Java-多线程+并发编程-01
文章目录
- Java多线程,并发编程(Thread)
-
- 线程的创建
-
- Thread基类:extends Thread
-
- 多线程下载图片
- Runnable接口:implements Runnable
- Callable接口:implements Callable
- 静态代理模式
- Lamda表达式
- 线程状态
-
- 线程的停止
- 线程休眠
- 线程礼让:yield
- 强制执行-join
- 线程状态---Thread.State
- 线程优先级----PRIORITY
- 守护线程:daemon
- 线程同步----synchronized(方法、块)
- 死锁
- Lock(锁)----ReentrantLock
- 线程协作---并发协助模型
-
- 生产者消费者问题----管程法
-
- 生产者消费者问题----信号灯法
- 线程池:ExecutorServer和Executors
- JUC并发编程
-
- Lock+Condition(同步监视器)
- 锁
-
- 读写锁
- 继续更新
- 集合类不安全
-
- List不安全
- set不安全(HashSet)
- HashMap不安全
- 三大常用辅助类
-
- CountDownLatch(减法计数器)
- CyclicBarrier(加法计数器)
- Semaphore(信号量)
Java多线程,并发编程(Thread)
- main函数是主线程
- 线程由操作系统调度
- 存在资源抢夺时,要加入并发控制
线程的创建
Thread基类:extends Thread
- 继承Thread类
- 重写Run方法,编写线程实体
- 创建线程对象,调用start()方法启动线程
public class ThreadTest extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
//run方法线程体
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
System.out.println("多线程------");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadTest a=new ThreadTest();
a.start();
for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){
System.out.println("主线程");
}
}
}
多线程下载图片
文件下载包
public class ThreadTest extends Thread{
private String url;
private String file;
public ThreadTest(String url,String file) {
//构造函数
this.url=url;
this.file=file;
}
@Override
public void run() {
WebDownLoader down=new WebDownLoader();
down.download(url,file);
System.out.println("下载完成:"+file);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadTest down1=new ThreadTest("https://ss1.bdstatic.com/70cFvXSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=3769272980,4240368075&fm=26&gp=0.jpg","01.jpg");
ThreadTest down2=new ThreadTest("https://ss0.bdstatic.com/70cFvHSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=1393799263,3304349115&fm=26&gp=0.jpg","02.jpg");
ThreadTest down3=new ThreadTest("https://ss3.bdstatic.com/70cFv8Sh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=134213255,2108409328&fm=26&gp=0.jpg","03.jpg");
down1.start();
down2.start();
down3.start();
}
}
class WebDownLoader{
//下载器
public void download(String url,String file){
try {
FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url),new File(file));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("IO错误");
}
}
}
Runnable接口:implements Runnable
- 定理类实现Runnable接口
- 实现run()方法体
- 创建线程对象,传入实现类,调用start()方法
public class RunnableTest implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
System.out.println("111");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Runnable实现接口类
Runnable test=new RunnableTest();
//创建线程对象,通过线程对象开启线程
Thread thread=new Thread(test);
thread.start();
for(int i=0;i<100;i++)
System.out.println("222");
}
}
Callable接口:implements Callable
好处
- 可以返回值
- 可以抛出异常
实现过程
- 实现Callable接口
- 重写call()方法,要抛出异常
- 创建目标对象
- 创建执行服务:
- 提交执行结果:
- 获取结果:
- 关闭服务:
public class CallableTest implements Callable<Boolean> {
@Override
public Boolean call() throws Exception {
for(int i=0;i<100;i++)
System.out.println("run");
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
CallableTest c1=new CallableTest();
CallableTest c2=new CallableTest();
CallableTest c3=new CallableTest();
CallableTest callable=new CallableTest();
//创建执行服务
