用深度遍历找出图中两点间全部的路径
用深度遍历找出图中两点间全部的路径
1.遍历的思路图解
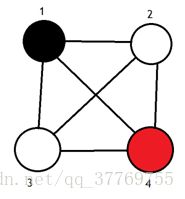
为了更直接的表示出我的算法思路现在用几张图来说明(这样即便是我没有很好的在第二部分用文字说明算法我相信你也能理解我的算法思路了):
1.首先确定了出发点和结束点(出发点用黑色标记 结束点用红色标记)
2.从2开始先进行深度遍历(先走2还是先走3由初始化输入决定)
3.遍历到3的邻近点没有白点此时有红点就输出路径一次(因为2周围还有白色点3所以要先遍历3),输出路径后3点变白且找3周围的灰点2返回;
4.此时2周围也无其余白点且有红点输出一次
5.回到初始状态(2点输出后就要复原,因为找不到灰点所以找黑点1)
6.点3被遍历
7. 点2被遍历周围无白点且周围有红点输出一次路径
8.点3周围除了已经遍历过的2无其余白点且周围有红点输出一次
在算法中优先级:找白点>找红点>找灰点>找黑点,具体的伪码看下一部分;
2.思路及伪代码
在看思路之前我觉得先看一下我写的2
在讲自己的思路之前把最开始想的时候的图拿出来:
我把每个点归为一类:
class Vertax{
public:
intid;
intcolor; ->每个点的颜色标记,把起始点设置为BLACK(黑色),要到的点 设置为RED(红色),初始颜色为WHITE(白色),遍历时走过的点为GRAY(灰色)
Vertax*Adj[50]; ->表示一个点的邻接点
intrecord[50];
intcount;
Vertax*next; ->在输出的时候按顺序输出点时用到
Vertax(intid){ ->含有初始化的构造方法
this->color=WHITE;
this->id=id;
this->Adj[50]=NULL;
this->record[50]=0;
this->count=0;
this->next=NULL;
}
voidwriteAdj(){ ->写入全部邻接点的方法
intnum;
inti;
cout<<"hou many Adjvertaxs thisvertax has? "< cin>>num; for(i=0;i cout<<"the "< cin>>this->record[i]; count++; } return; } }; 同时把图也写作一类: class Graph{ public: Vertax*vertax[50]; Graph(inti){ this->vertax[50]=NULL; intm=0; for(;m vertax[m]=newVertax(m+1); cout<<"please input the "< vertax[m]->writeAdj(); } for(m=0;m intr=0; for(;r this->vertax[m]->Adj[r]=this->vertax[this->vertax[m]->record[r]-1]; } } } }; 遍历的伪代码: Visit(Vertax *v1,Vertax *v2,int num,Graph*graph) foreachv∈v1->adj[] ifv1->adj[i]->color==WHITE v1>adj[i]->color= GRAY v1->next=v1->adj[i] ->绑定下一个邻接点 Visit(Vertax*v1.adj[i],Vertax *v2,int num,Graph *graph) v1->next=NULL; ->解除绑定 foreachv∈v1->adj[] ifv1->adj[i]->color==RED ifv1->color==BLACK cout< else v1->next=v1->adj[i] findthe start vertax and let it be a starting flag findthe end vertax and let it be a ending flag outputthe path ->输出路径 foreachv∈v1->adj[] ifv1->adj[i]->color==GRAY v1->color=WHITE foreachv∈v1->adj[] ifv1->adj[i]->color==BLACK v1->color=WHITE 以上就是我的遍历的伪代码,里面的输出路径的伪代码在下面给出: Out(Vertax *start,Vertax *end) ifstart->if==end->id return else cout< out(start->next,end) 这里我给出自己编写的程序: #include static int WHITE=0; static int GRAY=1; static int BLACK=2; static int RED=3; class Vertex{ public: intid; intcolor; Vertex*Adj[50]; intrecord[50]; intcount; Vertex*next; Vertex(intid){ this->color=WHITE; this->id=id; this->Adj[50]=NULL; this->record[50]=0; this->count=0; this->next=NULL; } voidwriteAdj(){ intnum; inti; cout<<"houmany Adjvertaxs this vertax has? "< cin>>num; for(i=0;i cout<<"the "< cin>>this->record[i]; count++; } return; } }; class Graph{ public: Vertex*vertex[50]; Graph(inti){ this->vertex[50]=NULL; intm=0; for(;m vertex[m]=newVertex(m+1); cout<<"pleaseinput the "< vertex[m]->writeAdj(); } for(m=0;m intr=0; for(;r this->vertex[m]->Adj[r]=this->vertex[this->vertex[m]->record[r]-1]; } } } }; void out(Vertex *start,Vertex *end){ if(start->id==end->id){ cout< return; } cout< out(start->next,end); } void visit(Vertex *v1,Vertex *v2,intnum,Graph *graph){ inti; intm; Vertex*start,*end; for(i=0;i if(v1->Adj[i]->color==WHITE){ v1->Adj[i]->color=GRAY; v1->next=v1->Adj[i]; visit(v1->Adj[i],v2,num,graph); v1->next=NULL; } } for(i=0;i if(v1->Adj[i]->color==RED){ //复原并且路径输出 if(v1->color==BLACK){ cout< return; } else{ v1->next=v1->Adj[i]; for(m=0;m if(graph->vertex[m]->color==BLACK){ start=graph->vertex[m]; } if(graph->vertex[m]->color==RED){ end=graph->vertex[m]; } } out(start,end); v1->color=WHITE; v1->next=NULL; return; } } } for(i=0;i if(v1->Adj[i]->color==GRAY){ //复原不输出路径 v1->color=WHITE; return; } } for(i=0;i if(v1->Adj[i]->color==BLACK){ //复原不输出路径 v1->color=WHITE; } } } void main(){ inti,o,t,m; Vertex*v1,*v2; cout<<"pleaseinput how many vertaxs in your Graph"< cin>>i; Graph*graph=new Graph(i); cout<<"pleaseinput the two vertaxs (first for origin and last fortermini)"< cin>>o>>t; for(m=0;m if(graph->vertex[m]->id==o){ v1=graph->vertex[m]; } if(graph->vertex[m]->id==t){ v2=graph->vertex[m]; } } v1->color=BLACK; v2->color=RED; visit(v1,v2,i,graph); return; } 实际的运行图为: 当然,这个算法既适合有相图也适合无向图,所有的图结果均正确(只有是你画的出来的图).3.编写主方法已经程序运行的实际结果