缓存加速--Squid代理服务器应用(ACL 访问控制、 Squid 日志分析、反向代理)
文章目录
- 一、 ACL 访问控制
-
- 1.1 定义访问控制列表
- 1.2 设置访问权限
- 1.3 ACL 访问控制实验(基于传统模式)
-
- 1. 手工编译安装squid
- 2. 修改配置文件
- 3. 传统代理配置
- 4. 在web服务器上安装httpd,并启动服务
- 5. 在win10虚拟机上测试,传统代理是否配置成功
- 6. 进行ACL列表访问控制
- 二、Squid 日志分析
-
- 2.1 安装部署SARG
- 三、 squid反向代理
-
- 3.1 工作机制
- 3.2 搭建squid反向代理
一、 ACL 访问控制
Squid 提供了强大的代理控制机制,通过合理设置 ACL(Access Control List,访问控制列表)并进行限制,可以针对源地址、目标地址、访问的 URL 路径、访问的时间等各种条件进行过滤。
在配置文件 squid.conf 中,ACL 访问控制通过以下两个步骤来实现:
- 使用 acl 配置项定义需要控制的条件;
- 通过 http_access 配置项对已定义的列表做“允许”或“拒绝”访问的控制。
1.1 定义访问控制列表
每行 acl 配置可以定义一条访问控制列表
acl格式
acl 列表名称 列表类型 列表内容 …
- 列表名称可以自行指定,用来识别控制条件。
- 列表类型必须使用 Squid 预定义的值,对应不同类别的控制条件;常用的包括源地址、目标地址、访问时间、 访问端口等。
- 列表内容是要控制的具体对象,不同类型的列表所对应 的内容也不一样,可以有多个值(以空格分隔,为“或”的关系)。
| 列表类型 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| src | 源 IP 地址、网段、IP 地址范围,多个地址之间以空格分隔 |
| dst | 目标 IP 地址、网段、主机名 ,多个地址之间以空格分隔 |
| port | 目标端口 |
| dstdomain | 目标域,匹配域内所有站点 |
| time | 使用代理服务的时间段,例如MTWHF 、8:30-17:30 12:00-13:00、 AS;字母表示一星期中各天的英文缩写M—Monday 、 T—Tuesday 、 W—Wednesday 、 H—Thursday、F—Friday、A—Saturday、S—Sunday |
| maxconn | 每个客户机的并发连接数 |
| url_regex | 目标资源的 URL 地址,-i 表示忽略大小写 |
| urlpath_regex | 网址中主机名后面的部分,-i 表示忽略大小写 |
在定义访问控制列表时,应该根据需求来,精确控制。当需要限制的同一类对象较多时,可以使用独立的文件来存放,在 acl 配置行的列表内容处指定对应的文件位置即可,这里指的是文件的绝对路径。
1.2 设置访问权限
定义好各种访问控制列表以后,需要使用 httpd_access 配置项来进行控制。必须注意的是,http_access 配置行必须放在对应的 acl 配置行之后。每行 http_access 配置确定一条访问控制规则。
格式
http_access allow 或 deny 列表名……
在每条 http_access 规则中,可以同时包含多个访问控制列表名,各个列表之间以空格 分隔,为“与”的关系,表示必须满足所有访问控制列表对应的条件才会进行限制。需要使用 取反条件时,可以在访问控制列表前添加“!”符号。
- http_access deny MEDIAFILE —> 禁止客户机下载 MP3、MP4 等文件
- http_access deny IPBLOCK —> 禁止客户机访问黑名单中的 IP 地址
- http_access deny DMBLOCK —> 禁止客户机访问黑名单中的网站域
- http_access deny MC20 —> 客户机的并发连接超过 20 时将被阻止
- http_access allow WORKTIME —> 允许客户机在工作时间上网
- http_access deny all —> 默认禁止所有客户机使用代理
执行访问控制时,Squid 将按照各条规则的顺序依次进行检查,如果找到一条相匹配的规则就不再向后搜索。
- 没有设置任何规则时:Squid 服务将拒绝客户端的请求。
- 有规则但找不到相匹配的项:Squid 将采用与最后一条规则相反的动作,即如果最后一条规则是 allow,就拒绝客户端的请求,否则允许该请求。
通常情况下,把最常用到的控制规则放在最前面,以减少 Squid 的负载。在访问控制的总体策略上,建议采用“先拒绝后允许”或“先允许后拒绝”的方式,最后一条规则设为默认策略,设为“http_access allow all”或者“http_access deny all”。
1.3 ACL 访问控制实验(基于传统模式)
1. 手工编译安装squid
手工编译过程在做传统代理的时候就安装过了,可以参考https://blog.csdn.net/kimowinter/article/details/108430935这篇博客。
2. 修改配置文件
[root@localhost init.d]# vim /etc/squid.conf
http_access allow all
cache_effective_user squid
cache_effective_group squid
[root@localhost init.d]# squid -k parse ##检查语法
[root@localhost init.d]# squid -z ##初始化缓存
[root@localhost init.d]# service squid start
正在启动 squid....
[root@localhost init.d]# netstat -ntap | grep squid
tcp6 0 0 :::3128 :::* LISTEN 49191/(squid-1)
3. 传统代理配置
[root@localhost init.d]# vim /etc/squid.conf
cache_mem 64 MB ##自定义缓存空间大小,容量最好为4的倍数
reply_body_max_size 10 MB ##允许下载最大文件大小,以字节为单位,默认设置0表示不进行限制
maximum_object_size 4096 KB ##允许保存到缓存空间的最大对象的大小,以KB为单位,超过限制不会缓存,直接转到web端
[root@squid init.d]# iptables -F
[root@squid init.d]# iptables -t nat -F
[root@squid init.d]# setenforce 0
[root@squid init.d]# iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 3128 -j ACCEPT
[root@squid init.d]# service squid reload
4. 在web服务器上安装httpd,并启动服务
[root@localhost ~]# yum install httpd -y
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start httpd
[root@localhost ~]# netstat -antp | grep httpd
tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 80909/httpd
5. 在win10虚拟机上测试,传统代理是否配置成功
在web服务器上查看
[root@localhost ~]# cat /var/log/httpd/access_log
6. 进行ACL列表访问控制
有两种方法设置
方法一:
直接在条目中写出来,适用于写入条目比较少的情况
[root@localhost init.d]# vim /etc/squid.conf
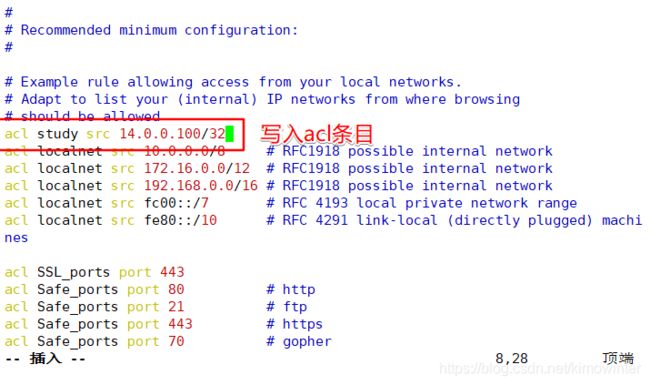
acl study src 14.0.0.100/32
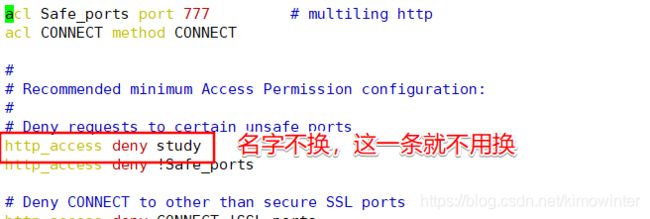
http_access deny study
[root@localhost init.d]# service squid reload
方法二:
在配置文件中指明一个文件的绝对路径,这个文件中写入需要进行访问控制的IP、网段或域名等等。
先将之前写的acl条目注释掉,在win10进行访问

