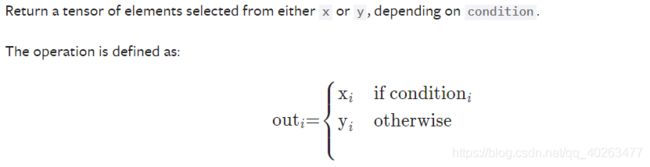Pytorch函数使用记录
文章目录
-
-
- F.conv2d (函数式接口)
- torch.nonzero
- torch.where
- torch.clamp
- torch.linspace
- torch.repeat
- torch.topk|torch.sort|torch.ne|torch.min|torch.max|torch.lt|torch.le|torch.kthvalue|torch.gt|torch.ge|torch.equal|torch.eq
- torch.numel
-
Pytorch API文档
F.conv2d (函数式接口)
Pytorch里一般小写的都是函数式的接口,相应的大写的是类式接口,函数式的更加low-level一些。
nn.Conv2d是[2D卷积层],而F.conv2d是[2D卷积操作]
import torch
from torch.nn import functional as F, Conv2d
input = torch.randn(1, 3, 28, 28) #[batch_size, in_channel, h, w]
#手动定义卷积核的wight和bias参数
w = torch.randn(16, 3, 5, 5) #[out_channel, in_channel, h_size, w_size)
b = torch.randn(16) #和卷积核的个数保持一致,不同通道下共用一个bias
output = F.conv2d(input, w, b, stride=1, padding=1)
print(output.size())
>>>torch.Size([1, 16, 26, 26])
#利用卷积层参数大小自动根据输入输出设定
conv = Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=16, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=1)
output_ = conv(input)
print(output_.size())
>>>torch.Size([1, 16, 26, 26])
torch.nonzero
作用:返回Tensor中非零元素所在的位置下标 (进而可用下标得到非零值等作用)
torch.nonzero(input, *, out=None, as_tuple=False) → LongTensor or tuple of LongTensors
- 当as_tuple=False(default),返回2-D张量的形式,每一行表示非零元素的下标,行数为非零数的个数。
- 当as_tuple=True,返回一个1-D的下标张量,each index tensor contains nonzero indices for a certain dimension。
##as_tuple=False(default)
#1-D input
output = torch.nonzero(torch.tensor([1, 1, 1, 0, 1]))
>>> tensor([[ 0],
[ 1],
[ 2],
[ 4]]) #[4, 1]
#2-D input
output = torch.nonzero(torch.tensor([[0.6, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.4, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.0, 1.2, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0,-0.4]]))
>>> tensor([[ 0, 0],
[ 1, 1],
[ 2, 2],
[ 3, 3]])
##as_tuple=True
#1-D input
torch.nonzero(torch.tensor([1, 1, 1, 0, 1]), as_tuple=True)
>>>(tensor([0, 1, 2, 4]),)
input = torch.nonzero(torch.tensor([[0.6, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.4, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.0, 1.2, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0,-0.4]]), as_tuple=True)
>>>output = (tensor([0, 1, 2, 3]), tensor([0, 1, 2, 3]))
#As a special case, when input has zero dimensions and a nonzero scalar value, it is treated as a one-dimensional tensor with one element.当只有一个非零元素时视为一维张量处理
torch.nonzero(torch.tensor(5), as_tuple=True)
>>>(tensor([0]),)
#根据元组下标,取出非零元素值
get_elem = input[output]
>>>tensor([ 0.6000, 0.4000, 1.2000, -0.4000])
torch.where
作用:根据条件选择元素,有点类似三元表达式:exp?a:b
torch.where(condition, x, y) → Tensor
torch.where(condition) → tuple of LongTensor #torch.where(condition) is identical to torch.nonzero(condition, as_tuple=True).
x = torch.randn(3, 2)
y = torch.ones(3, 2)
>>>x
tensor([[-0.4620, 0.3139],
[ 0.3898, -0.7197],
[ 0.0478, -0.1657]])
>>>torch.where(x > 0, x, y)
tensor([[ 1.0000, 0.3139],
[ 0.3898, 1.0000],
[ 0.0478, 1.0000]])
torch.clamp
作用:将输入input张量每个元素的夹紧到区间 [min,max]内,并返回结果到一个新张量
torch.clamp(input, min, max, out=None) → Tensor
torch.linspace
作用:线性等分向量 Returns a one-dimensional tensor of steps equally spaced points between start and end.
torch.linspace(start, end, steps=100, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False) → Tensor
>>> torch.linspace(3, 10, steps=5)
tensor([ 3.0000, 4.7500, 6.5000, 8.2500, 10.0000])
>>> torch.linspace(-10, 10, steps=5)
tensor([-10., -5., 0., 5., 10.])
>>> torch.linspace(start=-10, end=10, steps=5)
tensor([-10., -5., 0., 5., 10.])
>>> torch.linspace(start=-10, end=10, steps=1)
tensor([-10.])
torch.repeat
作用:在指定维度上重复元素
>>> x = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3])
>>> x.repeat(4, 2)
tensor([[ 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3],
[ 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3],
[ 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3],
[ 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3]])
>>> x.repeat(4, 2, 1).size()
torch.Size([4, 2, 3])
torch.topk|torch.sort|torch.ne|torch.min|torch.max|torch.lt|torch.le|torch.kthvalue|torch.gt|torch.ge|torch.equal|torch.eq
作用:pytorch张量的比较操作
torch.numel
作用:Returns the total number of elements in the input tensor.
torch.numel(input) → int