visual studio配置 新版 ffmpeg 开发环境
1、下载编译好的ffmpeg库
https://ffmpeg.zeranoe.com/builds/
选择想使用的库的类型。
我这里使用动态库。需要下载Shared和Dev这2个
2、打开visual studio,新建任意类型的C/C++工程
3、配置工程属性
- 追加工程的头文件路径:$(Dev_DIR)/include (下载的Dev项解压出来的include文件夹)
- 追加预编译宏:__STDC_CONSTANT_MACROS和__STDC_FORMAT_MACROS
- 追加库文件路径:$(Dev_DIR)/lib (下载的Dev项解压出来的lib文件夹)
- 追加运行环境(或者添加到系统环境PATH中):$(Shared_DIR)/bin (下载的Shared项解压出来的bin文件夹。)
- 追加链接的lib文件(如果使用LoadLibrary等直接从dll中获取函数指针,可以不添加):
- avcodec.lib 用于各种类型声音/图像编解码。该库是音视频编解码核心,实现了市面上可见的绝大部分解码器的功能, libavcodec 库被其他各大解码器 ffdshow, Mplayer 等所包含或应用
- avdevice.lib 硬 件 采 集 、 加 速 、 显 示 。 操 作 计 算 机 中 常 用 的 音 视 频 捕 获 或 输 出 设 备 :ALSA,AUDIO_BEOS,JACK,OSS,1394, VFW。
- avfilter.lib :filter(FileIO、 FPS、 DrawText) 音视频滤波器的开发,如宽高比 裁剪 格式化 非格式化 伸缩。
- avformat.lib 用于各种音视频封装格式的生成和解析,包括获取解码所需信息以生成解码上下文结构和读取音视频帧等功能;音视频的格式解析协议,为 libavcodec 分析码流提供独立的音频或视频码流源。
- avutil.lib 包含一些公共的工具函数的使用库,包括算数运算 字符操作。
- postproc.lib (同步、时间计算的简单算法) 用于后期效果处理;音视频应用的后处理,如图像的去块效应。
- swresample.lib 原始音频格式转码。
- swscale.lib 原始视频格式转换) 用于视频场景比例缩放、色彩映射转换;图像颜色空间或格式转换,如 rgb565、rgb888 等与 yuv420 等之间转换。
4、可能缺失的inttypes.h 和 stdint.h
inttypes.h vs2013之后包含,vs2013之前的版本需要添加此文件到合适的目录,例如$(Dev_DIR)/include (下载的Dev项解压出来的include文件夹)(下面是可用的inttypes.h)
stdint.h vs2010之后版本包含,vs2010之前版本需要添加此文件到合适的目录,例如 $(Dev_DIR)/include (下载的Dev项解压出来的include文件夹)(下面是可用的stdint.h)
inttypes.h
// ISO C9x compliant inttypes.h for Microsoft Visual Studio
// Based on ISO/IEC 9899:TC2 Committee draft (May 6, 2005) WG14/N1124
//
// Copyright (c) 2006 Alexander Chemeris
//
// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
//
// 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice,
// this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
//
// 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
// documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
//
// 3. The name of the author may be used to endorse or promote products
// derived from this software without specific prior written permission.
//
// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE AUTHOR ``AS IS'' AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
// WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
// MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO
// EVENT SHALL THE AUTHOR BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
// PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS;
// OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY,
// WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR
// OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF
// ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
//
///
#ifndef _MSC_VER // [
#error "Use this header only with Microsoft Visual C++ compilers!"