[root@localhost init.d]# vim /etc/squid.conf
acl study src "/etc/squid/study.list"
http_access deny study
[root@localhost init.d]# mkdir /etc/squid
[root@localhost init.d]# cd /etc/squid/
[root@localhost squid]# touch study.list
[root@localhost squid]# vim study.list
[root@localhost init.d]# service squid reload
二、Squid 日志分析
SARG 全称是 SquidAnalysis Report Generator,是一款 Squid 日志分析工具,采用HTML 格式,详细列出每位用户访问 Internet 的站点信息、时间占用信息、排名、连接次数、访问量等。
2.1 安装部署SARG
安装包拷贝到当前目录下
[root@localhost ~]# tar zvxf sarg-2.3.7.tar.gz -C /opt ##解压到/opt目录下
[root@localhost ~]# yum install gd gd-devel -y
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /usr/local/sarg
[root@localhost ~]# cd /opt/sarg-2.3.7/
[root@localhost sarg-2.3.7]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/sarg \ ##指定sarg目录
--sysconfdir=/etc/sarg \ ##配置文件
--enable-extraprotection ##开启安全防护
[root@localhost sarg-2.3.7]# make && make install ##编译安装
[root@localhost sarg-2.3.7]# cd /etc/sarg/
[root@localhost sarg]# vim sarg.conf
配置文件中默认注释了所有的文件,需要取消注释激活功能
7行
access_log /usr/local/squid/var/logs/access.log ##指定访问日志文件
25行
title "Squid User Access Reports" ##网页标题
120行
output_dir /var/www/html/squid-reports ##报告输出目录
178行
user_ip no ##使用用户名显示
184行
topuser_sort_field connect reverse ##top排序中有连接次数,访问字节,降序排列,升序是normal
190行(一定要注释掉,否则报错)
#user_sort_field BYTES reverse ##用户访问记录连接次数、访问字节按降序排序
206行
exclude_hosts /usr/local/sarg/noreport ##不计入排序的站点列表文件
257行
overwrite_report no ##同名日志是否覆盖
289行
mail_utility mailq.postfix ##发送邮件报告命令
434行
charset UTF-8 ##使用字符集
518行
weekdays 0-6 ##top排行的时间周期
525行
hours 0-23 ##top排行的时间周期
633行
www_document_root /var/www/html ##网页根目录
[root@localhost sarg]# touch /usr/local/sarg/noreport ##添加不计入站点文件,添加的域名将不被显示
[root@localhost sarg]# ln -s /usr/local/sarg/bin/sarg /usr/local/bin/ ##建sarg命令的软连接
[root@localhost sarg]# sarg ##生成报告
[root@localhost sarg]# sarg
SARG: 纪录在文件: 294, reading: 100.00%
SARG: 成功的生成报告在 /var/www/html/squid-reports/2020Sep07-2020Sep07 ##提示报告生成在这个目录,我们进入这个目录查看
[root@localhost sarg]# ls /var/www/html/squid-reports/
2020Sep07-2020Sep07 images index.html
这个目录是httpd的站点目录,所以我们要安装httpd服务
[root@localhost sarg]# yum install httpd -y
[root@localhost sarg]# systemctl start httpd
在win10虚拟机中查看日志统计

