2020蓝旭工作室后端第六次讨论班之JDBC
JDBC
JDBC(Java DataBase Connectivity)是Java和数据库之间的一个桥梁,是一个规范而不是一个实现,能够执行SQL语句。它由一组用Java语言编写的类和接口组成。各种不同类型的数据库都有相应的实现,本文中的代码都是针对MySQL数据库实现的。
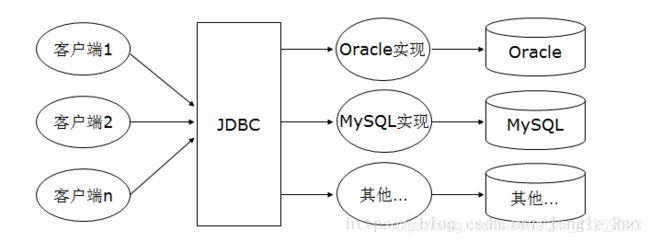
JDBC编程
一.装载相应数据库的JDBC驱动并进行初始化
-
导入jar包(不同的数据库需要的jar包不同)
访问MySQL数据库需要用到第三方的类,这些第三方的类,都被压缩在一个.Jar的文件里。我们这里使用mysql-connector-java-5.0.8-bin.jar。 -
初始化驱动
通过初始化驱动类com.mysql.jdbc.Driver,该类就在 mysql-connector-java-5.0.8-bin.jar中。
package com.bluemsun.zbc.dao;
public class DriverDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
//初始化驱动
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
System.out.println("数据库驱动加载成功");
}catch (ClassNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Class.forName是把这个类加载到JVM中,加载的时候,就会执行其中的静态初始化块,完成驱动的初始化的相关工作。
注意:Class.forName需要捕获ClassNotFoundException.
关于Class.forName这个方法的详解可以参考下面这篇博客:
https://blog.csdn.net/fengyuzhengfan/article/details/38086743
二.建立JDBC和数据库之间的Connection连接
package com.bluemsun.zbc.dao;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class ConnectionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//建立与数据库连接
// 这里需要提供:
// 数据库所处于的ip:127.0.0.1 (本机)
// 数据库的端口号: 3306 (mysql专用端口号)
// 数据库名称 jdbc_demo
// 编码方式 UTF-8
// 账号 root
// 密码 root
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/jdbc_demo?characterEncoding=UTF-8","root","root");
System.out.println("连接成功:" + connection);
}catch (ClassNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Connection是与特定数据库连接会话的接口,使用的时候需要导包,而且必须在程序结束的时候将其关闭。DriverManager.getConnection方法也需要捕获SQLException异常。
因为在进行数据库的增删改查的时候都需要与数据库建立连接,所以可以在项目中将建立连接写成一个工具方法,用的时候直接调用即可:
package com.bluemsun.zbc.util;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class DBUtil {
public static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/jdbc_demo?characterEncoding=UTF-8";
public static final String USER = "root";
public static final String PASSWORD = "root";
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection connection = null;
try{
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL,USER,PASSWORD);
}catch (ClassNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return connection;
}
}
三.创建Statement或者PreparedStatement接口,执行SQL语句
- 使用Statement接口
package com.bluemsun.zbc.dao;
import com.bluemsun.zbc.util.DBUtil;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class StatementDemo {
public static Connection connection = null;
public static Statement statement = null;
public static void main(String[] args){
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "INSERT INTO `user` ( id, user_name, `password`, grades ) VALUES( " + 1 + ", '曾波淳', " + 123456 + "," + 100 + " )";
statement.execute(sql);
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (statement != null){
try {
statement.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (connection != null){
try {
connection.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
Statement接口创建之后,可以执行SQL语句,完成对数据库的增删改查。其中 ,增删改只需要改变SQL语句的内容就能完成,然而查询略显复杂。在Statement中使用字符串拼接的方式,该方式存在句法复杂,容易犯错等缺点,具体在下文中的对比中介绍。
- 使用PreparedStatement接口
与 Statement一样,PreparedStatement也是用来执行sql语句的与创建Statement不同的是,需要根据sql语句创建PreparedStatement。除此之外,还能够通过设置参数,指定相应的值,而不是Statement那样使用字符串拼接。
package com.bluemsun.zbc.dao;
import com.bluemsun.zbc.util.DBUtil;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class PreparedStatementDemo {
public static Connection connection = null;
public static PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
public static void main(String[] args){
String sql = "INSERT INTO `user` (id,user_name,`password`,grades) VALUES(?,?,?,?)";
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setInt(1,1);
preparedStatement.setString(2,"曾波淳");
preparedStatement.setString(3,"123456");
preparedStatement.setInt(4,100);
preparedStatement.execute();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (preparedStatement != null){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null){
try {
connection.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
由上面的增删改程序可以看出,他们的代码都是大同小异的,主要是SQL语句存在差异,其他的地方几乎是完全相同的。但是可以看到PreparedStatement比Statement方便很多。
- PreparedStatement的优点
1.Statement 需要进行字符串拼接,可读性和维护性比较差;PreparedStatement 使用参数设置,可读性好,不易犯错;
2.PreparedStatement有预编译机制,性能比Statement更快;