ExecutorService ser= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
//提交执行
Future<Boolean> r1=ser.submit(c1);
Future<Boolean> r2=ser.submit(c2);
Future<Boolean> r3=ser.submit(c3);
//获取结果
Boolean res1=r1.get();
Boolean res2=r2.get();
Boolean res3=r3.get();
//关闭服务
ser.shutdown();
}
}
另一种启动方法:FutureTask
- 有缓存
- 结果可能需要等待,会阻塞。
//借助futureTask 类
FutureTask<integer> futureTask = new FutureTask(new Thread());
new Thread(futureTask,"name").start();
//返回结果
Integer integer=futureTask.get();
静态代理模式
- 代理对象可以做真实对象做不了的事情
- 真实对象和代理对象都要实现同一个接口
- 代理对象代理真实角色
//静态代理
public class StaticProxy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Poxy poxy=new Poxy(new You());
poxy.HappyMarry();
}
}
//建立一个接口
interface Marry{
public void HappyMarry();
}
//真实对象
class You implements Marry{
@Override
public void HappyMarry() {
System.out.println("I am Marray");
}
}
//代理对象
class Poxy implements Marry{
private You you;
Poxy(You you){
this.you=you;
}
@Override
public void HappyMarry() {
System.out.println("brfore marry");
you.HappyMarry();
System.out.println("after marry");
}
}
Lamda表达式
- 避免匿名内部类定义过多
- 实质数据函数式编程
- 去掉一堆没有意义的代码
()->表达式;
函数式接口:
- 任何接口如果只包含唯一一个抽象方法,那么他就是一个函数式接口
- 对于函数式接口我们用lambda表达式来实现
public class LambdaTest {
//3.静态内部类
static class Two implements Father{
@Override
public void lambda() {
System.out.println("静态内部类");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//4.局部内部类
class Three implements Father{
@Override
public void lambda() {
System.out.println("局部内部类");
}
}
Father father=null;
father=new One();
father.lambda();
father=new Two();
father.lambda();
father=new Three();
father.lambda();
father=new Father() {
//匿名内部类
@Override
public void lambda() {
System.out.println("匿名内部类");
}
};
father.lambda();
//lambda表达式
father=()->{
System.out.println("Lambda表达式");
};
father.lambda();
}
}
//1.定义一个接口
interface Father{
void lambda();
}
//2.实现一个类
class One implements Father{
@Override
public void lambda() {
System.out.println("一般实现方法");
}
}
简化Lambda表达式
- lambda表达式只能有一行代码的情况才能简化成一行,如果有多行,要用代码块包裹
- 接口位函数式接口,只有一个函数
//原表达式
Father2 father2=(int n)->{
System.out.println("简化"+n);
};
father2.lambda(0);
//去掉参数类型
father2=(n)->{
System.out.println("简化"+n);
};
father2.lambda(1);
//去掉括号
father2=n->{
System.out.println("简化"+n);
};
father2.lambda(2);
//去掉花括号
father2=n->System.out.println("简化"+n);
father2.lambda(3);
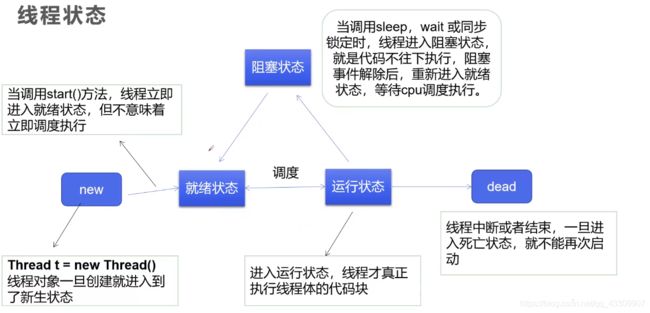
线程状态
线程的停止
- 建议线程正常停止—利用次数,不建议死循环
- 建议使用标志位—设置标志位
- 不要使用stop()或者destroy()等过时方法
//线程停止
public class StopTest implements Runnable{
//设置一个标志位
private boolean flag=true;
@Override
public void run() {
int i=0;
while(flag){
System.out.println("Runinng-----"+i++);
}
}
//设置一个公开方法停止线程,转换标志位
public void stop(){
this.flag=false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
StopTest stop=new StopTest();
new Thread(stop).start();
for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
if(i==99)
stop.stop();
System.out.println("main"+i);
}
}
}
线程休眠
- sleep(time)指定当前线程阻塞毫秒数
- sleep存在异常InterruptedExcrption;
- sleep时间打倒后线程进入就绪状态
- sleep可以模拟网络延时(放大问题的发生性),倒计时等
- 每一个对象都有一个锁,sleep不会释放锁
//获取当前系统时间
public class SleepTest {
public void printCurrentTime(){
Date currentTime=null;
while(true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (Exception a){