如果我们把win10的地址换一个,在重新生成日志,日志系统也会改变
[root@localhost sarg]# sarg -l /usr/local/squid/var/logs/access.log -o /var/www/html/squid-reports/ -z -d $(date -d "1 day ago" +%d/%m/%Y)-$(date +%d/%m/%Y)
三、 squid反向代理
如果Squid反向代理服务器中缓存了该请求的资源,则将该请求的资源直接返回给客户端;否则反向代理服务器将向后台的WEB服务器请求资源,然后将请求的应答返回给客户端,同时也将该应答缓存在本地,供下一个请求者使用。
3.1 工作机制
- 缓存网页对象,减少重复请求
- 将互联网请求轮训或按权重分配到内网Web服务器
- ·代理用户请求,避免用户直接访问Web服务器,提高安全
3.2 搭建squid反向代理
在14.0.0.110web服务器上写一个网页首页
[root@localhost ~]# cd /var/www/html/
[root@localhost html]# vim index.html
<h1>this is web01</h1>
开启另一台web服务器14.0.0.177,安装httpd,并写入网页首页
[root@localhost ~]# yum install httpd -y
[root@localhost ~]# cd /var/www/html/
[root@localhost html]# vim index.html
<h1>this is web02</h1>
[root@localhost html]# systemctl start httpd
[root@localhost html]# iptables -F
[root@localhost html]# setenforce 0
[root@localhost sarg]# vim /etc/squid.conf
http_port 14.0.0.7:80 accel vhost vport
cache_peer 14.0.0.110 parent 80 0 no-query originserver round-robin max_conn=30 weight=1 name=web1
cache_peer 14.0.0.177 parent 80 0 no-query originserver round-robin max_conn=30 weight=1 name=web2
cache_peer_domain web1 web2 www.yun.com

因为监听的是80端口,所以需要将做日志分析的httpd服务停掉,否则80端口被占用,会导致的服务重载失败,也可以换一个其他的端口。
[root@localhost sarg]# systemctl stop httpd
[root@localhost ~]# service squid restart
正在关闭 squid...
正在启动 squid...
最后在win10虚拟机中进行设置,并测试

改hosts文件,将IP与域名的对应关系修改与squid中一致,hosts文件路径:C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc

编辑hosts文件