JDBC知识
参考:
博客园-cmlx
JDBC-MySQL连接步骤:
- 导jar包:驱动
- 加载驱动类:Class.forName(“类名”);
- 给出url、usename、password,其中url靠背
- 使用DriverManager类来得到Connection对象
jdbc四大配置参数:
- driverClassName:com.mysql.jdbc.Driver:靠背
- url:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb3:靠背
- usename:root
- password:xxx
连接数据库,得到Connection就算成功
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");//加载驱动类/注册驱动类
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb3";
String user = "root";
String password = "xxx";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);//使用url、username、password,得到连接对象
原理
JDBC其实是对类的规范,是一大堆接口
可以访问各种数据库的API被称为驱动
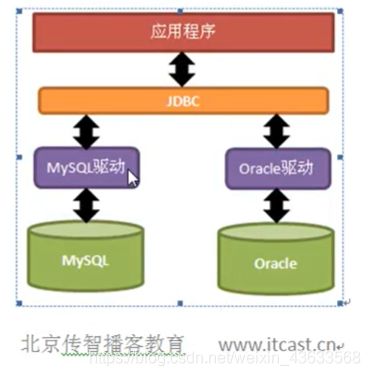
所有的java.sql.Driver实现类,都提供了static块,块内的代码就是把自己注册到DriverManager中!即加载驱动时就运行static中的注册信息。
JDBC增删改查
准备:
一、得到Connection
- 得到四大参数
- 加载驱动类
- 得到Connection
jdbc协议的格式
jdbc:厂商的名称:子协议(有厂商自己来规定)
对mysql而言,它的子协议结构://主机:端口号/数据库名称
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb3";
其中Connection导包是JDBC的包,因为可能是MySQL或者其他的数据库
二、对数据库做增删改
- 通过Connection对象创建Statement
Statement:语句的发送器
功能:向数据库发送sql语句 - 调用int executeUptate(String sql),它可以发送DML、DDL
//准备四大参数
String driverClassName = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb3";
String username = "root";
String password = "xxx";
//加载驱动类
Class.forName(driverClassName);
//使用DriverManager,以及剩下的3个参数,得到Connection
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
//通过Connection得到Statement对象
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
//使用Statement发送sql语句,写sql语句不需要再加上分号
String sql = “INSERT INTO stu VALUES('ITCAST_0003','wangwu',88,'male')”;
String sql = “UPDATE stu SET name = 'zhaoLiu',age = 22, gender = 'female' WHERE number = 'ITCAST_0003'”;
String sql = “DELETE FROM stu”;
int r = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);//插入一句sql语句,r=1;如果删除3行,r=3
三、对数据库做增删改
- 得到Connection
- 得到Statement,发送select语句
- 对查询返回的“表格”进行解析
String driverClassName = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb3";
String username = "root";
String password = "xxx";
//加载驱动类
Class.forName(driverClassName);
//使用DriverManager,以及剩下的3个参数,得到Connection
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
//通过Connection得到Statement对象
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
//得到Statement对象,Connection的createStatement()方法
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
//调用Statement的ResultSet executeQuery(String querySql),返回的是表格,要解析,顺序:从首行前一行->尾行后一行,所以可以用next
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("select * from emp");
//Result的next()方法可以把光标向下移动1行
//next()返回的boolean值,表示当前行是否存在!
while(rs.next()){//while改成if:把光标向下移动一行,并判断下一行是否存在!
int empno = rs.getInt(1);//通过列名来获取该列的值!
String ename = rs.getString ("ename");//通过列名来获取该列的值
double sal = rs.getDouble("sal");
}
四、关闭资源
倒关
rs.close();
stmt.close();
con.close();//不关就死
JDBC代码规范化
由于可能出现异常,close方法不一定会被执行。
办法:
try外:给出引用的定义
try内:对象实例化
finally中进行关闭
public void func3() throws Exception {
Connection con = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// 得到连接
String driverClassName = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student";
String username = "root";
String password = "123";
Class.forName(driverClassName);
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);// 实例化
// 创建Statement
stmt = con.createStatement();
String sql = "SELECT * FROM emp";
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
// 循环遍历rs,打印其中数据
// getString()和getObject()是通用的!
