SpringBoot
SpringBoot
1、SpringBoot 简介
设计目的:简化 Spring应用的 初始搭建及开发过程
SpringBoot = SpringMVC + Spring
2、SpringBoot 的特点
1. 嵌入 Tomcat ,无需部署 WAR 文件
2. 简化 Maven 配置
3. 自动配置 Spring,没有 xml 配置
3、SpringBoot 的约定大于配置
1. SpringBoot 项目必须在 src/main/resources 中放入 application.yml(.properties) 核心配置文件
2. SpringBoot 项目必须在 src/main/java 中所有子包之外构建全局入口类型:xxxApplication.java 一个项目中只能有一个
4、快速开始
搭建环境
在 pom.xml 中
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASEversion>
parent>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
根据约定创建相应的目录
第一个测试程序
//@EnableAutoConfiguration //作用:开启自动配置 初始化spring环境 初始化springmvc环境
//@ComponentScan //作用:用来扫描相关注解 扫描范围:当前入口类及其所在的子包
//@SpringBootApplication = @ComponentScan + @EnableAutoConfiguration + @SpringBootConfiguration
@SpringBootApplication 注解就有了自动配置功能 、扫描包功能。
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//SpringApplication spring应用类 作用:用来启动springboot应用
//参数1:传入入口类的类对象 参数2:main函数的参数
SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}
}
//cf.duanzifan.controller.HelloController
@RestController
@Requestmappering("/hello")
public class HelloController{
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
System.out.println("hello springboot!!!!!");
return "hello world";
}
}
5、注解详解
1. @EnableAutoConfiguration:开启自动配置,修饰范围:只能在类上
根据 pom.xml 文件中依赖自动判断,例如:我们引入 spring-boot-starter-web,会自动根据引入的这个依赖构建相关环境【springmvc环境 web容器环境】
2. @ComponentScan:开启注解扫描,修饰范围:只能在类中
扫描范围:默认当前包及其子包
3. @SpringBootApplication:有了此注解就有了自动配置和扫描包的作用
@SpringBootApplication==@ComponentScan + @EnableAutoConfiguration + @SpringBootConfiguration
4. @RestController:用来实例化对象为控制器对象,并将类中方法的返回值转为json,修饰范围:用在类上
@RestController==@Controller(实例化为一个控制器) + @ResponseBody(将方法返回值转为json,响应)
5. @RequestMapping:用来加入访问路径,修饰范围:方法上,类上
@GetMapping:限定请求方式只能是 GET 并指定路径,修饰范围:方法上
类似的:@PostMapping
6、main 方法
作用:
1. 通过标准的 java 入口的方式,委托给SpringApplication,并告知springboot主应用类是谁
2. 通过上面来启动 springboot 的 Tomcat 容器
3. args作用:可以在启动时指定外部参数。
7、自动配置 和 starters
自动配置:pom.xml
- spring-boot-starter-parent ====> spring-boot-dependencies:核心依赖全在这个的父工程中
- 我们在引入springboot依赖的时候,不需要指定版本,就是因为有这些版本仓库
starters:启动器,是一组方便的依赖关系描述符
spring-boot-starter-xxx
例如
spring-boot-starter-web
就会自动导入web环境的所有依赖
8、配置Bean
在 Springboot 中提供了两中方式配置 class,管理javaBean
1. 注解 【推荐】
@Configuration 注解类似于 @Component
2. xml 【了解】
9、Spring-boot banner
在资源文件中创建 banner.txt 在里面书写内容就可以改变默认的 banner
- 默认banner
- 设置 banner
${AnsiColor.BRIGHT_YELLOW}
// _ooOoo_ //
// o8888888o //
// 88" . "88 //
// (| ^_^ |) //
// O\ = /O //
// ____/`---'\____ //
// .' \\| |// `. //
// / \\||| : |||// \ //
// / _||||| -:- |||||- \ //
// | | \\\ - /// | | //
// | \_| ''\---/'' | | //
// \ .-\__ `-` ___/-. / //
// ___`. .' /--.--\ `. . ___ //
// ."" '< `.___\_<|>_/___.' >'"". //
// | | : `- \`.;`\ _ /`;.`/ - ` : | | //
// \ \ `-. \_ __\ /__ _/ .-` / / //
// ========`-.____`-.___\_____/___.-`____.-'======== //
