spring IOC源码学习(一):资源定位过程,类加载器的使用
1、spring IOC类加载器在载入
spring资源定位过程中,通过前面一系列的调用,到达DefaultResourceLoader类。
public class DefaultResourceLoader implements ResourceLoader {
private ClassLoader classLoader;
public DefaultResourceLoader() {
this.classLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
}
public DefaultResourceLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.classLoader = classLoader;
}
public void setClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.classLoader = classLoader;
}
@Override
public ClassLoader getClassLoader() {
return (this.classLoader != null ? this.classLoader : ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
@Override
public Resource getResource(String location) {
Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null");
if (location.startsWith("/")) {
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
else if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader());
}
else {
try {
// Try to parse the location as a URL...
URL url = new URL(location);
return new UrlResource(url);
}
catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
// No URL -> resolve as resource path.
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
}
}
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
return new ClassPathContextResource(path, getClassLoader());
}
protected static class ClassPathContextResource extends ClassPathResource implements ContextResource {
public ClassPathContextResource(String path, ClassLoader classLoader) {
super(path, classLoader);
}
@Override
public String getPathWithinContext() {
return getPath();
}
@Override
public Resource createRelative(String relativePath) {
String pathToUse = StringUtils.applyRelativePath(getPath(), relativePath);
return new ClassPathContextResource(pathToUse, getClassLoader());
}
}
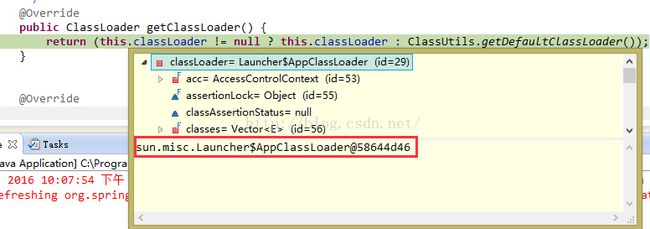
}首先调用getResourcePath方法,返回定位的资源。
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
return new ClassPathContextResource(path, getClassLoader());
} public ClassLoader getClassLoader() {
return (this.classLoader != null ? this.classLoader : ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}调试模式,可看到classLoader不为null,表示类加载器存在。在类加载器双亲委派模型中(可看本文后面的双亲委派模型介绍),应用程序加载器的定义是:这个类加载器由sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader加载实现。spring的类加载器的类型为“”应用程序加载器“”怎么看出来的呢。下图:
这个类加载器是什么时候设置的呢?看DefaultResourceLoader的无参构造函数,在类初始化时设置的。
public DefaultResourceLoader() {
this.classLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
}可以进一步查看类加载器的生成。进入ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader()方法如下。
public static ClassLoader getDefaultClassLoader() {
ClassLoader cl = null;
try {
cl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Cannot access thread context ClassLoader - falling back...
}
if (cl == null) {
// No thread context class loader -> use class loader of this class.
cl = ClassUtils.class.getClassLoader();
if (cl == null) {
// getClassLoader() returning null indicates the bootstrap ClassLoader
try {
cl = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Cannot access system ClassLoader - oh well, maybe the caller can live with null...
}
}
}
return cl;
}Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();表示当前线程的类加载器——应用程序类加载器
ClassUtils.class.getClassLoader()当前类的加载器——扩展类加载器
ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader()系统初始化的类加载器——启动类加载器
2、 双亲委派模型介绍(摘自《深入理解java虚拟机》虚拟机类加载机制)
类加载器的双亲委派模型,如下图所示,双亲委派模型要求除了顶层的启动类加载器外,其余的类加载器都应当有自己的父类加载器。这里类加载器之间的父子关系一般不会以继承的关系来实现,而是都使用组合关系来复用父加载器。spring中提供的方法 getDefaultClassLoader()就是使用组合关系来复用父类加载器。
双亲委派模型的工作过程是:如果一个类加载器收到了类加载请求,它首先不会自己去尝试加载这个类,而是把这个请求委派给父类加载器去完成,每一个层次的类加载器都是如此,因此所有的加载请求都应该传送到顶层的启动类加载器中,只有当父加载器反馈自己无法完成这个加载请求(它的搜索范围中没有找到所需的类)时,子加载器才会尝试自己去加载。
从java虚拟机的角度讲,只存在两种不同的类加载器:一种是启动类加载器(Bootstrap ClassLoader),由C++实现,另一种就是所有其它的加载器,是由java实现的,独立于虚拟机外部,并且全都继承自java.lang.ClassLoader。
从java开发人员来讲,类加载器还可以划分的更细致一些:
1、 启动类加载器(Bootstrap ClassLoader):这个类加载器负责将存放在
2、 扩展类加载器(Extension ClassLoader):这个加载器由sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader实现,它负责加载
3、 应用程序类加载器(Application ClassLoader):这个类加载器由sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader实现。由于这个类加载器是ClassLoader中的getSystemClassLoader()方法的返回值,所以一般也称它为系统类加载器,它负责加载用户类路径(classpath)上指定的类库,开发者可以直接使用这个类加载器,如果应用程序中没有自定义过自己的类加载器,一般情况下这个就是程序中的默认类加载器。