多线程之Thread、Runnable、Callable、Future、FutureTask
一、知识基础:
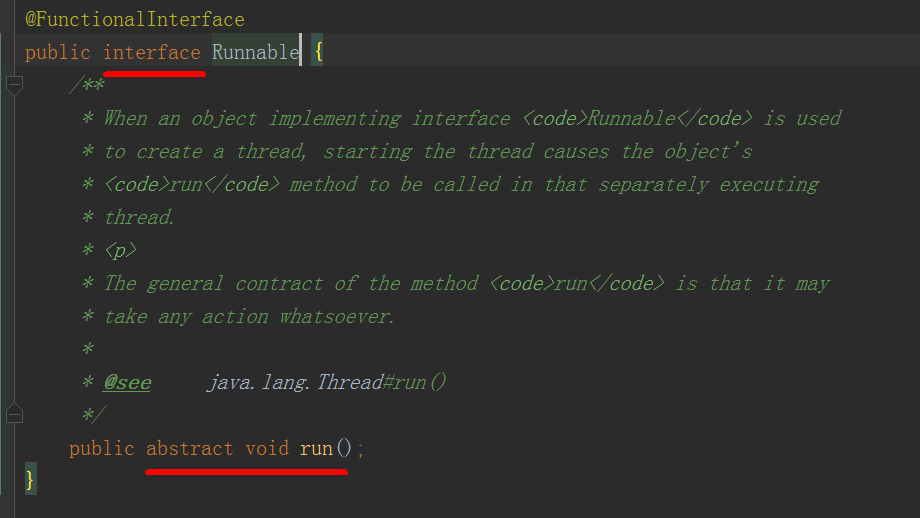
1.Thread、Runnable、Callable:都是线程
2.Thread特点:提供了线程等待(wait)、线程睡眠(sleep)、线程礼让(yield)等操作。
3.Runnable和Callable特点:都是接口,并提供对应的实现方法。
4.Runnable和Callable的区别:Runnable无返回值,Callable有返回值。
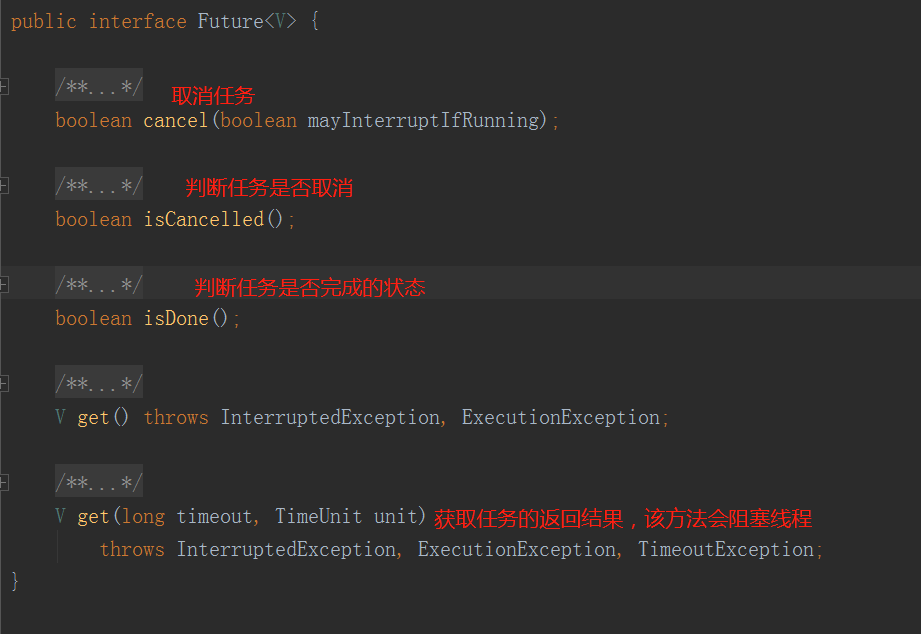
5.Future:提供了对Runnable和Callable任务的执行结果进行取消、查询是否完成、获取结果、设置结果等操作。
6.FutureTask:Runnable和Future的结合体,即拥有Future的特性。
二、Thread和Runnable的关系
线程使用有两种最常用的写法:
new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run(){
//子线程操作
}
}).start();new Thread(){
@Override
public void run(){
//子线程操作
}
}.start();三、从源码分析:
class Thread implements Runnable {
private Runnable target;
//构造函数
public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target) {
init(group, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0);
}
//继续追踪init()方法
private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize) {
Thread parent = currentThread();
if (g == null) {
g = parent.getThreadGroup();
}
g.addUnstarted();
this.group = g;
this.target = target;
this.priority = parent.getPriority();
this.daemon = parent.isDaemon();
setName(name);
init2(parent);
/* Stash the specified stack size in case the VM cares */
this.stackSize = stackSize;
tid = nextThreadID();
}
}Thread就是Runnable实现的。我们创建Thread的第一步是new Thread(),而Thread的构造函数会调用一个init方法,这个方法会传入一个Runnable参数,也就是我们的Thread其实就是Runnable。
