULL)
return ;
else if(aheadOfDelete->next == NULL)
return ;
else if (aheadOfDelete->next->col==col && aheadOfDelete->next->row==row){
deletedNode = aheadOfDelete->next;
aheadOfDelete->next = aheadOfDelete->next->next;
length--;
}
delete deletedNode;
}
//根据列,查找坐标(row,col)的值
int getValueByCol(int row, int col){
//Search in col where nextCol > col
//搜索得到要查找结点的前驱结点
//返回结果有如下情况
//1、NULL:找到了该结点,且该结点是头结点,所以没有前驱结点;
//2、NULL:没有找到该结点,表现为链表不为空但是返回了NULL;
//3、NULL:链表为空
//4、NULL:没有找到该结点
//5、不为空,说明找到了前驱结点,寻找的依据是后继结点的坐标大于要插入的坐标,所以后继结点并不一定是要删除的结点
Node* aheadOfNode = searchInCol(row);
//情况1
if (aheadOfNode == NULL && !isEmpty()
&& head->col==col && head->row==row){
return head->value;
}
//情况2
else if (aheadOfNode == NULL && !isEmpty())
return -1;
//情况3
else if (aheadOfNode==NULL && isEmpty())
return -1;
//情况4
else if(aheadOfNode->next == NULL)
return -1;
//情况5
else if (aheadOfNode->next->col==col && aheadOfNode->next->row==row){
return aheadOfNode->next->value;
}
return -1;
}
//根据行,查找坐标(row,col)的值
int getValueByRow(int row, int col){
//Search in col where nextCol > col
//搜索得到要查找结点的前驱结点
//返回结果有如下情况
//1、NULL:说明找到了该结点,且该结点是头结点,所以没有前驱结点;
//2、NULL:链表为空
//3、NULL:没有找到该结点
//4、不为空,说明找到了前驱结点,寻找的依据是后继结点的坐标大于要插入的坐标,所以后继结点并不一定是要删除的结点
Node* aheadOfNode = searchInRow(col);
//情况1
if (aheadOfNode == NULL && !isEmpty()
&& head->col==col && head->row==row){
return head->value;
}
//情况2
else if (aheadOfNode == NULL && !isEmpty())
return -1;
//情况3
else if (aheadOfNode==NULL && isEmpty())
return -1;
//情况4
else if(aheadOfNode->next == NULL)
return -1;
//情况5
else if (aheadOfNode->next->col==col && aheadOfNode->next->row==row){
return aheadOfNode->next->value;
}
return -1;
}
//把当前链表当作列链表,搜索行坐标为row的结点
Node* searchInCol(int row){
//return NULL if list is empty;
//如果链表为空或者头节点的row坐标已经大于要查找的结点row坐标,返回空
if (isEmpty() || head->row>=row)
return NULL;
Node* now;
//循环查找
//循环终止的条件有两个:
//1、到达链表尾,仍然没有找到。对应now->next!=NULL
//2、下一个结点的row坐标已经小于要查找的row坐标,对应now->next->rownext!=NULL && now->next->rownext);
return now;
}
//同理
//把当前链表当作行链表,搜索列坐标为row的结点
Node* searchInRow(int col){
//return NULL if list is empty;
if (isEmpty() || head->col>=col)
return NULL;
Node* now;
for (now=head; now->next!=NULL && now->next->colnext);
return now;
}
int isEmpty(){ //判断链表是否为空,头指针为0代表空
return head == 0;
}
void printSelf(){ //打印链表内容
}
};
//稀疏表
class SparseTable{
public:
int rowTotalNum; //总行数
int colTotalNum; //总列数
LinkedList* row[500]; //行链表的指针,大小需要与下方一致
LinkedList* col[500]; //列链表的指针,大小需要与下方一致
//构造方法
SparseTable(){
rowTotalNum = 500;
colTotalNum = 500;
for (int i=0; i= rowTotalNum || colIndex >= colTotalNum)
return ;
if(getValue(rowIndex, colIndex) != -1)
return ;
//向行链表和列链表分别插入结点
row[rowIndex]->insertToRow(value, rowIndex, colIndex);
col[colIndex]->insertToCol(value, rowIndex, colIndex);
}
//删除某个坐标(rowIndex,colIndex)的结点
void remove(int rowIndex, int colIndex){
if (rowIndex >= rowTotalNum || colIndex >= colTotalNum)
return ;
//删除行链表和列链表上的结点
row[rowIndex]->deleteByRow(rowIndex, colIndex);
col[colIndex]->deleteByCol(rowIndex, colIndex);
}
//获取指定坐标(rowIndex,colIndex)的值
//如果没有该结点,返回-1
//这里提供了两种方法,按列查找和按行查找
int getValue(int rowIndex, int colIndex){
if (rowIndex >= rowTotalNum || colIndex >= colTotalNum)
return -1;
//return col[colIndex]->getValueByCol(rowIndex, colIndex);
return row[rowIndex]->getValueByRow(rowIndex, colIndex);
}
//通过行链表打印稀疏表
void printSelfByRow(){
cout<<"By row--------------------------"<head; now!=NULL; now=now->next){
cout<<"("<row<<", "<col<<"): "<value<<" ";
}
cout<head; now!=NULL; now=now->next){
cout<<"("<row<<", "<col<<"): "<value<<" ";
}
cout<insert(1,1,2);
st->insert(2,1,3);
st->insert(3,2,4);
st->insert(4,3,3);
st->insert(44,3,5);
st->insert(42,3,2);
st->insert(42,3,2);
st->printSelfByRow();
st->printSelfByCol();
st->remove(2,4);
st->remove(2,4);
st->printSelfByRow();
st->printSelfByCol();
st->remove(1,2);
st->printSelfByRow();
st->printSelfByCol();
cout<<"Get value: (3,5)"<getValue(3,5)<getValue(3,4)<getValue(3,2)<