OKHttp 快速开始
OKHttp 快速开始
- OKHttp 快速开始
-
- 同步请求
-
- get
- 异步请求
-
- get
- post
- 设置请求头
- 下载文件
- 封装
- 拦截器
-
-
-
-
- 应用拦截器
- 网络连接器
-
-
-
OKHttp 快速开始
官方网址:https://square.github.io/okhttp/
代码仓库:https://github.com/square/okhttp
该库是一个第三方库,用于请求网络,支持同步和异步两种请求方式
同步请求
get
对于同步请求在请求时需要开启子线程,请求成功后需要跳转到UI线程修改UI。
public void getDatasync(){
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();//创建OkHttpClient对象
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://www.baidu.com")//请求接口。如果需要传参拼接到接口后面。
.build();//创建Request 对象
Response response = null;
response = client.newCall(request).execute();//得到Response 对象
if (response.isSuccessful()) {
Log.d("kwwl","response.code()=="+response.code());
Log.d("kwwl","response.message()=="+response.message());
Log.d("kwwl","res=="+response.body().string());
//此时的代码执行在子线程,修改UI的操作请使用handler跳转到UI线程。
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
此时打印结果如下:
response.code()==200;
response.message()OK;
res{“code”:200,“message”:success};
注意事项:
Response.code是http响应行中的code,如果访问成功则返回200.这个不是服务器设置的,而是http协议中自带的。res中的code才是服务器设置的。注意二者的区别。response.body().string()本质是输入流的读操作,所以它还是网络请求的一部分,所以这行代码必须放在子线程。response.body().string()只能调用一次,在第一次时有返回值,第二次再调用时将会返回null。原因是:response.body().string()的本质是输入流的读操作,必须有服务器的输出流的写操作时客户端的读操作才能得到数据。而服务器的写操作只执行一次,所以客户端的读操作也只能执行一次,第二次将返回null。
异步请求
get
这种方式不用再次开启子线程,但回调方法是执行在子线程中,所以在更新UI时还要跳转到UI线程中。
使用示例如下:
private void getDataAsync() {
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://www.baidu.com")
.build();
client.newCall(request).enqueue(new Callback() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) {
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException {
if(response.isSuccessful()){
//回调的方法执行在子线程。
Log.d("kwwl","获取数据成功了");
Log.d("kwwl","response.code()=="+response.code());
Log.d("kwwl","response.body().string()=="+response.body().string());
}
}
});
}
异步请求的打印结果与注意事项与同步请求时相同。最大的不同点就是异步请求不需要开启子线程,enqueue方法会自动将网络请求部分放入子线程中执行。
注意事项:
- 回调接口的onFailure方法和onResponse执行在子线程。
response.body().string()方法也必须放在子线程中。当执行这行代码得到结果后,再跳转到UI线程修改UI。
post
private void postDataWithParame() {
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();//创建OkHttpClient对象。
FormBody.Builder formBody = new FormBody.Builder();//创建表单请求体
formBody.add("username","zhangsan");//传递键值对参数
Request request = new Request.Builder()//创建Request 对象。
.url("http://www.baidu.com")
.post(formBody.build())//传递请求体
.build();
client.newCall(request).enqueue(new Callback() {
。。。});//回调方法的使用与get异步请求相同,此时略。
}
注意:request.post接受的是一个requestbody对象,只要是该对象的子类,都可以作为参数传递,而formbody就是该对象的一个子类
传参总结:
字符串key value对:
参考上面的表单体
json串:
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();//创建OkHttpClient对象。 MediaType mediaType = MediaType.parse("application/json; charset=utf-8");//数据类型为json格式, String jsonStr = "{\"username\":\"lisi\",\"nickname\":\"李四\"}";//json数据. RequestBody body = RequestBody.create(mediaType, josnStr); Request request = new Request.Builder() .url("http://www.baidu.com") .post(body) .build(); client.newCall(request).enqueue(new Callback() { 。。。});//此处省略回调方法。文件对象:
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();//创建OkHttpClient对象。 MediaType fileType = MediaType.parse("File/*");//数据类型为json格式, File file = new File("path");//file对象. RequestBody body = RequestBody.create(fileType , file ); Request request = new Request.Builder() .url("http://www.baidu.com") .post(body) .build(); client.newCall(request).enqueue(new Callback() { 。。。});//此处省略回调方法。混合对象:
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient(); MultipartBody multipartBody =new MultipartBody.Builder() .setType(MultipartBody.FORM) .addFormDataPart("groupId",""+groupId)//添加键值对参数 .addFormDataPart("title","title") .addFormDataPart("file", file.getName(), RequestBody.create(MediaType.parse("file/*"), file))//添加文件 .build(); final Request request = new Request.Builder() .url(URLContant.CHAT_ROOM_SUBJECT_IMAGE) .post(multipartBody) .build(); client.newCall(request).enqueue(new Callback() { 。。。});注意:addFormDataPart和addPart并无区别,只是多了一层封装
