目的
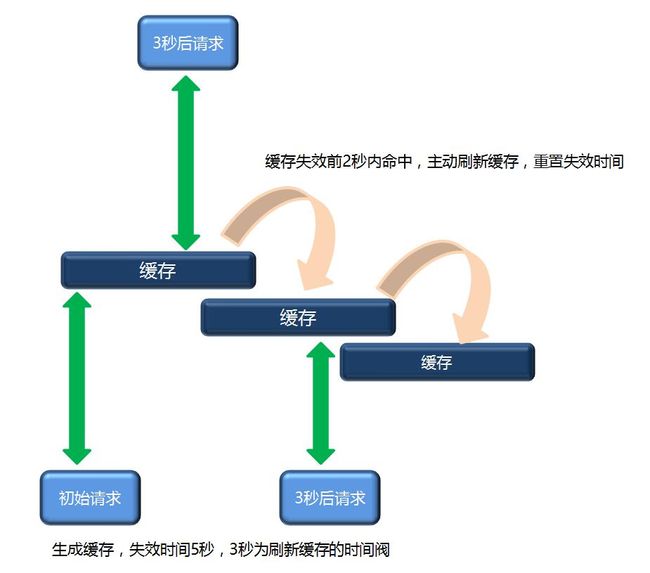
之前在github上找了一个开源的项目,改了改缓存的扩展,让其支持在缓存注解上控制缓存失效时间以及多长时间主动在后台刷新缓存以防止缓存失效( Spring Cache扩展:注解失效时间+主动刷新缓存 )。示意图如下:
那篇文章存在两个问题:
- 所有的配置是建立在修改缓存容器的名称基础上,与传统缓存注解的写法有所区别,后续维护成本会增加;
- 后台刷新缓存时会存在并发更新的问题
另外,当时项目是基于springboot 1.x,现在springboot2.0对缓存这块有所调整,需要重新适配。
SpringBoot 2.0对缓存的变动
RedisCacheManager
看看下面的构造函数,与1.x有比较大的改动,这里就不贴代码了。
public RedisCacheManager(RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter, RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfiguration) {
this(cacheWriter, defaultCacheConfiguration, true);
}
public RedisCacheManager(RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter, RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfiguration, String... initialCacheNames) {
this(cacheWriter, defaultCacheConfiguration, true, initialCacheNames);
}RedisCache
既然上层的RedisCacheManager变动了,这里也就跟着变了。
protected RedisCache(String name, RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter, RedisCacheConfiguration cacheConfig) {
super(cacheConfig.getAllowCacheNullValues());
Assert.notNull(name, "Name must not be null!");
Assert.notNull(cacheWriter, "CacheWriter must not be null!");
Assert.notNull(cacheConfig, "CacheConfig must not be null!");
this.name = name;
this.cacheWriter = cacheWriter;
this.cacheConfig = cacheConfig;
this.conversionService = cacheConfig.getConversionService();
}
方案
针对上述的三个问题,分别应对。
将缓存配置从注解上转移到初始化缓存的地方
创建一个类用来描述缓存配置,避免在缓存注解上通过非常规手段完成特定的功能。
public class CacheItemConfig implements Serializable {
/**
* 缓存容器名称
*/
private String name;
/**
* 缓存失效时间
*/
private long expiryTimeSecond;
/**
* 当缓存存活时间达到此值时,主动刷新缓存
*/
private long preLoadTimeSecond;
}具体的应用参见下面两步。
适配springboot 2.0
修改CustomizedRedisCacheManager
构造函数:
public CustomizedRedisCacheManager(
RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory,
RedisOperations redisOperations,
List cacheItemConfigList) 参数说明:
- connectionFactory,这是一个redis连接工厂,用于后续操作redis
- redisOperations,这个一个redis的操作实例,具体负责执行redis命令
- cacheItemConfigList,这是缓存的配置,比如名称,失效时间,主动刷新时间,用于取代在注解上个性化的配置。
具体实现如下:核心思路就是调用RedisCacheManager的构造函数。
private RedisCacheWriter redisCacheWriter;
private RedisCacheConfiguration defaultRedisCacheConfiguration;
private RedisOperations redisOperations;
public CustomizedRedisCacheManager(
RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory,
RedisOperations redisOperations,
List cacheItemConfigList) {
this(
RedisCacheWriter.nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(connectionFactory),
RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig().entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(30)),
cacheItemConfigList
.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(CacheItemConfig::getName,cacheItemConfig -> {
RedisCacheConfiguration cacheConfiguration =
RedisCacheConfiguration
.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(cacheItemConfig.getExpiryTimeSecond()))
.prefixKeysWith(cacheItemConfig.getName());
return cacheConfiguration;