a.printStackTrace();
}
//获取当前系统时间
currentTime=new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(currentTime));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SleepTest().printCurrentTime();
}
}
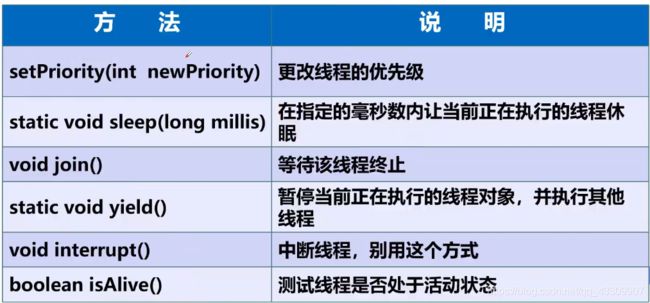
线程礼让:yield
- 礼让线程,让当前正在执行的线程暂停,但不阻塞
- 将线程从运行状态转换为就绪状态
- 让CPU重新调度,礼让不一定成功
public class YieldTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
myYield yield=new myYield();
new Thread(yield,"a").start();
new Thread(yield,"b").start();
}
}
class myYield implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":start");
Thread.yield();//礼让
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":stop");
}
}
强制执行-join
- join合并线程,待此线程执行完毕后,再执行其他线程,其他线程阻塞
- 可以想象成阻塞
public class JoinTest implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (Exception a){
a.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("VIP线程---"+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//插入线程开始
JoinTest join=new JoinTest();
Thread thread=new Thread(join);
thread.start();
//主线程
for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){
if(i==200)
thread.join();
System.out.println("main---"+i);
}
}
}
线程状态—Thread.State
- NEW:未启动状态
- RUNNABLE:在Java虚拟机中执行的线程
- BLOCKED:被阻塞等待监视器锁定的线程
- WAITING:正在等待另一个线程执行特定的动作
- TIME_WAITING:正在等待另一个线程执行动作达到指定等待时间的线程状态
- TERMINATED:已经退出的线程处于次状态
//线程状态
public class StateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(()->{
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
//检测状态
Thread.State state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state); //NEW
//启动
thread.start();
state=thread.getState();
System.out.println(state); //RUN
while (state!=Thread.State.TERMINATED){
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//只要不停止就输出状态
state=thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
}
System.out.println(state);
}
}
线程优先级----PRIORITY
- Java提供一个线程调度器来监控程序中启动后进入就绪状态的所有线程,线程调度器按照优先级决定该调度哪个线程来执行
- 优先级用数字表示:
- Thread.MIN_PRIORITY=1
- Thread.MAX_PRIORITY=10
- Thread.NORM_PRIORITY=5
- 使用 getPriority(),setPriority(int a),来获取改变优先级
- 优先级低只是意味着获得调度的概率低,并不是优先级低就不会被调用了,这都看CPU的调度。
守护线程:daemon
- 线程分为用户线程和守护线程
- 虚拟机必须确保用户线程执行完毕
- 虚拟机不用等待守护线程执行完毕
- 如:后台记录操作日志,监控内存,垃圾回收gc
public class DaemonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
God god=new God();
You you=new You();
Thread thread=new Thread(god);
thread.setDaemon(true); //默认式false,默认都是用户线程
thread.start();
new Thread(you).start(); //用户线程
}
}
class God implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
System.out.println("I see you");
}
}
}
class You implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<365;i++){
System.out.println("aLive:"+i);
}
System.out.println("dead!!!");
}
}
线程同步----synchronized(方法、块)
- 多线程操作同一个资源
- 并发:同一个对象被多个线程同时操作
- 线程同步是一种等待机制,多个需要同时访问此对象的线程进入这个对象的等待池形成队列,等待前面线程使用完毕,下一个线程再使用
- 形成条件:队列+锁
- 当一个线程获得对象的排他锁,独占资源,其他线程必须等待,使用后释放锁即可
- synchronized方法控制对象的访问,每一个对象对应一个锁,方法必须获得锁才能进行,否则会阻塞
- 方法一旦执行,就独占该锁,直到方法释放才返回锁,后面的阻塞线程才能得到这个锁、
- synchronized方法:
- synchronized默认锁的是this
- synchronized块:
- synchronized(Obj){}
- Obj称为同步监视器:推荐使用共享资源作为监视器
- 锁的对象是变化的量
###GUC里的安全类型的集合
//测试GUC安全类型的集合
public class GUCTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> list=new CopyOnWriteArrayList<String>();