/** Add a form data part to the body. */ public Builder addFormDataPart(String name, String value) { return addPart(Part.createFormData(name, value)); } /** Add a form data part to the body. */ public Builder addFormDataPart(String name, String filename, RequestBody body) { return addPart(Part.createFormData(name, filename, body)); } public static Part createFormData(String name, String value) { return createFormData(name, null, RequestBody.create(null, value)); } public static Part createFormData(String name, String filename, RequestBody body) { if (name == null) { throw new NullPointerException("name == null"); } StringBuilder disposition = new StringBuilder("form-data; name="); appendQuotedString(disposition, name); if (filename != null) { disposition.append("; filename="); appendQuotedString(disposition, filename); } return create(Headers.of("Content-Disposition", disposition.toString()), body); }流对象:
RequestBody body = new RequestBody() { @Override public MediaType contentType() { return null; } @Override public void writeTo(BufferedSink sink) throws IOException { //重写writeTo方法 FileInputStream fio= new FileInputStream(new File("fileName")); byte[] buffer = new byte[1024*8]; if(fio.read(buffer) != -1){ sink.write(buffer); } } }; OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();//创建OkHttpClient对象。 Request request = new Request.Builder() .url("http://www.baidu.com") .post(body) .build(); client.newCall(request).enqueue(new Callback() { 。。。});以上代码的与众不同就是body对象,这个body对象重写了write方法,里面有个sink对象。这个是OKio包中的输出流,有write方法。使用这个方法我们可以实现上传流的功能。
使用RequestBody上传文件时,并没有实现断点续传的功能。我可以使用这种方法结合RandomAccessFile类实现断点续传的功能
设置请求头
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://www.baidu.com")
.header("User-Agent", "OkHttp Headers.java")
.addHeader("token", "myToken")
.build();
下载文件
在OKHttp中并没有提供下载文件的功能,但是在Response中可以获取流对象,有了流对象我们就可以自己实现文件的下载。代码如下:
这段代码写在回调接口CallBack的onResponse方法中:
try{
InputStream is = response.body().byteStream();//从服务器得到输入流对象
long sum = 0;
File dir = new File(mDestFileDir);
if (!dir.exists()){
dir.mkdirs();
}
File file = new File(dir, mdestFileName);//根据目录和文件名得到file对象
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
byte[] buf = new byte[1024*8];
int len = 0;
while ((len = is.read(buf)) != -1){
fos.write(buf, 0, len);
}
fos.flush();
return file;
}
文件下载的另外一个例子:
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(url)
.build();
client.newCall(request).enqueue(new Callback() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException {
if (response.isSuccessful()){
downlodefile(response, Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getAbsolutePath(),"text.txt");
}
}
});
private void downlodefile(Response response, String url, String fileName) {
InputStream is = null;
byte[] buf = new byte[2048];
int len = 0;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
is = response.body().byteStream();
//文件大小
long total = response.body().contentLength();
File file = new File(url, fileName);
fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
long sum = 0;
while ((len = is.read(buf)) != -1) {
fos.write(buf, 0, len);
// 进度条
// sum += len;
// int progress = (int) (sum * 1.0f / total * 100);
}
fos.flush();
Log.e("xxxxxxxx", "下载成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
try {
if (is != null)
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
try {
if (fos != null)
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
封装
对于OKHttp的封装首推的就是hongyang大神的OKHttpUtils
拦截器
Interceptors是Okhttp中的拦截器,官方介绍拦截器是一个强大的监听器,可以重写,重试请求(calls)详细了解可以看下Okhttp-wiki 之 Interceptors 拦截器,这篇文章可以算是中文版。
Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException {
// Build a full stack of interceptors.
List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
interceptors.addAll(client.interceptors());
interceptors.add(retryAndFollowUpInterceptor);
interceptors.add(new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar()));
interceptors.add(new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache()));
interceptors.add(new ConnectInterceptor(client));
if (!forWebSocket) {
interceptors.addAll(client.networkInterceptors());
}
interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket));
Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain(
interceptors, null, null, null, 0, originalRequest);
return chain.proceed(originalRequest);
}
从这可以发现okhttp在处理网络响应时采用的是拦截器机制。okhttp用ArrayList对interceptors进行管理,interceptors将依次被调用。
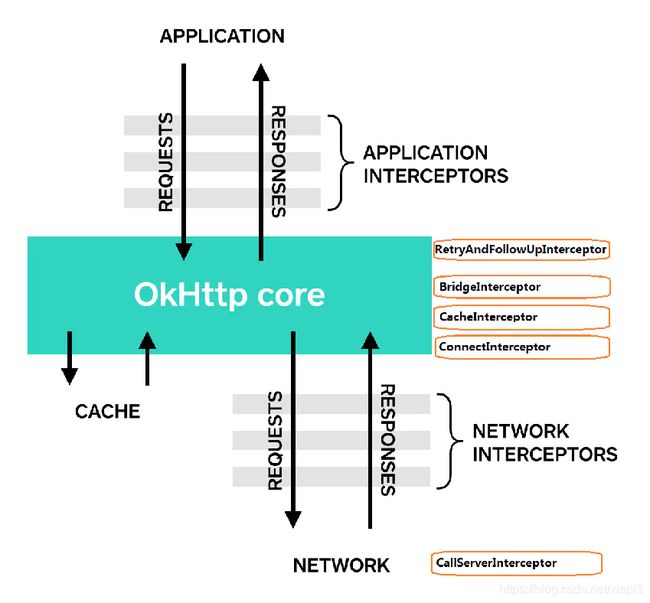
如上图:
-
橙色框内是okhttp自带的Interceptors的实现类,它们都是在call.getResponseWithInterceptorChain()中被添加入 InterceptorChain中,实际上这几个Interceptor都是在okhttp3后才被引入,它们非常重要,负责了重连、组装请求头部、读/写缓存、建立socket连接、向服务器发送请求/接收响应的全部过程。
-
在okhttp3之前,这些行为都封装在HttpEngine类中。okhttp3之后,HttpEngine已经被删去,取而代之的是这5个Interceptor,可以说一次网络请求中的细节被解耦放在不同的Interceptor中,不同Interceptor只负责自己的那一环节工作(对Request或者Response进行获取/处理),使得拦截器模式完全贯穿整个网络请求。
-
用户可以添加自定义的Interceptor,okhttp把拦截器分为应用拦截器和网络拦截器
public class OkHttpClient implements Cloneable, Call.Factory {
final List<Interceptor> interceptors;
final List<Interceptor> networkInterceptors;
......
}
- 调用OkHttpClient.Builder的addInterceptor()可以添加应用拦截器,只会被调用一次,可以处理网络请求回来的最终Response
- 调用addNetworkInterceptor()可以添加network拦截器,处理所有的网络响应(一次请求如果发生了redirect ,那么这个拦截器的逻辑可能会被调用两次)
- Application interceptors与Network Interceptors
应用拦截器
不需要担心中间过程的响应,如重定向和重试.
总是只调用一次,即使HTTP响应是从缓存中获取.
观察应用程序的初衷. 不关心OkHttp注入的头信息如: If-None-Match.
允许短路而不调用 Chain.proceed(),即中止调用.
允许重试,使 Chain.proceed()调用多次.
网络连接器
能够操作中间过程的响应,如重定向和重试.
当网络短路而返回缓存响应时不被调用.
只观察在网络上传输的数据.
携带请求来访问连接.
CopyFrom:
https://blog.csdn.net/fightingxia/article/details/70947701
https://www.jianshu.com/p/f5320b1e0287
Reference:
OkHttp源码解析——HTTP请求的逻辑流程
Okhttp-wiki 之 Interceptors 拦截器