数据结构与算法:02 C#语言基本语法结构
02 C#语言基本语法结构
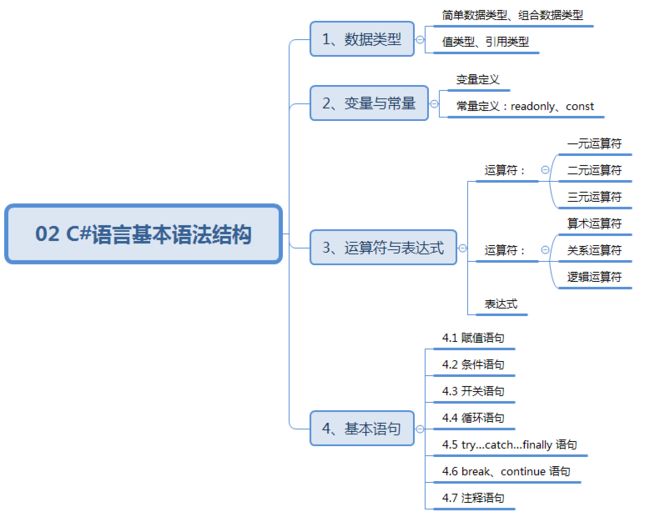
知识结构:
1、数据类型
第一种分类:
- 简单数据类型:
byte、short、int、long、float、double、char、bool - 组合数据类型:
struct、enum、class、interface
| 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| byte | 无符号8位整型 |
| (ushort) short | (无)有符号16位整型 |
| (uint) int | (无)有符号32位整型 |
| (ulong) long | (无)有符号64位整型 |
| float | 32位浮点型 |
| double | 64位浮点型 |
| char | 16位unicode字符(国际标准字符集) |
| bool | 布尔型 |
第二种分类:
- 值类型:作为参数传递时,传递拷贝。
- 包括:简单数据类型、struct类型、enum类型
- 引用类型:作为参数传递时,传递地址。
- 包括:class类型、数组
例1:
public struct Book
{
public double Price;
public string Title;
public string Author;
}
class Program
{
static void ChangeBook(Book bk)
{
bk.Price = 1.01;
bk.Title = "Spss";
bk.Author = "John";
}
static void PrintBook(Book bk)
{
Console.WriteLine("Book Infor:\n Price={0},Tile={1},Author={2}",
bk.Price, bk.Title, bk.Author);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Book bk;// = new Book();
bk.Price = 10.01;
bk.Title = "MatLab";
bk.Author = "Tom";
PrintBook(bk);
ChangeBook(bk);
PrintBook(bk);
//Book Infor:
//Price=10.01,Tile=MatLab,Author=Tom
//Book Infor:
//Price=10.01,Tile=MatLab,Author=Tom
}
}
该例子说明“值类型”传递拷贝,不改变本身所存储的值。
例2:
public class Book
{
public double Price;
public string Title;
public string Author;
}
class Program
{
static void ChangeBook(Book bk)
{
bk.Price = 1.01;
bk.Title = "Spss";
bk.Author = "John";
}
static void PrintBook(Book bk)
{
Console.WriteLine("Book Infor:\n Price={0}, Tile={1}, Author={2}",
bk.Price, bk.Title, bk.Author);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Book bk = new Book(); //错误 Book bk;
bk.Price = 10.01;
bk.Title = "MatLab";
bk.Author = "Tom";
PrintBook(bk);
// Book Infor:
// Price = 10.01, Tile = MatLab, Author = Tom
ChangeBook(bk);
PrintBook(bk);
// Book Infor:
// Price = 1.01, Tile = Spss, Author = John
}
}
例3:
class Program
{
static void ChangeArrayItem(int[] array)
{
for (int i = array.Length - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
array[i] = array.Length - 1 - i;
}
}
static void PrintArrayItem(int[] arry)
{
for (int i = 0; i < arry.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write("{0} ", arry[i]);
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] arr = new int[3];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
arr[i] = i;
}
PrintArrayItem(arr); // 0 1 2
ChangeArrayItem(arr);
PrintArrayItem(arr); // 2 1 0
}
}
例2,例3说明“引用类型”传递地址,要改变本身所存储的值。具体应用时,要注意“值类型”和“引用类型”的区别。
2、变量与常量
- 变量定义:
变量类型 变量名; - 常量定义:
readonly在声明或构造函数中初始化const在声明时初始化
例4:
public class SimpleClass
{
public int X;
public readonly int Y = 2;
public readonly int Z;
public const double Pi = 3.1415926;
public const string Etc = "...";
public SimpleClass()
{
Z = 3;
}
public SimpleClass(int p1, int p2, int p3)
{
X = p1;
Y = p2;
Z = p3;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
SimpleClass sp1 = new SimpleClass();
sp1.X = 1;
Console.WriteLine("sp1:x={0}, y={1}, z={2}", sp1.X, sp1.Y, sp1.Z);
// sp1: x = 1, y = 2, z = 3
SimpleClass sp2 = new SimpleClass(-1, -2, -3);
Console.WriteLine("sp2:x={0} ,y={1}, z={2}", sp2.X, sp2.Y, sp2.Z);
// sp2: x = -1 ,y = -2, z = -3
Console.WriteLine("PI={0}{1}", SimpleClass.Pi, SimpleClass.Etc);
// PI = 3.1415926...
