GMM混合高斯背景建模C++结合Opencv实现(内附Matlab实现)
最近在做视频流检测方面的工作,一般情况下这种视频流检测是较复杂的场景,比如交通监控,或者各种监控摄像头,场景比较复杂,因此需要构建背景图像,然后去检测场景中每一帧动态变化的前景部分,GMM高斯模型是建模的一种方法,关于高斯建模的介绍有很多博客了,大家可以去找一找,本篇博客主要依赖于上一个老兄,他用matlab实现了GMM模型,我在其基础上利用C++和OpenCV进行了重写,下面会给出C++代码,希望能给大家一点帮助,本文能力有限,如有问题可以一起交流,一起改进。
先展示结果吧,不要问我的图像是神马图像,哈哈哈 感觉很low b。 其实都是视频中的某一帧图像。方法可以用就行啦!!
背景图像:
![]()
待检测图像:
![]()
检测结果:
![]()
我其实是想检测出图片中的缺口,以下是检测结果,我改变一下形式吧 ,这样能更清楚的看出结果
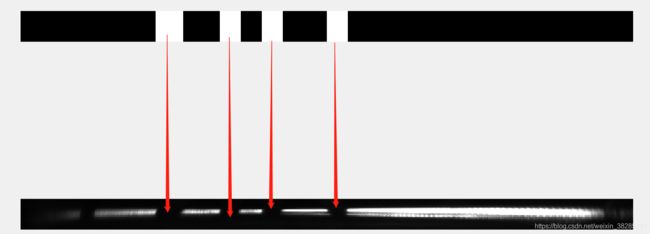
其实还是很精准的嘛,来来来,下面上代码~
C++结合OpenCV代码
//Writen by 蘇丶 2018//11/04
//转载请附转载链接
#includeMatlab代码:
我主要是针对以为老哥的Matlab代码改出来的C++版本,所以把老哥的博客链接附在下面,然后把代码也展示一下吧
Matlab GMM实现
麻鸡,再次吐槽这个配色,我不知道怎么改啊 ,有没有人会改 请给我留言,我看着这个配色好不爽
clear;
fr=imread('first.jpg');
% 读取该图像作为背景
fr_bw1 = rgb2gray(fr);
% 将背景转换为灰度图像
fr_size = size(fr);
%取帧大小
width = fr_size(2);
height = fr_size(1); %获取原图像的尺寸
fg = zeros(height, width); %前景,读取的第二张图片获得
bg_bw = zeros(height, width);%背景,读取的第一张图片获得
fr_bw1 = double(fr_bw1);
% --------------------- mog variables -----------------------------------
C = 3; % 组成混合高斯的单高斯数目 (一般3-5)
D = 2.5; % 阈值(一般2.5个标准差)
alpha = 0.01; % learning rate 学习率决定更新速度(between 0 and 1) (from paper 0.01)
thresh = 0.25; % foreground threshold 前景阈值(0.25 or 0.75 in paper)
sd_init = 36; % initial standard deviation 初始化标准差(for new components) var = 36 in paper
w = zeros(height,width,C); % initialize weights array 初始化权值数组
w(:,:,1) = 1;
w(:,:,2:C) = 2^-10; % 第一个高斯分布的初始权重为1,其余分布的权重为0
mean = zeros(height,width,C); % pixel means 像素均值
mean(:,:,1) = fr_bw1; % 第一个高斯分布的初始均值为参考帧的值,其余分布的均值为0s
sd = sd_init*ones(height,width,C); % pixel standard deviations 像素标准差
matchcnt = ones(height, width,C); % 匹配的次数,初始值都设为1
u_diff = zeros(height,width,C); % difference of each pixel from mean 图片与高斯均值的差
fr = imread('second.jpg'); % read in frame 读取帧
fr_bw = rgb2gray(fr); % convert frame to grayscale 转换为灰度图像
fr_bw = double(fr_bw); % 将灰度图值设置为双精度
%求导入进来的图片与各个高斯均值的差
for m=1:C
u_diff(:,:,m) = abs(fr_bw - double(mean(:,:,m)));
end
% update gaussian components for each pixel 更新每个像素的背景模型
%rank_ind = zeros(C,1);
for i=1:height
for j=1:width
match = 0; %像素与高斯模型匹配的标识
match_ind = 0;%为该像素最匹配的高斯模型的标号
for k=1:C %与第k个高斯模型进行比对,然后更新参数
if (abs(u_diff(i,j,k)) <= D*sd(i,j,k) && (match == 0)) % pixel matches component像素匹配了高斯中的第k个模型
match = 1;
% variable to signal component match 设置匹配标记
match_ind = k;
% update weights, mean, sd, p 更新权值,均值,标准差和参数学习率