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getObject(1) + "," + rs.getString("name") + "," + rs.getInt("age")+","+rs.getString("gender"));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
// 关闭->倒关
if (rs != null)
rs.close();
if (stmt != null)
stmt.close();
if (con != null)
con.close();
}
}
JDBC核心类
参考链接参考这位同学写的
//获取总行数
rs.last();//把光标移动到最后一行
System.out.println(rs.getRow());
rs.beforeFirst();
使用getMetaData遍历列打印所有信息
int count = rs.getMetaData().getColumCount();
while(rs.next()){//遍历行
for(int i = 1; i <= count; i++){//遍历列
System.out.print(rs.getString(i))//使用getString和getObject方法都是万能的,因为所有东西都能转化成String
if(i < count){
System.out.print(", ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
- 概念:它是Statement接口的子接口
- 功能:
防sql攻击
提高代码可读性、维护性
提高效率
/**
*登陆
*使用username和password去查询数据
*若查出结果集,说明正确!返回true
*若查不出结果,说明用户名或密码错误,返回false
*/
public boolean login (String username, String password){
/**
*一、得到Connection
*二、得到Statement
*三、得到ResultSet
*四、rs.next()返回的是什么,我们就返回什么
*/
//准备四大参数
String driverClassName = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb3";
String mysqlUsername = "root";
String mysqlPassword = "xxx";
//加载驱动类
Class.forName(driverClassName);
//得到Connection
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,mysqlUsername ,mysqlPassword );
//得到Statement
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
//给出sql语句,调用stmt的executeQuery(),得到ResultSet
//查询表中的username和password
String sql = "select * from t_user where username=' " + username + " ' + " ' and password= ' " + password + " ' ";
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
return rs.next();
}
}
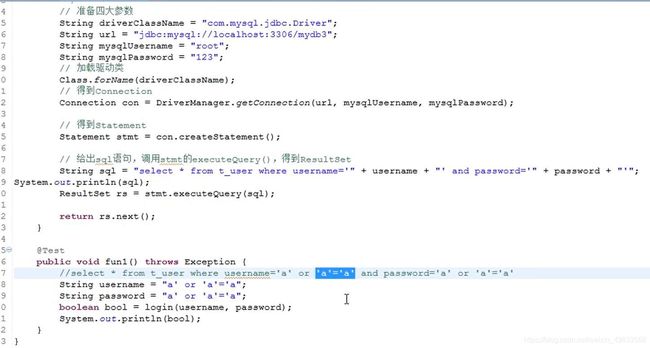
sql攻击
- 只要username和password写成’a’ or ‘a’ = ‘a’->即偷偷把名字写成sql true语句,一定会true,就会被攻击
学习PreparedStatement的用法
如何得到PreparedStatement对象: - 给出SQL模板!
- 调用Connection的PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql模板)
- 调用pstmt的setXxx()系列方法,为sql模板中的?赋值
- 调用pstmt的executeUpdate()或executeQuery(),但它们的方法都没有参数
public boolean login (String username, String password){
//准备四大参数
String driverClassName = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb3";
String mysqlUsername = "root";
String mysqlPassword = "xxx";
//加载驱动类
Class.forName(driverClassName);
//得到Connection
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,mysqlUsername ,mysqlPassword );
/*
*一、得到PreparedStatement
*1.给出sql模板:所有的参数使用?来替代
*2.调用Connection方法,得到PreparedStatement
*/
String sql = "select * from t_user where username=? and password=?";
PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatemtn(sql);
/*
*二、为参数赋值
*/
pstmt.setString(1,username);//给第1个问号赋值,值为username
pstmt.setString(2,password);//给第2个问号赋值,值为password
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery();//调用查询方法,向数据库发送查询语句;没有参数是因为前面的sql语句有了
return rs.next();
}
PreparedStatement/预处理的原理/
服务器的工作:
- 校验sql语句的语法
- 编译:一个与函数相似的东西
- 执行:调用函数
PreparedStatement: - 前提:连接的数据库必须支持预处理,都支持的
- 每个pstmt都与一个sql模板绑定在一起,先把sql模板给数据库,数据库先进行校验,再进行编译。执行时知识把参数传递过去而已!
- 若二次执行时,就不用再次校验语法,也不用再次编译!直接执行
mysql预处理默认关闭
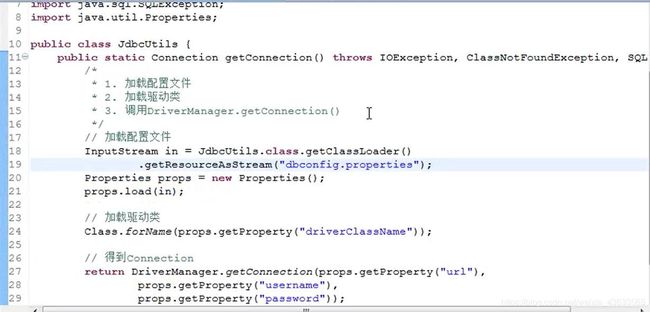
JdbcUtils工具类
参考JdbcUtils工具类
1.首先创建并编写src/dbconfig.properties配置文件
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student
username=root
password=123
2.创建JdbcUtils类,编写静态方法getConnection
public class JdbcUtil1 {
private static Properties props = null;->拿出来
//只在JdbcUtil1类被加载时执行一次
static {
//给props进行初始化,加载配置文件dbconfig.properties文件到props对象中
try {
InputStream in = JdbcUtil1.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("dbconfig.properties");
props = new Properties();
props.load(in);
}catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
//加载驱动类
try {
Class.forName(props.getProperty("driverClassName"));->利用键值对
}catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException{
//得到Connection
return DriverManager.getConnection(props.getProperty("url"), props.getProperty("username"), props.getProperty("password"));
}
}
(课时11)DAO模式
DAO模式就是写一个类,把访问数据库的代码封装起来。DAO在数据库与业务逻辑之间
(未完待续)