接着会调用start方法,该方法如下:
public synchronized void start() {
if (threadStatus != 0 || started)
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
/* Notify the group that this thread is about to be started
* so that it can be added to the group's list of threads
* and the group's unstarted count can be decremented. */
group.add(this);
started = false;
try {
//最后调用这里
nativeCreate(this, stackSize, daemon);//调底层了~
started = true; //标志位更改
} finally {
try {
if (!started) {
group.threadStartFailed(this);
}
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
/* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable then
it will be passed up the call stack */
}
}
}
所以Thread其实执行的就是一个封装了的Runnable,多了一些对于Runnable的处理而已。
四、Runnable和Callable的区别
源码分析:
可以发现,Callable是一个泛型的返回值,而Runnable没有返回值。
所以他们的区别就是,Callable会返回线程的结果,而Runnable不会。
五、Future
Future可以理解为对线程的一种管理,只是有一些方法而已。
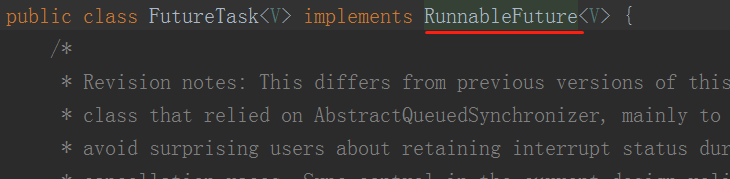
六、FutureTask
FutureTask只是Future的实现类,而且包装了Runnable、Callable,还是两者的合集。
从源码分析:
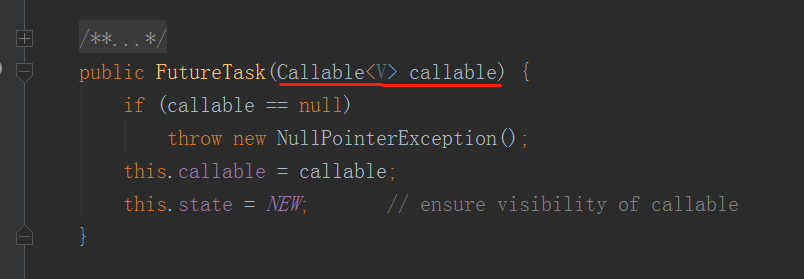
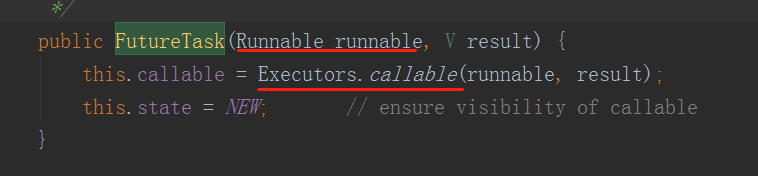
而在FutureTask的构造函数:
需要传入一个Callable对象作为参数。
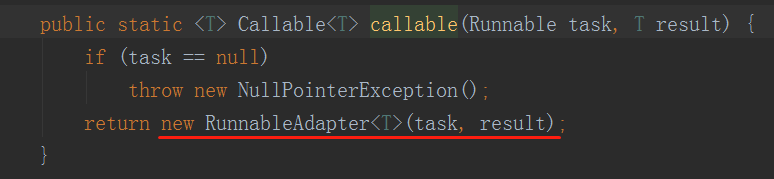
如果传入的是Runnable,则会被转化为Callable对象。
继续跟踪:
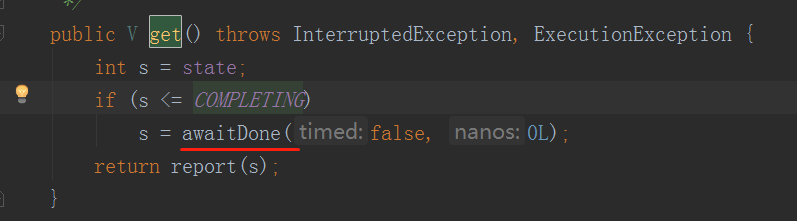
所以:FutureTask实现了Runnable,可以通过Thread来运行,也可以通过ExecuteService来运行,还可以通过get()方法获取结果。
该方法会阻塞,直到结果返回。