【JDK专题】——JDK数据结构——HashMap源码剖析(系列)
本篇文章没有过多介绍二进制运算、求模运算、哈希图,将到下一篇HashMap源码剖析(补充)中叙说
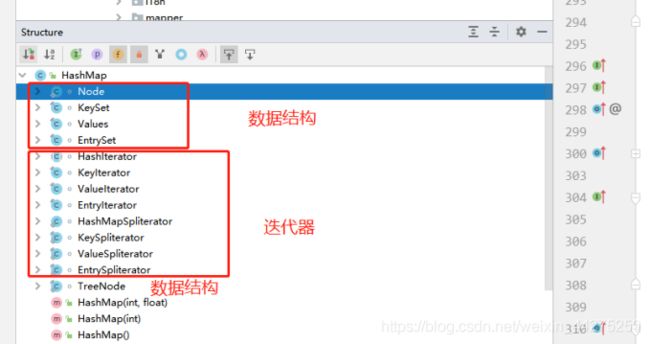
HashMap内部的类
HashMap静态常量
public class HashMap{
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // 默认容量;默认初始化的容量时16,必须是2的幂次方。
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;//最大容量,最大的容量是2^30
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;//默认负载因子,0.75就扩容
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;//链表变红黑树的阈值
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;//红黑树退回链表的阀值:
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;//最小红黑树的容量
}```
## HashMap关键数据
```java
public class HashMap{
transient Node<K,V>[] table;//table是一个用于存放键值对的数组,核心所在;第一次使用(插入元素)时被初始化,根据需要可以重新分配空间
transient int size;//该值用于存放Map中键值对的个数
transient int modCount;//HashMap被结构性修改的次数,用于判断是否发送了修改
int threshold;//thresold = capacity * loadFactor;;当HashMap中的键值对数量超过了阈值,就会扩容
final float loadFactor;//负载因子,上面的
}
HashMap核心源码
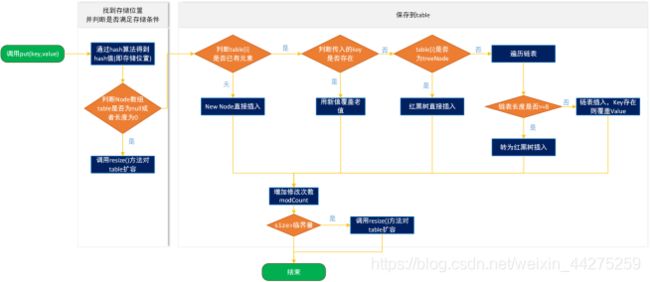
hashMap的本质:每一个元素的put的时候,所带的key利用哈希算法算出一个值,就是就是key决定映射出value的内存地址,这个值作为下标然后找到对应的数组位置存储我们的数据value,取出来也是一样的;哈希算法可以保证数据的散列性,就是保证不同对象或者值算出来的hashcode是不一样的,但是也会有冲突,晚一点我们讲hashcode是如何避免这一类的冲突
数组作为底层数据结构的原因: hashMap的本质实际上是一个数组,数组的优点在于空间连续分布易于管理;因此将数组作为hashMap的数据存储地是高性能的;这也是为什么选择数组作为底层数据结构的原因,那么带来的一个问题就是我们如何将key跟数组的下标进行关联,然后存储我们的value,那就是哈希算法;
hashcode值:默认由native方法实现,java帮我们是实现的这个值可以保证不同对象不一样
public class Object {
public native int hashCode();
}
插入:
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; //表的指针
Node<K,V> p; //存储与key可能相关的节点的数据指针
int n, i;//n:与数组长度的相关变量;i:存储与key可能相关的节点的下标
/**
* @初始化,hashMap默认是空的,put的是创建表
* 有可能put的时候初始化没未完成
*/
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
/**
* @p节点是空
* 则创建一个节点普通的节点
*/
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;//e指针是相邻节点的历史引用,k指针是key的引用
/**
* @如果哈希相等且key也相等直接替换节点
*/
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
/**
* @p节点是红黑树
*/
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
/**
* @p节点是普通节点,则进行链表操作
* 进行一个有自增变量。但没有终点的遍历,由break决定
* 每次不遍历不断更新p指针
* 注意代码如果来到这里,则最少链表有2个节点
*/
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
/**
* @链表的末尾插入元素
* 先进行e指针的的更新
* 如果下一个是空,证明是链表末端直接添加元素;此时e指针是null不参与外包的值更新
*/
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // 红黑树构建触发
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
/**
* @链表中找到了已经创建过的元素
* 如果不是null值判断哈希和key是否一致,然后证明在链表中
*/
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
/**
* 还没找到符合条件的,更新p指针继续向后推演
*/
p = e;
}
}
/**
* @将找到的e指针的值才这里单独进行value更新
*/
if (e != null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);//生命周期方法,空实现
return oldValue;
}
}
/**
* 每次添加后,检查是否需要扩容
*/
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);//生命周期方法,空实现
return null;
}
获取:
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
/**
* @如果第一个刚好哈希一致
* 则直接作为元素返回
*/
if (first.hash == hash &&
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
/**
* @红黑树获取法
*/
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
/**
* @链表获取法
* node中对比key相等的,注意不是hash链表中所有哈希都一致;
*/
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
删除:
先查找,后删除,然后返回
final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,
boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v;
/**
* 第一个是吗,直接查到
*/
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
node = p;
else if ((e = p.next) != null) {
/**
* @红黑树查找
*/
if (p instanceof TreeNode)
node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key);
/**
* @链表查找
*/
else {
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key ||
(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
node = e;
break;
}
p = e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
/**
* @执行删除操作,链表需要进行接轨处理
*/
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))) {
if (node instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable);
else if (node == p)
tab[index] = node.next;
else
p.next = node.next;
++modCount;
--size;
afterNodeRemoval(node);
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
HashMap哈希算法
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
Ps:很明显put的方法对key值又做了一次哈希处理;hashcode已经由native帮我们生成,但是为什么不直接用这个取余求下标呢
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(7));
/**
* %:转化成int再求模效率低;
* &:直接在内存中对二进制操作;效率高
* 【2的次放求模定理】
* a%2^n=(2^n-1)&a
* Ps:利用&效率最高,所以hashMap中求模用这个符号
*/
System.out.println(1005611%8);
System.out.println((8-1)&(10056011));
System.out.println((8-1)&(10056011)==1005611%8);//true
/**
* @【2^n-1次方的二进制特征】
* 很显然数组长度2^n时,&具备2^n-1的二进制特征
* 则即可(1)的把数字限制在数组长度内
* 又可以(2)因为长度内全是1的缘故,可以哈希后直接截取结果的长度位数,让结果均匀
* &操作符号效率也高
* 所以我们将数组的长度定位2^n
*/
System.out.println( Integer.toBinaryString((int)Math.pow(2,1)-1));
System.out.println( Integer.toBinaryString((int)Math.pow(2,2)-1));
System.out.println( Integer.toBinaryString((int)Math.pow(2,3)-1));
System.out.println( Integer.toBinaryString((int)Math.pow(2,4)-1));
System.out.println( Integer.toBinaryString((int)Math.pow(2,5)-1));
System.out.println( Integer.toBinaryString((int)Math.pow(2,6)-1));
System.out.println( Integer.toBinaryString((int)Math.pow(2,7)-1));
System.out.println( Integer.toBinaryString((int)Math.pow(2,8)-1));
System.out.println( Integer.toBinaryString((int)Math.pow(2,9)-1));
System.out.println( Integer.toBinaryString((int)Math.pow(2,10)-1));
System.out.println( Integer.toBinaryString((int)Math.pow(2,11)-1));
System.out.println( Integer.toBinaryString((int)Math.pow(2,12)-1));
System.out.println( Integer.toBinaryString((int)Math.pow(2,13)-1));
System.out.println( Integer.toBinaryString((int)Math.pow(2,14)-1));
System.out.println( Integer.toBinaryString((int)Math.pow(2,15)-1));
System.out.println( Integer.toBinaryString((int)Math.pow(2,16)-1));
/**
* 0b00000000000000000000000000000001;
* 0b00000000000000000000000000000011;
* 0b00000000000000000000000000000111;
* 0b00000000000000000000000000001111;
* 0b00000000000000000000000000011111;
* 0b00000000000000000000000000111111;
* 0b00000000000000000000000001111111;
* 0b00000000000000000000000011111111;
* 0b00000000000000000000000111111111;
* 0b00000000000000000000001111111111;
* 0b00000000000000000000011111111111;
* 0b00000000000000000000111111111111;
* 0b00000000000000000001111111111111;
* 0b00000000000000000011111111111111;
* 0b00000000000000000111111111111111;
* 0b00000000000000001111111111111111;
*/
}
}
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* @【高位丢失现象】
* 假设数组长度的是8,数组基数要减一
* 7的二进制是 :0b00000000000000000000000000000111
* hashcode二进制是:0b11111111010101011111111100011111
* 进行如下与运算:0b00000000000000000000000000000111&0b11111111010101011111111100011111=000000000100
* Ps:很明显与运算中哈希的特征高位部分全被0砍掉了根本没参与运算,然而大多数情况数组长度是很小的,所以回经常导致这个状况
*/
int hashcode =0b11111111010101011111111100011111;
int tableLength=0b00000000000000000000000000000111;
int index;
index=hashcode&tableLength;
System.out.println("index-result-byte:"+Integer.toBinaryString(index));
System.out.println("idnex-result-value:"+index);
}
}
Hash算法奥秘(2):
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* @【高位特征映射】
* 由于经常数组长度很小,所以高16位经常被&屏蔽掉;我们就得想办法让高16位特征混合倒低16位,高16位自己保持不变
* 经过数学理论验证,异或符号^是最佳选择; 异或运算能更好的保留各部分的特征,如果采用&运算计算出来的值会向0靠拢,采用|运算计算出来的值会向1靠拢
* hashcode是一个32位的数字,因为经常数组容量是很小的,所以我们取高位变成低16位 highCode=allcode>>>16
* 混合:allcode^highCode=allcode^allcode>>>16
* 用allcode的好处是,低位混合高位,高位也仍然存在
*/
int index;
int newHashCode;
int hashcode =0b11111111010101011111111100011111;
int tableLength=0b00000000000000000000000000000111;
int highHashCode=hashcode>>>16;
/**
* @(1)结果非常明显,高位用异或保留的原来的特征;但是低位混合了高位的特征
*/
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(highHashCode));
newHashCode=hashcode^highHashCode;
System.out.println("HighCode-byte:"+Integer.toBinaryString(highHashCode));
System.out.println("HashCode-byte:"+Integer.toBinaryString(hashcode));
System.out.println("newHashCode-byte:"+Integer.toBinaryString(newHashCode));
System.out.println("tableLength-byte:"+Integer.toBinaryString(tableLength));
/**
* @(2)利用新的哈希求出index值
*/
index=tableLength&newHashCode;
System.out.println("index-byte:"+Integer.toBinaryString(index));
System.out.println("index-value:"+index);
}
}
HashMap扩容机制(预备)
(1)对象的hash值不受到扩容的影响
需要数组容量无关,但是映射到的位置跟数组容量相关
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
(2)链表中所有哈希值一致,扩容后仍然是同一个链表不会拆分——————所以我们需要改头节点的位置即可
public class Test01 {
static class Node{
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return 10;
}
}
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sizeOne=(int)Math.pow(2,1)-1;
int sizeTwo=(int)Math.pow(2,2)-1;
int sizeThree=(int)Math.pow(2,3)-1;
int sizeFour=(int)Math.pow(2,4)-1;
int sizeFive=(int)Math.pow(2,5)-1;
/*
@模拟多个链表中node同一个hachcode
*/
Node node1 = new Node();
Node node2 = new Node();
Node node3 = new Node();
System.out.println("容量基数是:"+sizeOne+";node1索引的位置计算:"+String.valueOf(sizeOne & hash(node1)));
System.out.println("容量基数是:"+sizeOne+";node2索引的位置计算:"+String.valueOf(sizeOne & hash(node2)));
System.out.println("容量基数是:"+sizeOne+";node3索引的位置计算:"+String.valueOf(sizeOne & hash(node3)));
System.out.println("容量基数是:"+sizeTwo+";node1索引的位置计算:"+String.valueOf(sizeTwo & hash(node1)));
System.out.println("容量基数是:"+sizeTwo+";node2索引的位置计算:"+String.valueOf(sizeTwo & hash(node2)));
System.out.println("容量基数是:"+sizeTwo+";node3索引的位置计算:"+String.valueOf(sizeTwo & hash(node3)));
System.out.println("容量基数是:"+sizeThree+";node1索引的位置计算:"+String.valueOf(sizeThree & hash(node1)));
System.out.println("容量基数是:"+sizeThree+";node2索引的位置计算:"+String.valueOf(sizeThree & hash(node2)));
System.out.println("容量基数是:"+sizeThree+";node3索引的位置计算:"+String.valueOf(sizeThree & hash(node3)));
System.out.println("容量基数是:"+sizeFour+";node1索引的位置计算:"+String.valueOf(sizeFour & hash(node1)));
System.out.println("容量基数是:"+sizeFour+";node2索引的位置计算:"+String.valueOf(sizeFour & hash(node2)));
System.out.println("容量基数是:"+sizeFour+";node3索引的位置计算:"+String.valueOf(sizeFour & hash(node3)));
System.out.println("容量基数是:"+sizeFive+";node1索引的位置计算:"+String.valueOf(sizeFive & hash(node1)));
System.out.println("容量基数是:"+sizeFive+";node2索引的位置计算:"+String.valueOf(sizeFive & hash(node2)));
System.out.println("容量基数是:"+sizeFive+";node3索引的位置计算:"+String.valueOf(sizeFive & hash(node3)));
}
}
hashcode分子1/数组分母
hashcode分子2/数组分母
hashcode分子3/数组分母
hashcode分子4/数组分母
hashcode分子5/数组分母
如果hashcode分子1=hashcode分子2=hashcode分子3=hashcode分子4 那么无论数组分母是多少
hashcode分子1/数组分母=hashcode分子2/数组分母=hashcode分子3/数组分母=hashcode分子4/数组分母=hashcode分子5/数组分母
除了求模后的比例会变 但是比例仍然是相等 所有链表仍然映射在同一个索引 只是可能索引的值发生了改变
(3)2的公倍数特性
上述实验证明,
原容量是偶次方倍 则加一倍后计算出来的值一致
原容量是奇次方倍 则加一倍后计算出来的值需要加上原来容量才一致
HashMap扩容机制(1.8)
HashMap扩容的时候,是扩充为原来的两倍,因此这种机制可以很方便扩容时的索引不变以及移位计算;
final Node<K, V>[] resize() {
/**
* @利用指针保存历史数据
* 以便于扩容的时候可以用好2^n的优点
*/
Node<K, V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
/**
* @步骤1:旧数组不为空
*/
if (oldCap > 0) {
// 步骤1.1:临界值更新(如果旧数组长度大于等于最大容量)
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
// 步骤1.2:双倍扩容更新(如果旧数组容量大于默认容量且右移一位小于最大容量)
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
/**
* @步骤2.如果旧数组为空,但有临界值大于0,设置新数组容量为临界值
*/
else if (oldThr > 0)
newCap = oldThr;
/**
* @步骤3.如果旧数组为空,且没有临界值小于等于0,设置容量与临界值为默认值
*/
else {
// zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int) (DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
/**
* @步骤4:如果新数组临界值为0,设置临界值
*/
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float) newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float) MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int) ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({
"rawtypes", "unchecked"})
/**
* @步骤5:创建新数组
*/
Node<K, V>[] newTab = (Node<K, V>[]) new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
/**
* @步骤6:如果旧数组不为空,遍历旧数组将结点平移至新数组
*/
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K, V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
/**
* @单节点的扩容,直接计算新的容量
*/
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
/**
* @红黑树的扩容,用于红黑树内部封装好的方法
*/
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K, V>) e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
/**
* @链表的扩容
* 如果刚进入时,e就是链表的头
*/
else {
/**
* @loHead:原链表头结点;loTail:原链表尾节点
* @hiHead:新链表头节点;hiTail:新链表尾节点
* @next:链表中每次元素的指针
*/
Node<K, V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K, V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K, V> next;
/**
* 通过链表遍历分别标记两种链表
* (1)被key hash之后2整除的链表 loHead
* (2)被key hash之后2不整除的链表 hiHead
* 通过链表把尾指针也找出来
*/
do {
next = e.next;
/*
【遍历链表处理连接】
注意以下if else在一个链表中只会出现一种情况,因为链表中所有哈希是一致的,所以取模2也是一致的
*/
/**
* 情况(1)hash取2的模是0
* 数学特性:如果旧数组哈希求模是0,则扩容后索引下表不变;2的公倍数特性
*/
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;//链表头赋值
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
/**
* 情况(2)hash取2的模不是0
*/
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);//直到链表遍历成
/**
* 以下两个一个链表只会出现一个通过
*/
/**
* 情况(1)hash取2的模是0
* 数学特性:如果旧数组哈希求模是0,则扩容后新链表头索引的位置索引下表不变;
*/
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;//之前设置尾部的next是e,这里处理一下
newTab[j] = loHead;//头索引进入数组
}
/**
* 情况(2)hash取2的模不是0
* 数学特性:由于扩容了一倍,代表不能被整除,所以直接再上旧容量就能算出新链表头索引的位置
*/
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;//之前设置尾部的next是e,这里处理一下
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;//头索引进入数组
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
HashMap扩容机制(1.7)
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
//判断是否有超出扩容的最大值,如果达到最大值则不进行扩容操作
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
/*
外部 已经扩大了的数字传进来了
*/
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
/*
接下来只需要迁移指针即可
*/
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
//设置hashmap扩容后为新的数组引用
table = newTable;
//设置hashmap扩容新的阈值
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}
transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
/*
遍历数组的每个元素
*/
for (Entry<K,V> e : table) {
while(null != e) {
//如果是链表的话,next会不断赋值给e
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
/*
重新计算当前e的下标位置
*/
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
/*
头插法,容易循环链表,jdk8用双向链表解决
双向处理:
当前元素下一个元素是原来数组索引的头元素
将数组索引的头元素指向当前元素,成为新的头元素
直到最后原链表的尾部成为了头节点
*/
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
/*
用于继续循环
*/
e = next;
}
}
}
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
}
GodSchool
致力于简洁的知识工程,输出高质量的知识产出,我们一起努力
博主私人微信:supperlzf