反射之使用自定义注解并处理自定义注解
注解:说起注解初学者可能不太明白,annotation是jdk1.5 引入的新特性,中文名叫注解,它提供了一种安全的类似注释的机制,用来将任何的信息或元数据(metadata)与程序元素(类、方法、成员变量等)进行关联。为程序的元素(类、方法、成员变量)加上更直观更明了的说明,这些说明信息是与程序的业务逻辑无关,并且供指定的工具或框架使用。Annontation像一种修饰符一样,应用于包、类型、构造方法、方法、成员变量、参数及本地变量的声明语句中。
什么是元注解?
java.lang.annotation提供了四种元注解,专门注解其他的注解(在自定义注解的时候,需要使用到元注解):
@Documented –注解是否将包含在JavaDoc中
@Retention –什么时候使用该注解
@Target –注解用于什么地方
@Inherited – 是否允许子类继承该注解
1.)@Retention– 定义该注解的生命周期
● RetentionPolicy.SOURCE : 在编译阶段丢弃。这些注解在编译结束之后就不再有任何意义,所以它们不会写入字节码。@Override, @SuppressWarnings都属于这类注解。
● RetentionPolicy.CLASS : 在类加载的时候丢弃。在字节码文件的处理中有用。注解默认使用这种方式
● RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME : 始终不会丢弃,运行期也保留该注解,因此可以使用反射机制读取该注解的信息。我们自定义的注解通常使用这种方式。
2.)Target – 表示该注解用于什么地方。默认值为任何元素,表示该注解用于什么地方。可用的ElementType参数包括
● ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR:用于描述构造器
● ElementType.FIELD:成员变量、对象、属性(包括enum实例)
● ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE:用于描述局部变量
● ElementType.METHOD:用于描述方法
● ElementType.PACKAGE:用于描述包
● ElementType.PARAMETER:用于描述参数
● ElementType.TYPE:用于描述类、接口(包括注解类型) 或enum声明
3.)@Documented–一个简单的Annotations标记注解,表示是否将注解信息添加在java文档中。
4.)@Inherited – 定义该注释和子类的关系
@Inherited 元注解是一个标记注解,@Inherited阐述了某个被标注的类型是被继承的。如果一个使用了@Inherited修饰的annotation类型被用于一个class,则这个annotation将被用于该class的子类。
自定义注解:
自定义注解类编写的一些规则:
1. Annotation型定义为@interface, 所有的Annotation会自动继承java.lang.Annotation这一接口,并且不能再去继承别的类或是接口.
2. 参数成员只能用public或默认(default)这两个访问权修饰
3. 参数成员只能用基本类型byte,short,char,int,long,float,double,boolean八种基本数据类型和String、Enum、Class、annotations等数据类型,以及这一些类型的数组.
4. 要获取类方法和字段的注解信息,必须通过Java的反射技术来获取 Annotation对象,因为你除此之外没有别的获取注解对象的方法
5. 注解也可以没有定义成员, 不过这样注解就没啥用了
PS:自定义注解需要使用到元注解
例如,这里定义 三个注解,StudentName,StudentAge,StudentSchool
代码示例:
@Target(value=ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface StudentName {
/**
* default 后面跟默认值
* @return
*/
String value() default "";
}@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(value=ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface StudentAge {
int value() default -1;
}public @interface StudentSchool {
String [] value() default {};
}
Student 类:
/**
* 学生类
* @author snow
*
*/
public class Student {
@StudentName(value="zhangzq")
public String name;
@StudentSchool(value="清华大学")
public String school;
@StudentAge(value=17)
public int age;
}这里使用第三个类,利用反射进行读取注解的数据
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.zzq.reflect.anotation.Student");
// 获取所有字段
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
// 判断该字段是否被 StudentAge 注解修饰了
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(StudentAge.class)) {
// 获取 字段上的 注解
StudentAge annotationAge = field.getAnnotation(StudentAge.class);
// 获取值
System.out.println( "年龄是:" + annotationAge.value() );
}
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(StudentName.class)) {
StudentName annotationName = field.getAnnotation(StudentName.class);
System.out.println( "姓名是:" + annotationName.value() );
}
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(StudentSchool.class)) {
StudentSchool annotationSchool = field.getAnnotation(StudentSchool.class);
System.out.println( "学校是:" + Arrays.toString(annotationSchool.value()) );
}
}
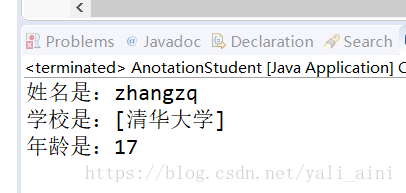
}运行效果: