pytorch 调用 deeplabv3模型,进行识别
from torchvision import models
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
import torchvision.transforms as T
import cv2
import numpy as np
def decode_segmap(image, source, nc=21):
label_colors = np.array([(0, 0, 0),
(128, 0, 0), (0, 128, 0), (128, 128, 0), (0, 0, 128), (128, 0, 128),
(0, 128, 128), (128, 128, 128), (64, 0, 0), (192, 0, 0), (64, 128, 0),
(192, 128, 0), (64, 0, 128), (192, 0, 128), (64, 128, 128), (192, 128, 128),
(0, 64, 0), (128, 64, 0), (0, 192, 0), (128, 192, 0), (0, 64, 128)])
r = np.zeros_like(image).astype(np.uint8)
g = np.zeros_like(image).astype(np.uint8)
b = np.zeros_like(image).astype(np.uint8)
for l in range(0, nc):
idx = image == l
r[idx] = label_colors[l, 0]
g[idx] = label_colors[l, 1]
b[idx] = label_colors[l, 2]
rgb = np.stack([r, g, b], axis=2)
plt.imshow(rgb)
plt.show()
foreground = cv2.imread(source)
foreground = cv2.cvtColor(foreground, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
foreground = cv2.resize(foreground, (r.shape[1], r.shape[0]))
background = 255 * np.ones_like(rgb).astype(np.uint8)
foreground = foreground.astype(float)
background = background.astype(float)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(rgb, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
th, binary = cv2.threshold(np.array(gray), 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
mask = cv2.GaussianBlur(binary, (7, 7), 0)
alpha = cv2.cvtColor(mask, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
alpha = alpha.astype(float) / 255
plt.imshow(alpha)
plt.show()
foreground = cv2.multiply(alpha, foreground)
background = cv2.multiply(1.0 - alpha, background)
outImage = cv2.add(foreground, background)
return outImage / 255
def segment(net, path, show_orig=True):
img = Image.open(path)
if show_orig:
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
trf = T.Compose([T.ToTensor(),
T.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])
inp = trf(img).unsqueeze(0)
out = net(inp)['out']
om = torch.argmax(out.squeeze(), dim=0).detach().cpu().numpy()
rgb = decode_segmap(om, path)
plt.imshow(rgb)
plt.show()
dlab = models.segmentation.deeplabv3_resnet101(pretrained=1).eval()
segment(dlab, './car.png')
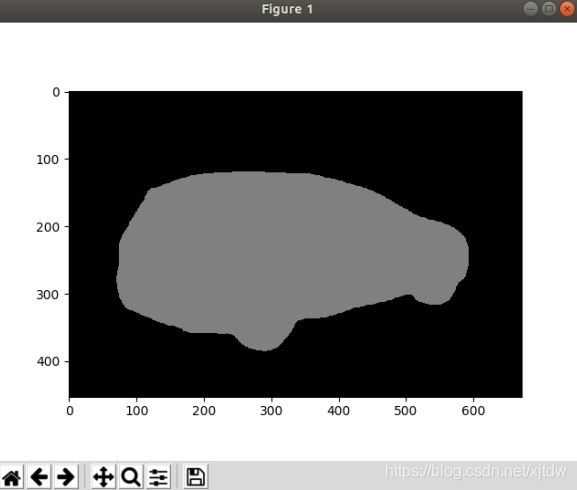
原图:

分割图: