图的最短路径算法——Floyd算法
图的最短路径算法
声明:图源 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35644234/article/details/60875818
算法代码源 https://www.jianshu.com/p/f910ce1fe7b1
本文主要是代码理解的注解以及调试。。。哇,我觉得代码写的清晰的人真的很厉害啊
Floyd算法
![]()
转自:作者:廖少少
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/f910ce1fe7b1
来源:简书
简书著作权归作者所有,任何形式的转载都请联系作者获得授权并注明出处。
import copy
#定义无穷值
inf=float("inf")
def Floyd(G):
n=len(G)
path=copy.deepcopy(G)
#vi源点,vj目的点,vk作为中间点
for k in range(0,n):
for i in range(0,n):
for j in range(0,n):
print("Comparing path[%s][%s] and {path[%s][%s]+path[%s][%s]}"%(i,j,i,k,k,j))
print("Former path[%s][%s]=%s"%(i,j,path[i][j]))
path[i][j]=min(path[i][k]+path[k][j],path[i][j])
print("Present path[%s][%s]=%s"%(i,j,path[i][j]))
return path
if __name__ == "__main__":
G=[
[inf,12,inf,inf,inf,16,14],
[12,inf,10,inf,inf,7,inf],
[inf,10,inf,3,5,6,inf],
[inf,inf,3,inf,4,inf,inf],
[inf,inf,5,4,inf,2,8],
[16,7,6,inf,2,inf,9],
[14,inf,inf,inf,8,9,inf]
]
print("---------------Floyd----------------")
path=Floyd(G)
print("Graph=")
for i in range(0,len(G)):
print((path[i]))
输出:
Graph=
[24, 12, 22, 22, 18, 16, 14]
[12, 14, 10, 13, 9, 7, 16]
[22, 10, 6, 3, 5, 6, 13]
[22, 13, 3, 6, 4, 6, 12]
[18, 9, 5, 4, 4, 2, 8]
[16, 7, 6, 6, 2, 4, 9]
[14, 16, 13, 12, 8, 9, 16]
算法描述
- 从任意一条单边路径开始。所有两点之间的距离是边的权,如果两点之间没有边相连,则权为无穷大。
- 对于每一对顶点 u 和 v,看看是否存在一个顶点 w (一般称为中间点)使得从 u 到 w 再到 v 比已知的路径更短。如果是,更新它(专业术语为:松弛)。
- 遍历直到结束,这时候存储图的数据结构就得到了多源最短路径。
Floyd 算法适用于 APSP(All Pairs Shortest Paths,多源最短路径),是一种动态规划算法,稠密图效果最佳,边权可正可负。此算法简单有效,由于三重循环结构紧凑,对于稠密图,效率要高于执行 | V | 次 Dijkstra 算法,也要高于执行 | V | 次 SPFA 算法。
- 优点:容易理解,可以算出任意两个节点之间的最短距离,代码编写简单。
- 缺点:时间复杂度比较高,不适合计算大量数据。时间复杂度 O(n 3 ^3 3),空间复杂度 O(n 2 ^2 2)
找最短路径以及全局最短路径[加入中间点k]
import copy
#定义无穷值
inf=float("inf")
def Floyd(G):
n=len(G)
path=copy.deepcopy(G)
#vi源点,vj目的点,vk作为中间点
for k in range(0,n):
for i in range(0,n):
for j in range(0,n):
print("Comparing path[%s][%s] and {path[%s][%s]+path[%s][%s]}"%(i,j,i,k,k,j))
print("Former path[%s][%s]=%s"%(i,j,path[i][j]))
path[i][j]=min(path[i][k]+path[k][j],path[i][j])