#endif // _MSC_VER ]
#ifndef _MSC_INTTYPES_H_ // [
#define _MSC_INTTYPES_H_
#if _MSC_VER > 1000
#pragma once
#endif
#include
// 7.8 Format conversion of integer types
typedef struct {
intmax_t quot;
intmax_t rem;
} imaxdiv_t;
// 7.8.1 Macros for format specifiers
#if !defined(__cplusplus) || defined(__STDC_FORMAT_MACROS) // [ See footnote 185 at page 198
// The fprintf macros for signed integers are:
#define PRId8 "d"
#define PRIi8 "i"
#define PRIdLEAST8 "d"
#define PRIiLEAST8 "i"
#define PRIdFAST8 "d"
#define PRIiFAST8 "i"
#define PRId16 "hd"
#define PRIi16 "hi"
#define PRIdLEAST16 "hd"
#define PRIiLEAST16 "hi"
#define PRIdFAST16 "hd"
#define PRIiFAST16 "hi"
#define PRId32 "I32d"
#define PRIi32 "I32i"
#define PRIdLEAST32 "I32d"
#define PRIiLEAST32 "I32i"
#define PRIdFAST32 "I32d"
#define PRIiFAST32 "I32i"
#define PRId64 "I64d"
#define PRIi64 "I64i"
#define PRIdLEAST64 "I64d"
#define PRIiLEAST64 "I64i"
#define PRIdFAST64 "I64d"
#define PRIiFAST64 "I64i"
#define PRIdMAX "I64d"
#define PRIiMAX "I64i"
#define PRIdPTR "Id"
#define PRIiPTR "Ii"
// The fprintf macros for unsigned integers are:
#define PRIo8 "o"
#define PRIu8 "u"
#define PRIx8 "x"
#define PRIX8 "X"
#define PRIoLEAST8 "o"
#define PRIuLEAST8 "u"
#define PRIxLEAST8 "x"
#define PRIXLEAST8 "X"
#define PRIoFAST8 "o"
#define PRIuFAST8 "u"
#define PRIxFAST8 "x"
#define PRIXFAST8 "X"
#define PRIo16 "ho"
#define PRIu16 "hu"
#define PRIx16 "hx"
#define PRIX16 "hX"
#define PRIoLEAST16 "ho"
#define PRIuLEAST16 "hu"
#define PRIxLEAST16 "hx"
#define PRIXLEAST16 "hX"
#define PRIoFAST16 "ho"
#define PRIuFAST16 "hu"
#define PRIxFAST16 "hx"
#define PRIXFAST16 "hX"
#define PRIo32 "I32o"
#define PRIu32 "I32u"
#define PRIx32 "I32x"
#define PRIX32 "I32X"
#define PRIoLEAST32 "I32o"
#define PRIuLEAST32 "I32u"
#define PRIxLEAST32 "I32x"
#define PRIXLEAST32 "I32X"
#define PRIoFAST32 "I32o"
#define PRIuFAST32 "I32u"
#define PRIxFAST32 "I32x"
#define PRIXFAST32 "I32X"
#define PRIo64 "I64o"
#define PRIu64 "I64u"
#define PRIx64 "I64x"
#define PRIX64 "I64X"
#define PRIoLEAST64 "I64o"
#define PRIuLEAST64 "I64u"
#define PRIxLEAST64 "I64x"
#define PRIXLEAST64 "I64X"
#define PRIoFAST64 "I64o"
#define PRIuFAST64 "I64u"
#define PRIxFAST64 "I64x"
#define PRIXFAST64 "I64X"
#define PRIoMAX "I64o"
#define PRIuMAX "I64u"
#define PRIxMAX "I64x"
#define PRIXMAX "I64X"
#define PRIoPTR "Io"
#define PRIuPTR "Iu"
#define PRIxPTR "Ix"
#define PRIXPTR "IX"
// The fscanf macros for signed integers are:
#define SCNd8 "d"
#define SCNi8 "i"
#define SCNdLEAST8 "d"
#define SCNiLEAST8 "i"
#define SCNdFAST8 "d"
#define SCNiFAST8 "i"
#define SCNd16 "hd"
#define SCNi16 "hi"
#define SCNdLEAST16 "hd"
#define SCNiLEAST16 "hi"
#define SCNdFAST16 "hd"
#define SCNiFAST16 "hi"
#define SCNd32 "ld"
#define SCNi32 "li"
#define SCNdLEAST32 "ld"
#define SCNiLEAST32 "li"
#define SCNdFAST32 "ld"
#define SCNiFAST32 "li"
#define SCNd64 "I64d"
#define SCNi64 "I64i"
#define SCNdLEAST64 "I64d"
#define SCNiLEAST64 "I64i"
#define SCNdFAST64 "I64d"
#define SCNiFAST64 "I64i"
#define SCNdMAX "I64d"
#define SCNiMAX "I64i"
#ifdef _WIN64 // [
