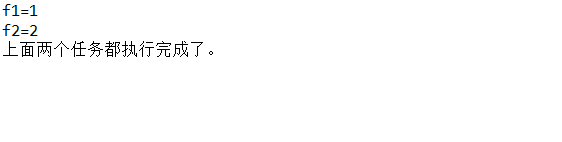CompletableFuture的使用,多个CompletableFuture的处理
对单个CompletableFuture的处理方式可以查看https://mp.csdn.net/mdeditor/91348503#
本文主要介绍如何组合使用多个CompletableFuture。
thenCombine
把两个 CompletableFuture的任务都执行完成后,把两个任务的结果一块交给 thenCombine 来处理。thenCombine是可以有返回的。
@Test
public void thenCombine() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<String> result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
delaySec(1);
printCurrTime("第一个CF");
return "hello1";
}).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
printCurrTime("第二个CF");
delaySec(3);
return "hello2";
}), (t, u) -> {
printCurrTime("组合");
return t + " " + u;
});
System.out.println(result.get());
}
执行结果:

可以看到两个线程的执行是并行的,thenCombine在两个线程都返回结果时执行。
注意:如果某个线程出现了异常,则thenCombine不会执行。
thenAcceptBoth
这个方法和上面的方法作用类似,都是接受两个线程的返回结果,并作出处理。只不过这个方法是消费式的,没有返回。注意这里的返回是指自定义接口方法中的返回。基本上所有的方法都会返回一个CompletionStage 至于泛型则由接口方法返回值决定。
@Test
public void thenAcceptBoth() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<Integer> f1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int t = new Random().nextInt(3);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(t);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("f1=" + t);
return t;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> f2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int t = new Random().nextInt(3);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(t);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("f2=" + t);
return t;
});
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
f1.thenAcceptBoth(f2, (t, u) -> {
System.out.println("f1=" + t + ";f2=" + u + ";");
});
}
applyToEither
哪个线程先返回就使用谁的返回结果进入该方法。另一个线程如果执行时间过长则不再执行。该方法参数为函数式接口是有返回类型的。
@Test
public void applyToEither() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<Integer> f1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int t = new Random().nextInt(3);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(t);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("f1=" + 1);
printCurrTime("f1返回时间");
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> f2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int t = new Random().nextInt(3);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(t);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("f2=" + 3);
printCurrTime("f2返回时间");
return 3;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> result = f1.applyToEither(f2, t -> {
System.out.println(t);
return t * 2;
});
System.out.println(result.get());
}
acceptEither
和上面的方法作用相似,但是该方法是消费式,不会线程不会返回执行结果。
@Test
public void acceptEither() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<Integer> f1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int t = new Random().nextInt(3);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(t);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("f1=" + t);
return t;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> f2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int t = new Random().nextInt(3);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(t);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("f2=" + t);
return t;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEither = f1.acceptEither(f2, t -> {
System.out.println(t);
});
}
runAfterEither
该方法非阻塞。只有在该方法执行之前有线程返回该方法才会执行。
@Test
public void runAfterEither() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<Integer> f1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("f1=" + 1);
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> f2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("f2=" + 2);
return 2;
});
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);
f1.runAfterEither(f2, () -> System.out.println("上面有一个已经完成了。"));
}
runAfterBoth
同样为非阻塞方法,且只有当两个线程都在该方法执行之前结束。才会执行该方法。
@Test
public void runAfterBoth() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<Integer> f1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("f1=" + 1);
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> f2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("f2=" + 2);
return 2;
});
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
f1.runAfterBoth(f2, () -> System.out.println("上面两个任务都执行完成了。"));
}
thenCompose
将两个线程串行连接起来,只有第一个线程返回结果时,才会将返回值作为参数传给第二个线程执行。
@Test
public void thenCompose() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<Integer> f = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int t = new Random().nextInt(3);
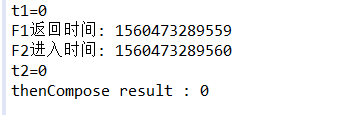
System.out.println("t1=" + t);
printCurrTime("F1返回时间");
return t;
}).thenCompose( param -> {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
printCurrTime("F2进入时间");
int t = param * 2;
System.out.println("t2=" + t);
return t;
});
});
System.out.println("thenCompose result : " + f.get());
}