2016第七届蓝桥杯大赛软件类B组C/C++省赛题解
2016第七届蓝桥杯大赛软件类B组C/C++省赛目录
-
-
- 试题A:煤球数目(结果填空)
- 试题B:生日蜡烛(结果填空)
- 试题 C:凑算式(结果填空)
- 试题 D:快速排序(结果填空)
- 试题 E:抽签(结果填空)
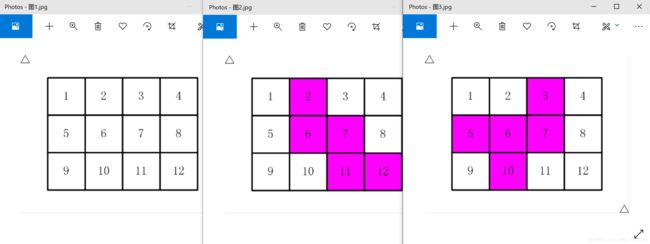
- 试题 F:方格填数(结果填空)
- 试题 G:剪邮票(结果填空)
- 试题 H:四平方和(程序设计)
- 试题 I:交换瓶子(程序设计)
- 试题 J:最大比例(程序设计)
-
试题A:煤球数目(结果填空)
做法:前缀前缀和
代码:
#include答案:171700
试题B:生日蜡烛(结果填空)
做法:前缀和累加,再双重循环判断区间差是否为236。
代码:
#include答案:26
试题 C:凑算式(结果填空)
题意:

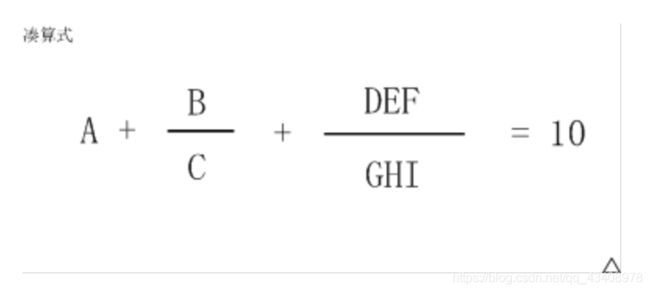
做法:全排列函数next_permutation
代码:
#include答案:29
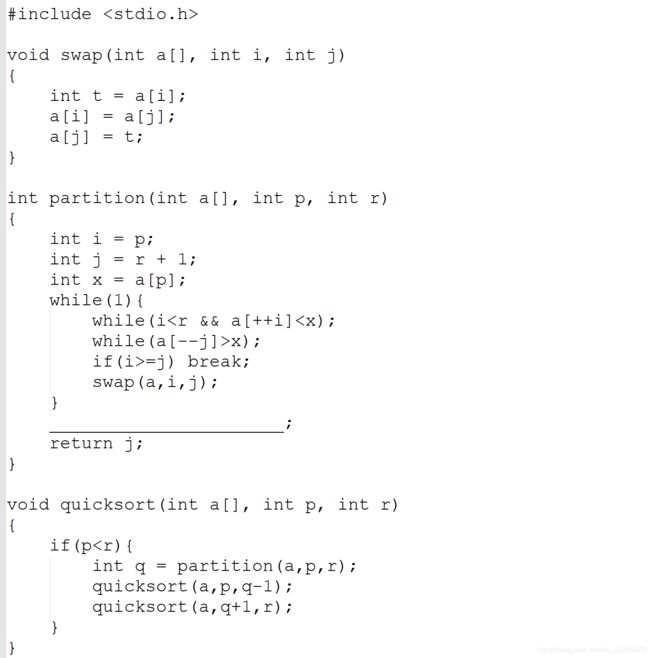
试题 D:快速排序(结果填空)
做法:凑
答案:swap(a, j, p);
试题 E:抽签(结果填空)
做法:凑,m-j也是可以的,i==j
答案:f(a, k+1, m-i, b);
试题 F:方格填数(结果填空)
做法:全排列函数next_permutation
代码:
#include答案:1580
试题 G:剪邮票(结果填空)
做法:先给每个格子标号,共 C 12 5 C_{12}^{5} C125种方法,五重循环选取五个格子,再判断这个方案是否正确即可,这篇题解很nice。
代码:
#include答案:116
试题 H:四平方和(程序设计)
题意:


做法:三重循环暴力三个数字,最后判断第四个数字是否是一个平方数,时间复杂度表面看上去很高,但是有四平方定理证明了四个数字中有一个数字很小,只有一组数据,一旦找到直接终止,复杂度近似 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)。
代码:
#include试题 I:交换瓶子(程序设计)
做法:模拟,每一次都将最小的那个未归位的数字归位,模拟过程中记录下标的数组更新很容易跟数组中两数字交换搞混,故用了四个变量记录。
代码:
#include