# define SCNdPTR "I64d"
# define SCNiPTR "I64i"
#else // _WIN64 ][
# define SCNdPTR "ld"
# define SCNiPTR "li"
#endif // _WIN64 ]
// The fscanf macros for unsigned integers are:
#define SCNo8 "o"
#define SCNu8 "u"
#define SCNx8 "x"
#define SCNX8 "X"
#define SCNoLEAST8 "o"
#define SCNuLEAST8 "u"
#define SCNxLEAST8 "x"
#define SCNXLEAST8 "X"
#define SCNoFAST8 "o"
#define SCNuFAST8 "u"
#define SCNxFAST8 "x"
#define SCNXFAST8 "X"
#define SCNo16 "ho"
#define SCNu16 "hu"
#define SCNx16 "hx"
#define SCNX16 "hX"
#define SCNoLEAST16 "ho"
#define SCNuLEAST16 "hu"
#define SCNxLEAST16 "hx"
#define SCNXLEAST16 "hX"
#define SCNoFAST16 "ho"
#define SCNuFAST16 "hu"
#define SCNxFAST16 "hx"
#define SCNXFAST16 "hX"
#define SCNo32 "lo"
#define SCNu32 "lu"
#define SCNx32 "lx"
#define SCNX32 "lX"
#define SCNoLEAST32 "lo"
#define SCNuLEAST32 "lu"
#define SCNxLEAST32 "lx"
#define SCNXLEAST32 "lX"
#define SCNoFAST32 "lo"
#define SCNuFAST32 "lu"
#define SCNxFAST32 "lx"
#define SCNXFAST32 "lX"
#define SCNo64 "I64o"
#define SCNu64 "I64u"
#define SCNx64 "I64x"
#define SCNX64 "I64X"
#define SCNoLEAST64 "I64o"
#define SCNuLEAST64 "I64u"
#define SCNxLEAST64 "I64x"
#define SCNXLEAST64 "I64X"
#define SCNoFAST64 "I64o"
#define SCNuFAST64 "I64u"
#define SCNxFAST64 "I64x"
#define SCNXFAST64 "I64X"
#define SCNoMAX "I64o"
#define SCNuMAX "I64u"
#define SCNxMAX "I64x"
#define SCNXMAX "I64X"
#ifdef _WIN64 // [
# define SCNoPTR "I64o"
# define SCNuPTR "I64u"
# define SCNxPTR "I64x"
# define SCNXPTR "I64X"
#else // _WIN64 ][
# define SCNoPTR "lo"
# define SCNuPTR "lu"
# define SCNxPTR "lx"
# define SCNXPTR "lX"
#endif // _WIN64 ]
#endif // __STDC_FORMAT_MACROS ]
// 7.8.2 Functions for greatest-width integer types
// 7.8.2.1 The imaxabs function
#define imaxabs _abs64
// 7.8.2.2 The imaxdiv function
// This is modified version of div() function from Microsoft's div.c found
// in %MSVC.NET%\crt\src\div.c
#ifdef STATIC_IMAXDIV // [
static
#else // STATIC_IMAXDIV ][
_inline
#endif // STATIC_IMAXDIV ]
imaxdiv_t __cdecl imaxdiv(intmax_t numer, intmax_t denom)
{
imaxdiv_t result;
result.quot = numer / denom;
result.rem = numer % denom;
if (numer < 0 && result.rem > 0) {
// did division wrong; must fix up
++result.quot;
result.rem -= denom;
}
return result;
}
// 7.8.2.3 The strtoimax and strtoumax functions
#define strtoimax _strtoi64
#define strtoumax _strtoui64
// 7.8.2.4 The wcstoimax and wcstoumax functions
#define wcstoimax _wcstoi64
#define wcstoumax _wcstoui64
#endif // _MSC_INTTYPES_H_ ]
stdint.h
// ISO C9x compliant stdint.h for Microsoft Visual Studio
// Based on ISO/IEC 9899:TC2 Committee draft (May 6, 2005) WG14/N1124
//
// Copyright (c) 2006-2008 Alexander Chemeris
//
// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
//
// 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice,
// this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
//
// 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
// documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
//
// 3. The name of the author may be used to endorse or promote products
// derived from this software without specific prior written permission.