print("Present path[%s][%s]=%s"%(i,j,path[i][j]))
return path
#递归回溯找最短路径
def back_path(path,i,j,shortestpath):
#path[i][j]的结果就是中转点
print("path[%s][%s]="%(i,j),path[i][j])
#如果两个顶点邻接path[i][j]=-1
if -1 != path[i][j]:
shortestpath=back_path(path,i,path[i][j],shortestpath)
shortestpath=back_path(path,path[i][j],j,shortestpath)
if j not in shortestpath:
shortestpath.append(j)
return shortestpath
#找两点之间最短路径
def getShortestPath(graph,path,i,j):
shortestPath=[]
if graph[i][j] == float("inf") or i == j :
print("顶点 %s 不能到达 %s"%(i,j))
return shortestPath
elif path[i][j] == -1:
shortestPath.append(i)
shortestPath.append(j)
else:
shortestPath.append(i)
shortestPath=back_path(path,i,j,shortestPath)
print("顶点%s 到 顶点%s 的路径为:"%(i,j),shortestPath)
return shortestPath
#找全局最短路径
def getAllShortestPath(graph,path):
print("----------全局最短路径-----------")
ShortestPath_dict = {}
for i in range(len(graph)):
ShortestPath_dict[i] = {}
for j in range(len(graph)):
print("生成顶点%s到顶点%s的最短路径"%(i,j))
if i != j:
shortestPath=getShortestPath(graph,path,i,j)
ShortestPath_dict[i][j] = shortestPath
return ShortestPath_dict
if __name__ == "__main__":
graph=[
[inf,12,inf,inf,inf,16,14],
[12,inf,10,inf,inf,7,inf],
[inf,10,inf,3,5,6,inf],
[inf,inf,3,inf,4,inf,inf],
[inf,inf,5,4,inf,2,8],
[16,7,6,inf,2,inf,9],
[14,inf,inf,inf,8,9,inf]
]
#更新图
# print("---------------Floyd----------------")
# path=Floyd(G)
# print("Graph=")
# for i in range(0,len(G)):
# print((path[i]))
path=[]
for i in range(len(graph)):
path.append([])
for j in range(len(graph)):
#邻接
path[i].append(-1)
print("original graph:\n",graph)
#加入中间点实现Floyd算法
for k in range(len(graph)):
for i in range(len(graph)):
for j in range(len(graph)):
if graph[i][k] + graph[k][j] <graph[i][j]:
graph[i][j] = graph[i][k] + graph[k][j]
#维护最短路径列表
path[i][j] =k
print("Shortestpath Graph:\n",graph)
print("Path:\n",path)
#获取全局最短路径
print("ShortestPath_dict=\n",getAllShortestPath(graph,path))
写的太好了!!
输出
original graph:
[ [inf, 12, inf, inf, inf, 16, 14],
[12, inf, 10, inf, inf, 7, inf],
[inf, 10, inf, 3, 5, 6, inf],
[inf, inf, 3, inf, 4, inf, inf],