}))
);
this.redisOperations=redisOperations;
CacheContainer.init(cacheItemConfigList);
}
public CustomizedRedisCacheManager(
RedisCacheWriter redisCacheWriter
,RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration,
Map redisCacheConfigurationMap) {
super(redisCacheWriter,redisCacheConfiguration,redisCacheConfigurationMap);
this.redisCacheWriter=redisCacheWriter;
this.defaultRedisCacheConfiguration=redisCacheConfiguration;
}
由于我们需要主动刷新缓存,所以需要重写getCache方法:主要就是将RedisCache构造函数所需要的参数传递过去。
@Override
public Cache getCache(String name) {
Cache cache = super.getCache(name);
if(null==cache){
return cache;
}
CustomizedRedisCache redisCache= new CustomizedRedisCache(
name,
this.redisCacheWriter,
this.defaultRedisCacheConfiguration,
this.redisOperations
);
return redisCache;
} 修改CustomizedRedisCache
核心方法就一个,getCache:当获取到缓存时,实时获取缓存的存活时间,如果存活时间进入缓存刷新时间范围即调起异步任务完成缓存动态加载。ThreadTaskHelper是一个异常任务提交的工具类。下面方法中的参数key,并不是最终存入redis的key,是@Cacheable注解中的key,要想获取缓存的存活时间就需要找到真正的key,然后让redisOptions去调用ttl命令。在springboot 1.5下面好像有个RedisCacheKey的对象,但在springboot2.0中并未发现,取而代之获取真正key是通过函数this.createCacheKey来完成。
public ValueWrapper get(final Object key) {
ValueWrapper valueWrapper= super.get(key);
if(null!=valueWrapper){
CacheItemConfig cacheItemConfig=CacheContainer.getCacheItemConfigByCacheName(key.toString());
long preLoadTimeSecond=cacheItemConfig.getPreLoadTimeSecond();
String cacheKey=this.createCacheKey(key);
Long ttl= this.redisOperations.getExpire(cacheKey);
if(null!=ttl&& ttl<=preLoadTimeSecond){
logger.info("key:{} ttl:{} preloadSecondTime:{}",cacheKey,ttl,preLoadTimeSecond);
ThreadTaskHelper.run(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
logger.info("refresh key:{}", cacheKey);
CustomizedRedisCache.this.getCacheSupport()
.refreshCacheByKey(CustomizedRedisCache.super.getName(), key.toString());
}
});
}
}
return valueWrapper;
}CacheContainer,这是一个辅助数据存储,将前面设置的缓存配置放入容器以便后面的逻辑获取。其中包含一个默认的缓存配置,防止 在未设置的情况导致缓存获取异常。
public class CacheContainer {
private static final String DEFAULT_CACHE_NAME="default";
private static final Map CACHE_CONFIG_HOLDER=new ConcurrentHashMap(){
{
put(DEFAULT_CACHE_NAME,new CacheItemConfig(){
@Override
public String getName() {
return DEFAULT_CACHE_NAME;
}
@Override
public long getExpiryTimeSecond() {
return 30;
}
@Override
public long getPreLoadTimeSecond() {
return 25;
}
});
}
};
public static void init(List cacheItemConfigs){
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(cacheItemConfigs)){
return;
}
cacheItemConfigs.forEach(cacheItemConfig -> {
CACHE_CONFIG_HOLDER.put(cacheItemConfig.getName(),cacheItemConfig);
});
}
public static CacheItemConfig getCacheItemConfigByCacheName(String cacheName){
if(CACHE_CONFIG_HOLDER.containsKey(cacheName)) {
return CACHE_CONFIG_HOLDER.get(cacheName);
}
return CACHE_CONFIG_HOLDER.get(DEFAULT_CACHE_NAME);
}
public static List getCacheItemConfigs(){
return CACHE_CONFIG_HOLDER
.values()
.stream()
.filter(new Predicate() {
@Override
public boolean test(CacheItemConfig cacheItemConfig) {
return !cacheItemConfig.getName().equals(DEFAULT_CACHE_NAME);
}
})
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
修改CacheManager加载方式
由于主动刷新缓存时需要用缓存操作,这里需要加载RedisTemplate,其实就是后面的RedisOptions接口。序列化机制可心随意调整。
@Bean
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer serializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
mapper.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
serializer.setObjectMapper(mapper);
template.setValueSerializer(serializer);
template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
}
加载CacheManager,主要是配置缓存容器,其余的两个都是redis所需要的对象。
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory,RedisTemplate redisTemplate) {
CacheItemConfig productCacheItemConfig=new CacheItemConfig();
productCacheItemConfig.setName("Product");
productCacheItemConfig.setExpiryTimeSecond(10);
productCacheItemConfig.setPreLoadTimeSecond(5);
List cacheItemConfigs= Lists.newArrayList(productCacheItemConfig);
CustomizedRedisCacheManager cacheManager = new CustomizedRedisCacheManager(connectionFactory,redisTemplate,cacheItemConfigs);
return cacheManager;
} 解决并发刷新缓存的问题
CustomizedRedisCache的get方法,当判断需要刷新缓存时,后台起了一个异步任务去更新缓存,此时如果有N个请求同时访问同一个缓存,就是发生类似缓存击穿的情况。为了避免这种情况的发生最好的方法就是加锁,让其只有一个任务去做更新的事情。Spring Cache提供了一个同步的参数来支持并发更新控制,这里我们可以模仿这个思路来处理。
- 将正在进行缓存刷新的KEY放入一个容器,其它线程访问时如果发现KEY已经存在就直接跳过;
- 缓存刷新完成后从容器中删除对应的KEY
- 在容器中未发现正在进行缓存刷新的KEY时,利用锁机制确保只有一个任务执行刷新,类似双重检查
public ValueWrapper get(final Object key) {
ValueWrapper valueWrapper= super.get(key);
if(null!=valueWrapper){
CacheItemConfig cacheItemConfig=CacheContainer.getCacheItemConfigByCacheName(key.toString());
long preLoadTimeSecond=cacheItemConfig.getPreLoadTimeSecond();
;
String cacheKey=this.createCacheKey(key);
Long ttl= this.redisOperations.getExpire(cacheKey);
if(null!=ttl&& ttl<=preLoadTimeSecond){
logger.info("key:{} ttl:{} preloadSecondTime:{}",cacheKey,ttl,preLoadTimeSecond);
if(ThreadTaskHelper.hasRunningRefreshCacheTask(cacheKey)){
logger.info("do not need to refresh");
}
else {
ThreadTaskHelper.run(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
REFRESH_CACKE_LOCK.lock();
if(ThreadTaskHelper.hasRunningRefreshCacheTask(cacheKey)){
logger.info("do not need to refresh");
}
else {
logger.info("refresh key:{}", cacheKey);
CustomizedRedisCache.this.getCacheSupport().refreshCacheByKey(CustomizedRedisCache.super.getName(), key.toString());
ThreadTaskHelper.removeRefreshCacheTask(cacheKey);
}
}
finally {
REFRESH_CACKE_LOCK.unlock();
}
}
});
}
}
}
return valueWrapper;
}以上方案是在单机情况下,如果是多机也会出现执行多次刷新,但这种代码是可接受的,如果做到严格意义的一次刷新就需要引入分布式锁,但同时会带来系统复杂度以及性能消耗,有点得不尝失的感觉,所以建议单机方式即可。
客户端配置
这里不需要在缓存容器名称上动刀子了,像正规使用Cacheable注解即可。
@Cacheable(value = "Product",key ="#id")
@Override
public Product getById(Long id) {
this.logger.info("get product from db,id:{}",id);
Product product=new Product();
product.setId(id);
return product;
}本文源码
- 缓存测试项目
- 缓存组件
文中代码是依赖上述项目的,如果有不明白的可下载源码