}
}
以上例子注意readonly与const定义常量以及使用该常量时的区别。
3、运算符与表达式
运算符:
- 一元运算符
x++,y++ - 二元运算符
x+y,x-y - 三元运算符
max = (x>y)?x:y;
运算符:
- 算术运算符
+、-、*、/、% - 关系运算符
>、>=、==、!=、<=、< - 逻辑运算符
!、&&、||
表达式:由运算符和变量或常量组成的式子。
4、基本语句
4.1 赋值语句
变量名 = 表达式;
4.2 条件语句
第一种:
if(条件表达式)
{
语句序列;
}
第二种:
if(条件表达式)
{
语句序列;
}
else
{
语句序列;
}
第三种:
if(条件表达式1)
{
语句序列1;
}
else if(条件表达式2)
{
语句序列2;
}
else if(条件表达式N)
{
语句序列N;
}
else
{
语句序列N+1;
}
4.3 开关语句
swith(表达式)
{
case 值1:语句序列1; break;
case 值2:语句序列2; break;
case 值N:语句序列N; break;
default:语句序列N+1; break;
}
例5:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Random rdm = new Random();
int i = rdm.Next(1, 5);
Console.WriteLine(i); // 1
switch (i)
{
case 1:
Console.WriteLine("Case 1.");
break;
case 2:
Console.WriteLine("Case 2.");
break;
case 3:
Console.WriteLine("Case 3.");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("Default Case.");
break;
}
// Case 1.
i = rdm.Next(1, 5);// 1
Console.WriteLine(i);
switch (i)
{
case 1:
case 2:
case 3:
Console.WriteLine("It's 1,2 or 3.");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("Not Sure What it is.");
break;
}
//It's 1,2 or 3.
}
}
以上例子注意switch语句的语法结构,特别是每个case语句都需要匹配break语句。
4.4 循环语句
第一种:
for(初始化循环计数器表达式;判断循环终止条件;递增或递减循环计数器表达式)
{
语句序列;
}
第二种:
while(条件表达式)
{
语句序列;
}
第三种:
do
{
语句序列
}while(条件表达式);
第四种:
foreach(元素类型 元素 in 集合)
{
语句序列;//通常用于遍历集合中的每个元素
}
例6:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int i;
int sum = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
sum += i;
}
Console.WriteLine(sum);// 55
sum = 0;
i = 1;
while (i <= 10)
{
sum += i;
i++;
}
Console.WriteLine(sum);// 55
sum = 0;
i = 1;
do
{
sum += i;
i++;
} while (i <= 10);
Console.WriteLine(sum);// 55
}
}
例7:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] arry = new int[] {
1, 3, 5, 7 };
foreach (int i in arry)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
// 1
// 3
// 5
// 7
}
}
4.5 try…catch…finally 语句
try
{
语句序列;
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
语句序列;
}
finally
{
语句序列;
}
例8:在屏幕上输入一个整数,则屏幕上显示该整数颗“*”号。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("请输入一个整数:");
// 请输入一个整数:
// abc
string sTemp = Console.ReadLine();
try
{
int iCount = int.Parse(sTemp);
for (int i = 0; i < iCount; i++)
{
Console.Write("*");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("错误原因为:" + ex.Message);
// 错误原因为:输入字符串的格式不正确。
}
finally
{
Console.WriteLine("结束.");
// 结束.
}
}
}
以上例子注意try…catch…finally语句的语法结构,该语句通常用来捕获并处理异常。
4.6 break、continue 语句
break语句:跳出最里面的封闭循环或switch语句中continue语句:将控制权传递给所在封闭循环的下一次迭代
例9:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
{
if (i == 5)
break;
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
// 1
// 2
// 3
// 4
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
{
if (i < 99)
continue;
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
// 99
// 100
}
}
4.7 注释语句
- 单行注释:
//文字序列 - 多行注释:
/*文字序列*/
后台回复「搜搜搜」,随机获取电子资源!
欢迎关注,请扫描二维码:
![]()
![]()
![]()