// `=---=' //
// ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ //
// 佛祖保佑 永不宕机 永无BUG //
10、yml 配置文件
server:
port: 8080 #修改内嵌 tomcat 容器的端口号
servlet:
context-path: /springboot-01 #指定当前应用在部署到内嵌容器中的项目名
spring:
mvc:
view:
prefix: /
suffix: .jsp
11、properties 配置文件
server.port=8080
server.servlet.context-path=/springboot-01
spring.mvc.view.prefix=/
spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp
12、模板集成
springboot中有两种模板集成
1. jsp 页面模板 EL + jstl
2. thymeleaf 页面模板【推荐,默认】------------》【静态页面】
12.1 集成 jsp 模板
- 引入 jsp 的集成 jar 包
<dependency>
<groupId>jstlgroupId>
<artifactId>jstlartifactId>
<version>1.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embedgroupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasperartifactId>
dependency>
-
配置视图解析器
在 application.properties 文件中写入
spring.mvc.view.prefix=/
spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp
- 解决 idea 和 springboot 的一个 bug,才能正常找到
- 修改 jsp 无需重启应用
server.port=8080
server.servlet.context-path=/springboot-01
spring.mvc.view.prefix=/
spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp
server.servlet.jsp.init-parameters.development=true
12.2 集成 thymeleaf 模板
Thymeleaf 是一个用于 web 和独立环境的现代服务器端 java 模板引擎
Thymeleaf可以完全替代 jsp,可以在有网络和无网络的环境下运行,既可以让美工在浏览器上查看静态效果,也可以让程序员在服务器查看带数据的动态页面的效果。
- 引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>
dependency>
-
编写配置
完全可以不写
spring.thymeleaf.prefix=classpath:/templates/ # 使用模板的目录
spring.thymeleaf.suffix=.html # 使用模板的后缀
spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8 # 使用模板的编码
spring.thymeleaf.enabled=true # 开始thymleaf模板
spring.thymeleaf.servlet.content-type=text/html #使用模板的响应类型
注意:在文件夹 templates 中的模板,默认情况下 在
控制器的跳转下才能访问。
我们可以设置配置,让可以不用经过控制器也可以访问
spring.resources.static-locations=classpath:/templates/,classpath:/static/
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/findAll")
public String findAll(){
System.out.println("查询All");
return "index"; //逻辑名 classpath:/templates/逻辑名.html
}
}
13、thymeleaf 语法
使用时必须先在页面中加入 thymeleaf 的命名空间
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymleaf.org"/>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
======================================================================================
<h1>展示单个数据h1>
用户名:<span th:text="${username}">注意,这里面不能有内容,会被覆盖span>
链接 : <span th:utext="${html}">注意:解析html用 utextspan>
放入表单:<input type="text" th:value="${username}"/>
======================================================================================
<h1>展示对象数据h1>
<ul>
<li>name:<span th:text="${user.name}">span>li>
<li>age:<span th:text="${user.age}">span>li>
ul>
======================================================================================
<h1>有条件的展示数据h1>
<span th:if="${user.age} <= 20" th:text="${user.name}"/>
======================================================================================