//
// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE AUTHOR ``AS IS'' AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
// WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
// MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO
// EVENT SHALL THE AUTHOR BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
// PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS;
// OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY,
// WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR
// OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF
// ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
//
///
#ifndef _MSC_VER // [
#error "Use this header only with Microsoft Visual C++ compilers!"
#endif // _MSC_VER ]
#ifndef _MSC_STDINT_H_ // [
#define _MSC_STDINT_H_
#if _MSC_VER > 1000
#pragma once
#endif
#include
// For Visual Studio 6 in C++ mode and for many Visual Studio versions when
// compiling for ARM we should wrap include with 'extern "C++" {}'
// or compiler give many errors like this:
// error C2733: second C linkage of overloaded function 'wmemchr' not allowed
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
# include
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
// Define _W64 macros to mark types changing their size, like intptr_t.
#ifndef _W64
# if !defined(__midl) && (defined(_X86_) || defined(_M_IX86)) && _MSC_VER >= 1300
# define _W64 __w64
# else
# define _W64
# endif
#endif
// 7.18.1 Integer types
// 7.18.1.1 Exact-width integer types
// Visual Studio 6 and Embedded Visual C++ 4 doesn't
// realize that, e.g. char has the same size as __int8
// so we give up on __intX for them.
#if (_MSC_VER < 1300)
typedef signed char int8_t;
typedef signed short int16_t;
typedef signed int int32_t;
typedef unsigned char uint8_t;
typedef unsigned short uint16_t;
typedef unsigned int uint32_t;
#else
typedef signed __int8 int8_t;
typedef signed __int16 int16_t;
typedef signed __int32 int32_t;
typedef unsigned __int8 uint8_t;
typedef unsigned __int16 uint16_t;
typedef unsigned __int32 uint32_t;
#endif
typedef signed __int64 int64_t;
typedef unsigned __int64 uint64_t;
// 7.18.1.2 Minimum-width integer types
typedef int8_t int_least8_t;
typedef int16_t int_least16_t;
typedef int32_t int_least32_t;
typedef int64_t int_least64_t;
typedef uint8_t uint_least8_t;
typedef uint16_t uint_least16_t;
typedef uint32_t uint_least32_t;
typedef uint64_t uint_least64_t;
// 7.18.1.3 Fastest minimum-width integer types
typedef int8_t int_fast8_t;
typedef int16_t int_fast16_t;
typedef int32_t int_fast32_t;
typedef int64_t int_fast64_t;
typedef uint8_t uint_fast8_t;
typedef uint16_t uint_fast16_t;
typedef uint32_t uint_fast32_t;
typedef uint64_t uint_fast64_t;
// 7.18.1.4 Integer types capable of holding object pointers
#ifdef _WIN64 // [
typedef signed __int64 intptr_t;
typedef unsigned __int64 uintptr_t;
#else // _WIN64 ][
