JDK1.8 源码 java.util.LinkedList
前言
今天我们来看下java.util.LinkedMap.
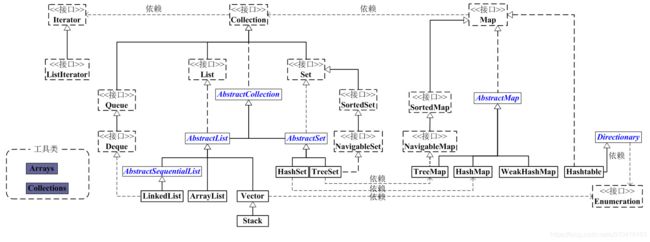
从上图可以看出. LinkedList和ArrayList同属List <-AbstractList流程下的不同实现.
此外, 因为链表的关系, LinkedList主要有2层继承关系.
Collection <-- List <-- AbstractList <-- AbstractSequentialList. 此为第一段继承关系.Collection <-- Queue <- Deque <-- LinkedList. 此为第二段继承关系.
正文
成员变量&方法
- 主要成员变量
transient int size = 0;
transient Node first;
transient Node last;
由于LinkedList是用链表进行实现. 所以, 其成员变量多于链表数据结构相关. Node头指针, Node 尾指针, size长度.
private static class Node {
E item;
Node next;
Node prev;
Node(Node prev, E element, Node next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
局部类Node, 可以看出, 实现是一个双向链表.
- 主要方法
- 构造函数
public LinkedList()/public LinkedList(Collection c) - 增
public boolean add(E e)/public boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) - 删
public E remove(int index)/public boolean remove(Object o) - 查
public E get(int index) - 查下标
public int indexOf(Object o)/public int lastIndexOf(Object o) - 改
public E set(int index, E element)
- 构造函数
- 对于头尾节点操作
- 增
public void addFirst(E e)/public void addLast(E e) - 删
public E removeFirst()/public E removeLast() - 查
public E getFirst()/public E getLast()
- 增
- 队列接口相关操作
public E peek()/public E peekFirst()/public E peekLast()public E poll()/public E pollFirst()/public E pollLast()public void push(E e)public E pop()
- 其余方法
toArray()clone()toString()equals()compareTo()writeObject/readObject()序列化&反序列化
类型声明
public class LinkedList
extends AbstractSequentialList
implements List, Deque, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
其中 LinkedList <-- AbstractSequentialList <-- AbstractList <-- List <-- Collection. 在上章已经讲过. 这章只记录下继承关系.
public abstract class AbstractSequentialList extends AbstractList {
public abstract class AbstractList extends AbstractCollection implements List {
public abstract class AbstractCollection implements Collection {
其中 Cloneable和Serializable分别是拷贝和序列化接口.
public interface Deque extends Queue {
void addFirst(E e);
void addLast(E e);
boolean offerFirst(E e);
boolean offerLast(E e);
E removeFirst();
E removeLast();
E pollFirst();
E pollLast();
E getFirst();
E getLast();
E peekFirst();
E peekLast();
boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o);
boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o);
boolean add(E e);
boolean offer(E e);
E remove();
E poll();
E element();
E peek();
void push(E e);
E pop();
boolean remove(Object o);
boolean contains(Object o);
public int size();
Iterator iterator();
Iterator descendingIterator();
}
- Queue 接口
public interface Queue extends Collection {
boolean add(E e);
boolean offer(E e);
E remove();
E poll();
E element();
E peek();
}
构造函数
- 空构造函数
public LinkedList() {
}
- 含参构造函数
// 将Collection对象放入List内
public LinkedList(Collection c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
public boolean addAll(Collection c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
// 转换为数组
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Node pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
// index是开始位置 index是指向的链表尾部
// 从尾部插入
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
// 非从尾部进行插入
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
// 链表队尾收尾操作
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
- 增 - 队尾增加元素
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node l = last;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
- 删除
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
E unlink(Node x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node next = x.next;
final Node prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
删除方法. 因为是双向链表. 所以略微繁琐一点, unlink()方法的逻辑:
- 节点前节点. 节点当前节点. 节点后节点.
- 节点前节点.next = 节点后节点 .
- 节点后节点.head = 节点前节点.
查
public E get(int index)
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
Node node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
这边有一个节点的优化. 判断index是偏向头还是尾巴. 为了搜索的速率更快一点.
- 改
public E set(int index, E element) {
checkElementIndex(index);
Node x = node(index);
E oldVal = x.item;
x.item = element;
return oldVal;
}
直接修改节点的值. 也就是node.item. 返回旧的数据oldVal.
Dequeue接口相关操作
增
- 增
public void addFirst(E e)/public void addLast(E e)
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
删
- 删
public E removeFirst()/public E removeLast()
public E removeFirst() {
final Node f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
public E removeLast() {
final Node l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
其中unlinkFirst()和unLinklast()都是前面unlink()方法的变种方法. 这边不在赘述.
查
- 查
public E getFirst()/public E getLast()
public E getFirst() {
final Node f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
public E getLast() {
final Node l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
- ToArray()
public Object[] toArray() {
Object[] result = new Object[size];
int i = 0;
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
result[i++] = x.item;
return result;
}
LinkedList的toArray()返回的是一个Object[].
Others
- for循环和迭代器循环 效率问题?
Q
Q1: 什么是Dqueue?
Q2: LinkedList的实现原理是什么? 具有什么优势?
链表. 增删快, 查询慢.
Q3: 链表如何增删节点?
Reference
[1]. JDK1.8源码(六)——java.util.LinkedList 类