[inf, inf, 5, 4, inf, 2, 8],
[16, 7, 6, inf, 2, inf, 9],
[14, inf, inf, inf, 8, 9, inf]]
Shortestpath Graph:
[ [24, 12, 22, 22, 18, 16, 14],
[12, 14, 10, 13, 9, 7, 16],
[22, 10, 6, 3, 5, 6, 13],
[22, 13, 3, 6, 4, 6, 12],
[18, 9, 5, 4, 4, 2, 8],
[16, 7, 6, 6, 2, 4, 9],
[14, 16, 13, 12, 8, 9, 16]]
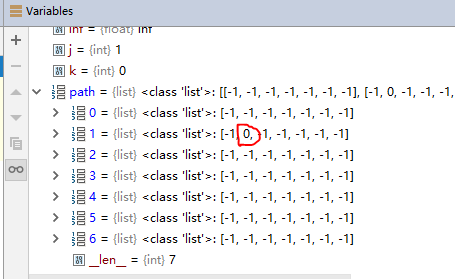
Path:
[ [1, -1, 1, 5, 5, -1, -1],
[-1, 5, -1, 2, 5, -1, 5],
[1, -1, 3, -1, -1, -1, 4],
[5, 2, -1, 2, -1, 4, 4],
[5, 5, -1, -1, 5, -1, -1],
[-1, -1, -1, 4, -1, 4, -1],
[-1, 5, 4, 4, -1, -1, 4]]
ShortestPath_dict=
{ 0: {1: [0, 1], 2: [0, 1, 2], 3: [0, 5, 4, 3], 4: [0, 5, 4], 5: [0, 5], 6: [0, 6]},
1: {0: [1, 0], 2: [1, 2], 3: [1, 2, 3], 4: [1, 5, 4], 5: [1, 5], 6: [1, 5, 6]},
2: {0: [2, 1, 0], 1: [2, 1], 3: [2, 3], 4: [2, 4], 5: [2, 5], 6: [2, 4, 6]},
3: {0: [3, 4, 5, 0], 1: [3, 2, 1], 2: [3, 2], 4: [3, 4], 5: [3, 4, 5], 6: [3, 4, 6]},
4: {0: [4, 5, 0], 1: [4, 5, 1], 2: [4, 2], 3: [4, 3], 5: [4, 5], 6: [4, 6]},
5: {0: [5, 0], 1: [5, 1], 2: [5, 2], 3: [5, 4, 3], 4: [5, 4], 6: [5, 6]},
6: {0: [6, 0], 1: [6, 5, 1], 2: [6, 4, 2], 3: [6, 4, 3], 4: [6, 4], 5: [6, 5]}}
多源最短路径!!!任意两点
过程描述:
1.读原始图
2.加入中间点实现Floyd算法
得到最短路径图ShortestPath graph
3.尝试顶点0到顶点2的最短路径
- 进入getShortestPath(graph,path,i,j),调用back_path(path,0,2,[0])
- 调用back_path(path,0,2,[0]),path[0][2]=1,需要顶点1的中转
- 再调用back_path(path,0,1,[0]),顶点0和顶点1直接邻接,不再递归,添加顶点1到最短路径shortestPath,[0,1]
- 返回上层,调用back_path(path,1,2,[0,1]),顶点1和顶点2直接邻接,添加顶点2到最短路径shortestPath,[0,1,2]
为了避免重复,加入了 if 判断,直接过滤掉重复的顶点,因为最短路径不可能绕圈子。
Debug
因为自己每次写代码都是静态检查,所以想借用这个算法学习一下python的Debug过程,观察一下程序的运行:
- 先看生成最短路径矩阵的过程
- Debug的代码段
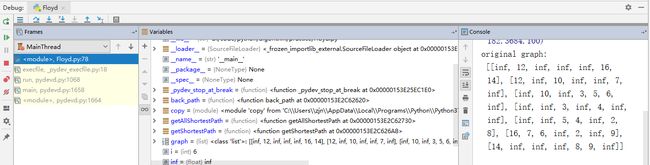
i=6,j=6,path:

- k=0,即从v1开始,作为中转点
i=0,v1,j=0,v1
graph[0][0]=inf,不成立,跳出
i=0,v1,j=1,v2
graph[0][0] +graph[0][1]=inf+12,不成立,跳出
i=0,v1,j=2,v3
graph[0][0] +graph[0][2]=inf+inf
…
包含graph[0][0]的都不成立 - i=1,v2,j=0,v1
graph[1][0]=12
graph[0][0]=inf,不成立,跳出
i=1,v2,j=1,v2
graph[1][0]=12
graph[0][1]=12
graph[1][0] +graph[0][1]=24< graph[1][1]=inf
更新path[1][1]=0,graph[1][1]=24,
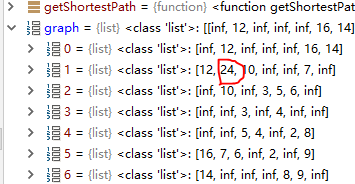
我天,debug也太好玩了吧。。。