p = alpha/w(i,j,k); %理应使用p = alpha/gaussian才对,这里勉强
w(i,j,k) = (1-alpha)*w(i,j,k) + alpha;
%p = alpha/w(i,j,k); %理应使用p = alpha/gaussian才对,这里勉强
mean(i,j,k) = (1-p)*mean(i,j,k) + p*double(fr_bw(i,j));
sd(i,j,k) = sqrt((1-p)*(sd(i,j,k)^2) + p*((double(fr_bw(i,j)) - mean(i,j,k)))^2);
if matchcnt(i, j, k) ~= 255 % 匹配次数达到255就不加了。在实时视频序列中,上限是必须的,否则可能溢出。
matchcnt(i, j, k) = matchcnt(i, j, k) + 1;
end
else
%当与第k个模型没有匹配的话,则第k个模型所占的比重自然而然地下降
w(i,j,k) = (1-alpha)*w(i,j,k); % weight slighly decreases 权值减小
end
end
% if no components match, create new component 如果没有匹配的模型则创建新模型
if(match==0) % 没有匹配的高斯,建立新的高斯取代:排序后排在最后面的那个
[min_w,min_w_index]=min(w(i,j,:));
matchcnt(i,j,min_w_index) = 1; % 匹配次数设为1,一个小值
w(i,j,min_w_index) = 1 / ( sum( matchcnt(i, j, :) ) - 1 );% 权值为其它高斯分布匹配次数之和的倒数
mean(i,j,min_w_index)=double(fr_bw(i,j));
sd(i,j,min_w_index)=sd_init;
end
%无论匹配是否成功,都要将该像素在不同模型上的权重标准归一化
w_sum = sum(w(i, j, :));
w(i, j, :) = w(i, j, :) / w_sum;
%针对该像素,计算多个模型的优先级(依据权重)
rank = w(i,j,:)./sd(i,j,:);
[sorted_rank, rank_ind] = sort(rank, 'descend');
%将前景的初始值设置为255,即为白色;
fg(i,j) = fr_bw(i,j);
%当该像素匹配成功的时候,利用高斯混合模型,将该像素值重新设置
if(match == 1)
switch match_ind
case rank_ind(1)% 与最优的高斯匹配,肯定是归为背景点
fg(i,j) = 0;
case rank_ind(2)% 与中间的高斯匹配,如果最上面一个高斯的权值小于thresh,则这点归为背景点
if w(i, j, rank_ind(1)) < thresh
fg(i, j) = 0;
end
case rank_ind(3)% 与最下面的高斯匹配,如果最下面的高斯权值大于1-thresh(或者前两个高斯权值和小于thresh),则这点归为背景点
if w(i, j, rank_ind(3)) > 1 - thresh
fg(i, j) = 0;
end
end
end
for k=1:C
bg_bw(i,j) = bg_bw(i,j)+ mean(i,j,k)*w(i,j,k);%更新背景
end
% % 根据rank的排序结果调整参数的顺序
% tmp_T = [mean(i, j, :); sd(i, j, :); w(i, j, :); matchcnt(i, j, :)]; % 为了排序时,几个参数同步调整,所以组合在一起
% mean(i, j, :) = tmp_T(1, rank_ind); %即同时利用rank,将mean进行了排序
% sd(i, j, :) = tmp_T(2, rank_ind); %同理
% w(i, j, :) = tmp_T(3, rank_ind); %同理
% matchcnt(i, j, :) = tmp_T(4, rank_ind);%同理
% if w(i, j, 1) > thresh %使用大于阈值的进行背景构造即可
% bg_bw(i, j) = w(i, j, 1) * mean(i, j, 1);
% else
% if w(i, j, 1) + w(i, j, 2) > thresh
% bg_bw(i, j) = w(i, j, 1) * mean(i, j, 1) + w(i, j, 2) * mean(i, j, 2);
% else
% bg_bw(i, j) = sum(w(i, j, :) .* mean(i, j, :));
% end
% end
end
end
figure(1),subplot(3,1,1),imshow(fr); %显示输入图像
subplot(3,1,2),imshow(uint8(bg_bw)); %显示背景图像
subplot(3,1,3),imshow(uint8(fg)); %显示前景图像
转载请附本博客链接地址:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_38285131/article/details/83721069