3.PreparedStatement能防止SQL注入式攻击;(比如攻击者请求数据为String userName = “‘曾波淳’ OR 1=1”;)
- excute、excuteQuery和excuteUpdate的使用方法以及区别
课上详解
四.处理和显示结果
执行查询语句,并把结果集返回给集合ResultSet,然后利用利用While(ResultSet.next()){…}循环将集合ResultSet中的结果遍历出来。代码如下:
package com.bluemsun.zbc.dao;
import com.bluemsun.zbc.entity.User;
import com.bluemsun.zbc.util.DBUtil;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class PreparedStatementDemo {
public static Connection connection = null;
public static PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
public static ResultSet resultSet = null;
public static void main(String[] args){
String sql = "select id,user_name,password,grades from `user` where grades=?";
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setInt(1,100);
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>();
while (resultSet.next()){
User user = new User();
user.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
user.setUserName(resultSet.getString("user_name"));
user.setPassword(resultSet.getString("password"));
user.setGrades(resultSet.getInt("grades"));
System.out.println(user.getUserName());
userList.add(user);
}
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (resultSet != null){
try {
resultSet.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (preparedStatement != null){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null){
try {
connection.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
五.释放资源
在JDBC编码的过程中我们创建了Connection、ResultSet等资源,这些资源在使用完毕之后是一定要进行关闭的。关闭的过程中遵循从里到外的原则。
package com.bluemsun.zbc.util;
import java.sql.*;
public class DBUtil {
public static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/jdbc_demo?characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=true";
public static final String USER = "root";
public static final String PASSWORD = "root";
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection connection = null;
try{
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL,USER,PASSWORD);
}catch (ClassNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return connection;
}
public static void close(Connection connection){
if (connection != null){
try{
connection.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void close(PreparedStatement preparedStatement){
if (preparedStatement != null){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void close(ResultSet resultSet){
if (resultSet != null){
try {
resultSet.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
事务
MySQL 事务主要用于处理操作量大,复杂度高的数据。比如说,在人员管理系统中,你删除一个人员,你既需要删除人员的基本资料,也要删除和该人员相关的信息,如信箱,文章等等,这样,这些数据库操作语句就构成一个事务!
一般来说,事务是必须满足4个条件(ACID)::原子性(Atomicity,或称不可分割性)、一致性(Consistency)、隔离性(Isolation,又称独立性)、持久性(Durability)。
- 原子性: 一个事务(transaction)中的所有操作,要么全部完成,要么全部不完成,不会结束在中间某个环节。事务在执行过程中发生错误,会被回滚(Rollback)到事务开始前的状态,就像这个事务从来没有执行过一样。
- 一致性: 在事务开始之前和事务结束以后,数据库的完整性没有被破坏。这表示写入的资料必须完全符合所有的预设规则,这包含资料的精确度、串联性以及后续数据库可以自发性地完成预定的工作。
- 隔离性: 数据库允许多个并发事务同时对其数据进行读写和修改的能力,隔离性可以防止多个事务并发执行时由于交叉执行而导致数据的不一致。事务隔离分为不同级别,包括读未提交(Read uncommitted)、读提交(read committed)、可重复读(repeatable read)和串行化(Serializable)。
- 持久性: 事务处理结束后,对数据的修改就是永久的,即便系统故障也不会丢失。
如果有一个记录学生考试成绩的表,由于之前系统错误的原因,将ben的一部分分数加到了lisa的成绩上。我们现在要将它改正过来,就需要执行两步,先把lisa的成绩减少,再把ben的成绩增加。这两步操作要不一起成功,要不一起失败,不能一个成功一个失败,如果那样的话就会出错,这就是一个事务。
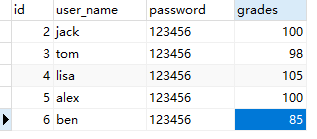
package com.bluemsun.zbc.dao;
import com.bluemsun.zbc.util.DBUtil;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class TransactionDemo {
public static Connection connection = null;
public static PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
public static ResultSet resultSet = null;
public static void main(String[] args){
String sql = "update student set score=? where user_name=?";
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 有事务的前提下
// 在事务中的多个操作,要么都成功,要么都失败
//关闭自动提交
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
preparedStatement.setInt(1,95);
preparedStatement.setString(2,"lisa");
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
preparedStatement.setInt(1,95);
preparedStatement.setString(2,"ben");
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
//手动提交
connection.commit();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
DBUtil.close(resultSet);
DBUtil.close(preparedStatement);
DBUtil.close(connection);
}
}
}