<h1>展示多个数据h1>
<ul th:each="user:${users}">
<li th:text="${user.name}">li>
<li th:text="${user.age}">li>
ul>
======================================================================================
<h1>展示多个数据(获取遍历状态)h1>
<ul th:each="user,userStat:${users}">
<li th:text="${user.name}">li>
<li th:text="${user.age}">li>
<li>集合中的总记录数:<span th:text="${userStat.size}"/>li>
ul>
body>
html>
@Controller
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("findAll")
public String findAll(HttpServletRequest request){
request.setAttribute("username", "张三");
request.setAttribute("html", "李四链接");
request.setAttribute("user", new User("王五",23));
List<User> users = Arrays.asList(new User("刘六",34),
new User("田七",37),
new User("老八",23));
request.setAttribute("users", users);
System.out.println("查询All");
return "index1";
}
}
14、SpringBoot 整合 MyBatis
- 引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>2.1.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druidartifactId>
<version>1.1.18version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>5.1.48version>
dependency>
- 在 application.properties 中配置数据源
# 数据源的配置
spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dzf
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
# mybatis的配置
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:cf.duanzifan.mapper/*Mapper.xml
mybatis.type-aliases-package=cf.duanzifan.entity
- 开发 dao、service、controller
# 注意:要在 UserDao 接口上加入 @Mapper 注解,或者在 Application启动类上加上 @MapperScan,只有这样我们才能将dao层的实现类交给 Spring 工厂管理
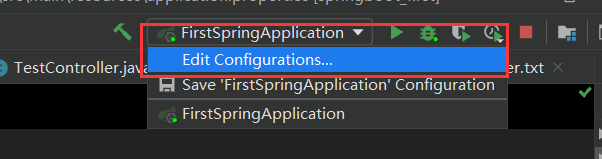
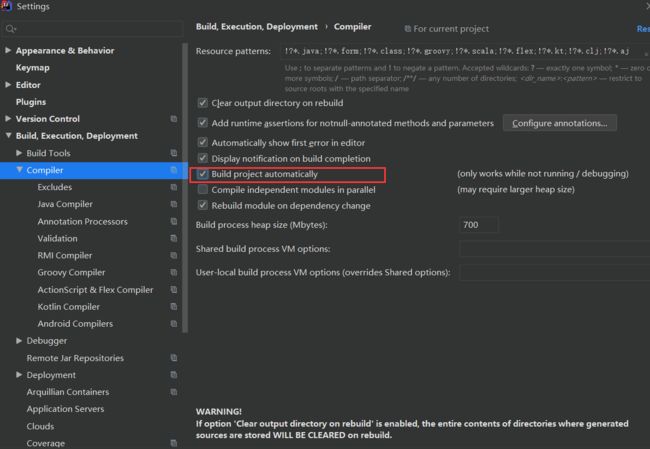
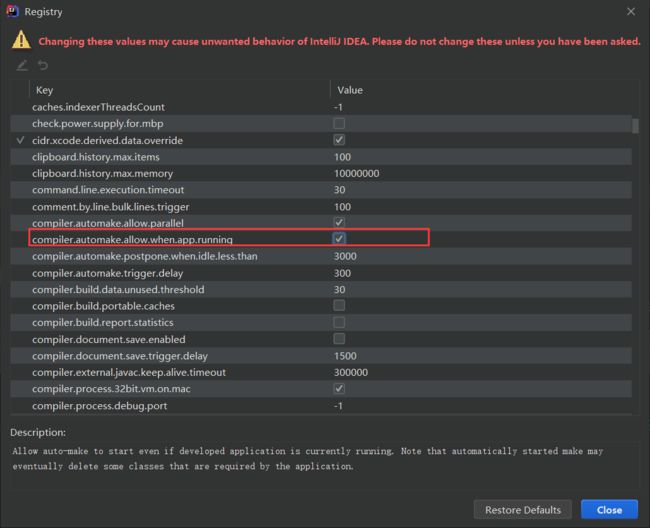
15、springboot 的 devtools 热部署
为了进一步提高开发效率,springboot 为我们提供了全局项目热部署,日后在开发的过程中修改了部分代码以及相关配置文件后,不需要每次重启使得修改生效,在项目中开启了 springboot 的全局热部署之后只需要在修改后等待几秒即可使修改生效。
- 开启热部署
- 项目引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
- 设置 idea 中支持自动编译
在代码界面快捷键:ctrl + alt + shift + /
当出现以下,就代表成功
16、logback 日志集成
- 日志的级别
> DEBUG < INFO < WARN < ERROR
> 日志级别由低到高:日志级别越高输出的日志信息越少
- 我们可以直接在 application.propeties 配置文件中设置日志的级别
logging.level.root=info
logging.level.cf.duanzifan.dao=debug
17、切面编程
- 引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aopartifactId>
dependency>
- 相关注解
1. @Aspect 用在类上,代表这个类是一个切面
2. @Before 用在方法上,代表这个方法是一个前置通知方法
3. @After 用在方法上,代表这个方法是一个后置通知方法
4. @Around 用在方法上,代表这个方法是一个环绕的方法
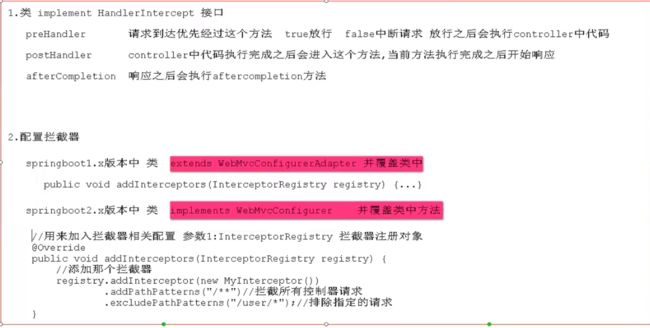
18、拦截器
ot=info
logging.level.cf.duanzifan.dao=debug
### 17、切面编程
- 引入依赖
```xml
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-aop
```
- 相关注解
~~~markdown
1. @Aspect 用在类上,代表这个类是一个切面
2. @Before 用在方法上,代表这个方法是一个前置通知方法
3. @After 用在方法上,代表这个方法是一个后置通知方法
4. @Around 用在方法上,代表这个方法是一个环绕的方法
18、拦截器
[外链图片转存中…(img-OE8gF7gQ-1599126798593)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-0CeHS7fr-1599126798597)]