深入理解Vector
Vector原理:基于数组
//元素存储区
protected Object[] elementData;
//Vector 集合大小
protected int elementCount;
为什么说Vector会有是线程安全的?
从下面的构造方法还有增删改查的操作可以看见,都有这么一个synchronized关键字,就是这个关键字为Vector容器提供了一个安全机制,保证了线程安全。
Vector类图关系:
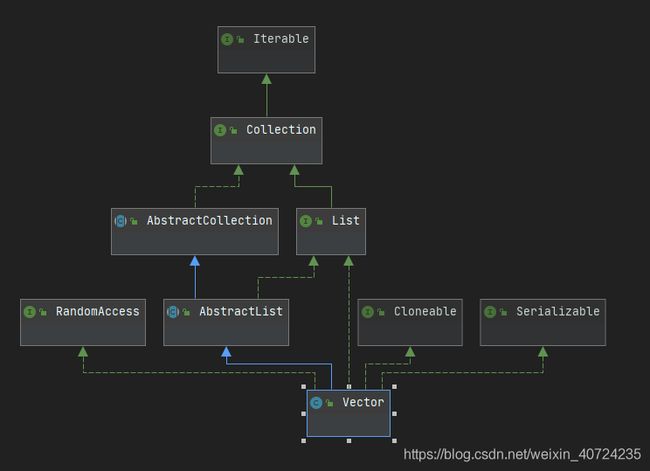
RandomAccess 支持可随机访问元素
Cloneable 支持可克隆功能
Serializable 支持该集合可序列化,
Vector 继承了AbstractList,实现了List接口
构造函数 一共有四个
//initialCapacity 初始容量 capacityIncrement扩容增长系数
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
//构造初始容量为initialCapacity的一个空Vector
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
//构造初始容量为10的一个空Vector
public Vector() {
this(10);
}
//根据一个非空集合,来构造一个新的Vector
public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
elementCount = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, Object[].class);
}
添加元素 (注意有synchronized关键字修饰)
1,将指定的元素追加到此Vector的末尾
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this Vector.
* 。
*/
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}
ensureCapacityHelper()方法 ,判断原始容量够不够,不够就扩容
//minCapacity 是添加新元素之后的容量 ,elementData.length原始容量
//如果mincapacity比原始容量大,就按照minCapacity 来扩容
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
扩容细节
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
//minCapacity加上扩容系数即可得新的容量
//如果没有指定增长系数,则按照原始容量x2扩容
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
//扩容系数比较小的时候,仍会会出现容量不足
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
//直接让当前容量覆盖 原始容量(新扩容容量)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
//MAX_ARRAY_SIZE=Integer.MAX_VALUE-8=2147483647-8
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
hugeCapacity()方法 ,最大扩容量
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
2,在指定的位置添加元素
public void add(int index, E element) {
insertElementAt(element, index);
}
insertElementAt()细节 (注意有synchronized关键字修饰)
public synchronized void insertElementAt(E obj, int index) {
modCount++;
//下标是否合规(不超出最大容量即可)
if (index > elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index
+ " > " + elementCount);
}
//是否还有足够的容量,不够就自动扩容
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, elementCount - index);
elementData[index] = obj;
elementCount++;
}
System.arraycopy 将指定源数组中的数组从指定位置复制到目标数组的指定位置参数说明
public static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length)
代码解释:
Object src : 原数组
int srcPos : 从元数据的起始位置开始
Object dest : 目标数组
int destPos : 目标数组的开始起始位置
int length : 要copy的数组的长度
删除元素(注意有synchronized关键字修饰)
public synchronized boolean removeElement(Object obj) {
modCount++;
int i = indexOf(obj);
if (i >= 0) {
removeElementAt(i);
return true;
}
return false;
}
removeElement()方法 (注意有synchronized关键字修饰)
public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
modCount++;
//下标是否合法
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
//下标是否合法
else if (index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
//将有numMOved个元素要移动
int j = elementCount - index - 1;
if (j > 0) {
//将index后面的元素整体向前移一步
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);
}
elementCount--;
elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
}
删除指定位置的元素 (注意有synchronized关键字修饰)
public synchronized E remove(int index) {
modCount++;
//下标是否合法
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
//取出指定下标的元素
E oldValue = elementData(index);
//将有numMOved个元素要移动
int numMoved = elementCount - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
//将index后面的元素整体向前移一步
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
//最后一个位置设空
elementData[--elementCount] = null; // Let gc do its work
//返回删除的元素
return oldValue;
更改元素(注意有synchronized关键字修饰)
public synchronized void setElementAt(E obj, int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
elementData[index] = obj;
}
查找元素
方法一 是否包含该元素
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o, 0) >= 0;
}
方法二 返回出现第一个目标元素的下标
public int indexOf(Object o) {
return indexOf(o, 0);
}
indexOf()方法
public synchronized int indexOf(Object o, int index) {
//分两种情况,一种是null,一种是非null
if (o == null) {
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
//这里相当于查找空值的位置
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
//查找非空值目标位置
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
方法三 查询最后一次出现的指定元素的索引
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
return lastIndexOf(o, elementCount-1);
}
lastIndexOf()方法
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o, int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= "+ elementCount);
if (o == null) {
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}