typedef _W64 signed int intptr_t;
typedef _W64 unsigned int uintptr_t;
#endif // _WIN64 ]
// 7.18.1.5 Greatest-width integer types
typedef int64_t intmax_t;
typedef uint64_t uintmax_t;
// 7.18.2 Limits of specified-width integer types
#if !defined(__cplusplus) || defined(__STDC_LIMIT_MACROS) // [ See footnote 220 at page 257 and footnote 221 at page 259
// 7.18.2.1 Limits of exact-width integer types
#define INT8_MIN ((int8_t)_I8_MIN)
#define INT8_MAX _I8_MAX
#define INT16_MIN ((int16_t)_I16_MIN)
#define INT16_MAX _I16_MAX
#define INT32_MIN ((int32_t)_I32_MIN)
#define INT32_MAX _I32_MAX
#define INT64_MIN ((int64_t)_I64_MIN)
#define INT64_MAX _I64_MAX
#define UINT8_MAX _UI8_MAX
#define UINT16_MAX _UI16_MAX
#define UINT32_MAX _UI32_MAX
#define UINT64_MAX _UI64_MAX
// 7.18.2.2 Limits of minimum-width integer types
#define INT_LEAST8_MIN INT8_MIN
#define INT_LEAST8_MAX INT8_MAX
#define INT_LEAST16_MIN INT16_MIN
#define INT_LEAST16_MAX INT16_MAX
#define INT_LEAST32_MIN INT32_MIN
#define INT_LEAST32_MAX INT32_MAX
#define INT_LEAST64_MIN INT64_MIN
#define INT_LEAST64_MAX INT64_MAX
#define UINT_LEAST8_MAX UINT8_MAX
#define UINT_LEAST16_MAX UINT16_MAX
#define UINT_LEAST32_MAX UINT32_MAX
#define UINT_LEAST64_MAX UINT64_MAX
// 7.18.2.3 Limits of fastest minimum-width integer types
#define INT_FAST8_MIN INT8_MIN
#define INT_FAST8_MAX INT8_MAX
#define INT_FAST16_MIN INT16_MIN
#define INT_FAST16_MAX INT16_MAX
#define INT_FAST32_MIN INT32_MIN
#define INT_FAST32_MAX INT32_MAX
#define INT_FAST64_MIN INT64_MIN
#define INT_FAST64_MAX INT64_MAX
#define UINT_FAST8_MAX UINT8_MAX
#define UINT_FAST16_MAX UINT16_MAX
#define UINT_FAST32_MAX UINT32_MAX
#define UINT_FAST64_MAX UINT64_MAX
// 7.18.2.4 Limits of integer types capable of holding object pointers
#ifdef _WIN64 // [
# define INTPTR_MIN INT64_MIN
# define INTPTR_MAX INT64_MAX
# define UINTPTR_MAX UINT64_MAX
#else // _WIN64 ][
# define INTPTR_MIN INT32_MIN
# define INTPTR_MAX INT32_MAX
# define UINTPTR_MAX UINT32_MAX
#endif // _WIN64 ]
// 7.18.2.5 Limits of greatest-width integer types
#define INTMAX_MIN INT64_MIN
#define INTMAX_MAX INT64_MAX
#define UINTMAX_MAX UINT64_MAX
// 7.18.3 Limits of other integer types
#ifdef _WIN64 // [
# define PTRDIFF_MIN _I64_MIN
# define PTRDIFF_MAX _I64_MAX
#else // _WIN64 ][
# define PTRDIFF_MIN _I32_MIN
# define PTRDIFF_MAX _I32_MAX
#endif // _WIN64 ]
#define SIG_ATOMIC_MIN INT_MIN
#define SIG_ATOMIC_MAX INT_MAX
#ifndef SIZE_MAX // [
# ifdef _WIN64 // [
# define SIZE_MAX _UI64_MAX
# else // _WIN64 ][
# define SIZE_MAX _UI32_MAX
# endif // _WIN64 ]
#endif // SIZE_MAX ]
// WCHAR_MIN and WCHAR_MAX are also defined in
#ifndef WCHAR_MIN // [
# define WCHAR_MIN 0
#endif // WCHAR_MIN ]
#ifndef WCHAR_MAX // [
# define WCHAR_MAX _UI16_MAX
#endif // WCHAR_MAX ]
#define WINT_MIN 0
#define WINT_MAX _UI16_MAX
#endif // __STDC_LIMIT_MACROS ]
// 7.18.4 Limits of other integer types
#if !defined(__cplusplus) || defined(__STDC_CONSTANT_MACROS) // [ See footnote 224 at page 260
// 7.18.4.1 Macros for minimum-width integer constants
#define INT8_C(val) val##i8
#define INT16_C(val) val##i16
#define INT32_C(val) val##i32
#define INT64_C(val) val##i64
#define UINT8_C(val) val##ui8
#define UINT16_C(val) val##ui16
#define UINT32_C(val) val##ui32
#define UINT64_C(val) val##ui64
// 7.18.4.2 Macros for greatest-width integer constants
#define INTMAX_C INT64_C
#define UINTMAX_C UINT64_C
#endif // __STDC_CONSTANT_MACROS ]
#endif // _MSC_STDINT_H_ ]
5、部分原始头文件按需修改
在$(Dev_DIR)/include/common下找到error.h、common.h、timestamp.h这3个文件
打开,做以下修改:
- error.h
- 在最后一个#include下添加
-
... #include#include /// 下面是添加的内容 #ifdef _MSC_VER # ifndef inline # define inline #endif #endif //_MSC_VER // 添加结束 ... - 替换av_err2str的实现(如果你在代码中使用这个宏的话。如果不使用请忽略)
- 下面提供一种不保证线程安全的实现(参考)
-
/// ...其他代码 /** * Convenience macro, the return value should be used only directly in * function arguments but never stand-alone. */ #if 0 /// 原始实现 #define av_err2str(errnum) \ av_make_error_string((char[AV_ERROR_MAX_STRING_SIZE]){0}, AV_ERROR_MAX_STRING_SIZE, errnum) #else /// 替换的实现 static inline char *av_err2str(int errnum) { static char errBuf[AV_ERROR_MAX_STRING_SIZE] = {0}; return av_make_error_string( errbuf, AV_ERROR_MAX_STRING_SIZE,errnum ); } #endif /// 其他代码
- common.h
- 在最后一个#include 后追加
-
... #include "libavutil/avconfig.h" /// 添加的内容 #ifdef _MSC_VER # define snprintf _snprintf #endif // _MSC_VER /// 添加结束 ...
- timestamp.h
- 替换av_ts2timestr的实现(如果你在代码中使用这个宏的话。如果不使用请忽略)
- 下面提供一种不保证线程安全的实现(参考)
-
/// 其他代码 /** * Convenience macro, the return value should be used only directly in * function arguments but never stand-alone. */ #if 0 /// 原始实现 #define av_ts2timestr(ts, tb) av_ts_make_time_string((char[AV_TS_MAX_STRING_SIZE]){0}, ts, tb) #else /// 替换的实现 static inline char *av_ts2timestr( int64_t ts, AVRational *tb) { static char buf[AV_TS_MAX_STRING_SIZE] = {0}; return av_ts_make_time_string(buf,ts,tb ); } #endif /// 其他代码
- 替换av_ts2timestr的实现(如果你在代码中使用这个宏的话。如果不使用请忽略)
6、创建测试程序
- 添加头文件(ffmpeg是C库,如果是c++代码必须类似下面方式写,以C形式引用)
-
#if defined(__cplusplus ) extern "C" { #endif // __cplusplus #include#include #include #include #if defined(__cplusplus ) }; #endif // __cplusplus -
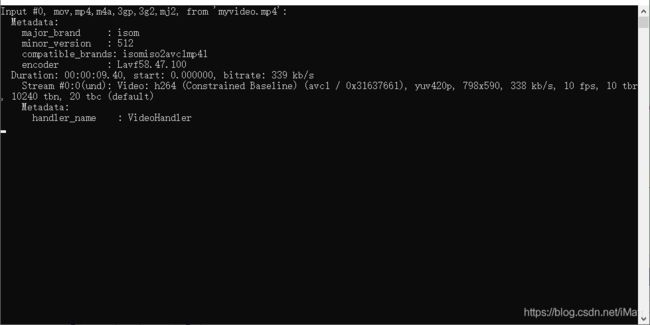
尝试解码一个视频文件,并输出视频的信息到标准错误输出窗口(默认为控制台)
-
bool test_open_video( ) { // 视频文件默认是myvideo.mp4 const char* src_filename = "myvideo.mp4"; AVFormatContext *fmt_ctx = NULL; // 打开文件,并初始化格式化IO上下文 if (avformat_open_input(&fmt_ctx, src_filename, NULL, NULL) < 0) { // 打开失败 fprintf(stderr, "Could not open source file %s\n", src_filename); return false; } /// 输出当前视频的信息到stderr av_dump_format(fmt_ctx, 0, src_filename, 0); /// 通过fmt_ctx,调用ffmpeg的函数获取视频、音频等 avformat_close_input(&fmt_ctx); return true; } /// 在main函数中调用 int main( int argc, char* argv[] ) { test_open_video( ); getch( ); return 0; }
7、运行结果