Java面向对象三大类及异常处理
Java包的作用:解决类名重复的问题
访问控制权限:
同包同类:4
同包不同类:3 无private
不同包子类:2 无默认
不同包中非子类:1 无protected
jar命令:先编译,后打包class文件。命令jar -cvf Test.jar *.class
String类:
实例化方式:
方式1:String str1 = "hello";
方式2:String str2 = new String("hello");
区别:str1会入池,在堆中存在一个对象。str2不会入对象池(存放字符串对象,每次执行(String str2 = "hello")都回去池中找看是否存在这个对象(按值比较)),在堆中有两个对象,一个会被GC回收(无指针指向)。
比较:使用equals不使用==
字符串修改:StringBuffer(多线程)和StringBuilder(单线程),不要用+号修改,每次使用+都会创建新对象。
String类常用方法:subString,split,valueOf,indexOf,length,toCharArray(按正则拆分);
Object类:
所有类的父类。
equals:比较两个对象的地址是否相同
toString:打印对象地址。
包装类:
对象型包装类(继承Object类):Boolean,Character(char)
数值型包装类(继承Number类):Byte,Short,Integer,Float,Double,Long
常用方法:类名.toString()。 Integer.parseInt("123");
2.编程题
/**
2.编程题:
要求:
1).Person类有name,age,salary属性,要求实现至少两个构造方法,并且属性私有,提供对应的getter、setter。
2).覆写toString方法,要求在System.out.println()函数中传递Person对象能打印出三个属性值而不是对象地址。
3).覆写equals方法,要求两个Person类对象的值相同时返回true。
*/
class Person{
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Integer salary;
public Person(){}
public Person(String name, Integer age, Integer salary) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(Integer salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
//2).覆写toString方法,要求在System.out.println()函数中传递Person对象能打印出三个属性值而不是对象地址。
@Override
public String toString(){
return "name:" + this.getName() + " Age:" + this.getAge() + " Salary:" + this.getSalary();
}
//3).覆写equals方法,要求两个Person类对象的值相同时返回true。
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(obj == null)
return false;
else if(this.getClass() != obj.getClass()){
return false;
}
else if(this == (Person)obj)
return true;
else{
Person tmpPerson = (Person)obj;
//name
if(this.getName() == null)
if(tmpPerson.getName() != null)
return false;
if(this.getName() != null)
if(!this.getName().equals(tmpPerson.getName()))
return false;
//age
if(this.getAge() == null)
if(tmpPerson.getAge() != null)
return false;
if(this.getAge() != null)
if(!this.getAge().equals(tmpPerson.getAge()))
return false;
//salary
if(this.getSalary() == null)
if(tmpPerson.getSalary() != null)
return false;
if(this.getSalary() != null)
if(!this.getSalary().equals(tmpPerson.getSalary()))
return false;
return true;
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Test test = new Test();
Person p1 = new Person("zhangsan", 15, 4545454);//可为空
Person p2 = new Person("zhangsan", 15, 4545454);
System.out.println(p1.toString());
p2.toString();
System.out.println(p2.equals(p1));
}
}3.程序阅读
//3.说出下列程序的执行结果,并说明原因:
//Integer a = 55;
//Integer b = 55;
//System.out.println(a==b); //true
//System.out.println(a==new Integer(55)); //false
//System.out.println(a.equals(new Integer(55))); //true
//Integer c = 129;
//Integer d = 129;
//System.out.println(c==d); //false
//true false true false结果分析:当给一个Integer类型的引用赋值范围在-128和127之间时,这个引用指向的数据会进入常量池,每次在创建其他Integer类型的引用时,会查看这个常量池里面有无这个数据。有就将这个引用指向这个常量。当数字不在这个范围时,就会在堆上创建对象。
4.懒汉式单例
//4.写出懒汉式单例模式
class Singleton{
private final static Singleton SINGLETON = new Singleton();
private Singleton(){}
public static Singleton getInstance(){
return Singleton.SINGLETON;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Singleton s1 = Singleton.getInstance();
Singleton s2 = Singleton.getInstance();
System.out.println(s1 == s2);//true
}
}//5.编程:
/**
* 1).定义一个MulException类继承Exception类,要求两数相乘等于100报错,在主类中定义一个方法,在方法中抛出此异常,在主方法观察结果。
* @author Z7M-SL7D2
*
*/
class MulException extends Exception{
public MulException(String err){
super(err);
}
}
/**
* 2).定义一个DivException类继承RuntimeException类,要求两数相除等于2报错,在主类中定义一个方法,在方法中抛出此异常,在主方法观察结果。
* @author Z7M-SL7D2
*
*/
class DivException extends RuntimeException{
public DivException(String err){
super(err);
}
}
public class Test {
public static void testMulException(int a, int b){
try{
if(a*b == 100)
throw new MulException("两数相乘不能等于100");
}catch(MulException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//throws可以省略,runtimeException抛出的异常不需要throws 和try
public static void testDivException(int a, int b) throws DivException{
if(a/b == 2)
throw new DivException("两数相除不能等于2");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
testMulException(50, 2);
testDivException(10, 5);
}
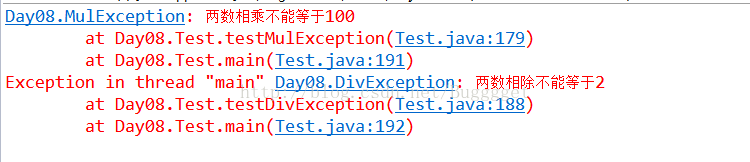
}运行结果:
区别:直接继承runtimeException类抛出的异常不处理不会报编译错误,直接继承Exception类抛出的异常必须要处理,不然编译会报错。6.算法
//6.(算法)
/**
* 题目:猴子吃桃问题:猴子第一天摘下若干个桃子,当即吃了一半,还不过瘾,又多吃了一个 第二天早上又将剩下的桃子吃掉一半,
又多吃了一个。以后每天早上都吃了前一天剩下的一半零一个。到第10天早上想再吃时,见只剩下一个桃子了。求第一天共摘了多少。
* @author Z7M-SL7D2
*
*/
public class Test{
//递归
public static int getMonkyEatPeachProblem(int day){
if(day == 1)
return 1;
return getMonkyEatPeachProblem(day-1)*2 + 1;
}
//递推
public static int getMonkyEatPeachProblem1(int day){
//第day天的数量
int count = 0;
while(day != 0){
count = count*2+1;
day--;
}
return count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(getMonkyEatPeachProblem(10));//1023
System.out.println(getMonkyEatPeachProblem1(10));//1023
}
}