for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){
new Thread(()->{
list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).start();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(list.size());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
死锁
- 多个线程占有一些共享资源,并且互相等待其他线程占有的资源才能运行
- 只要想办法破其一个或多个条件就可以避免死锁的发生
产生死锁的四个条件:
- 互斥条件:一个资源每次只能被一个进程使用
- 请求与保持条件:一个进程因请求资源而阻塞,对以获得的资源保持不放
- 不剥夺条件:进程以获得的资源,在未使用完之前,不能强行剥夺
- 循环等待条件:若干进程之间形成一种头尾相连的循环等待资源的关系
Lock(锁)----ReentrantLock
- 可重入锁
public class LockTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ticket ticket=new Ticket();
new Thread(ticket).start();
new Thread(ticket).start();
new Thread(ticket).start();
}
}
class Ticket implements Runnable{
private int ticketNum=10;
//定义lock锁
private ReentrantLock lock=new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
try {
lock.lock();
if(ticketNum>0){
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(this.ticketNum--);
}else
break;
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
- Lock是显式锁,手动关闭,出了所用域自动释放
- Lock只有代码块
- 使用Lock锁,JVM将花费较少的时间来调度线程,性能更好并且具有良好的扩展性(提供更多的子类)
- 优先使用顺序:Lock>同步代码块>同步方法
线程协作—并发协助模型
生产者消费者问题----管程法
- 生产者:负责生产数据的模块
- 消费者:负责处理数据的模块
- 缓冲区:消费者不能使用生产者的数据,生产者将生产好的数据放入缓冲区,消费者从缓冲区拿数据
//生产者消费者----管程法
public class PCTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//生产者,消费者,产品,缓冲区
SynContainer synContainer=new SynContainer();
new Thread(new Producter(synContainer)).start();
new Thread(new Consumer(synContainer)).start();
}
}
//生产者
class Producter implements Runnable{
SynContainer synContainer;
public Producter(SynContainer synContainer) {
this.synContainer = synContainer;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
synContainer.push(new Chichen(i));
System.out.println("生产了:"+i+"只鸡");
}
}
}
//消费者
class Consumer implements Runnable{
SynContainer synContainer;
public Consumer(SynContainer synContainer) {
this.synContainer = synContainer;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
Chichen num=synContainer.pop();
System.out.println("消费了--->"+num.id+"只鸡");
}
}
}
//产品
class Chichen{
int id;
public Chichen(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
//缓存区
class SynContainer{
//需要一个容器大小
Chichen[] chichens=new Chichen[10];
int count=0;
//生产者放入产品
public synchronized void push(Chichen chichen){
//如果容器满了,需要等待消费者消费
if(count==chichens.length){
//通知消费者消费,生产者等待
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//如果没有满,我们就丢入产品
chichens[count]=chichen;
count++;
//通知消费者消费
this.notifyAll();
}
//消费者消费产品
public synchronized Chichen pop(){
//判断能否消费
if(count==0){
//等待生产者生产,消费者等待
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//可以消费
count--;
Chichen chichenReturn=chichens[count];
//通知生产者生产
this.notifyAll();
return chichenReturn;
}
}
生产者消费者问题----信号灯法
package com.company;
//生产者消费者---》信号灯法
public class PCTeo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TV tv=new TV();
new Thread(new Player(tv)).start();
new Thread(new Watch(tv)).start();
}
}
//生产者--》演员
class Player implements Runnable{
TV tv;
public Player(TV tv) {
this.tv = tv;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
if(i%2==0){
tv.play("节目1");
}else
tv.play("节目2");
}
}
}
//消费者--》观众
class Watch implements Runnable{
TV tv;
public Watch(TV tv) {
this.tv = tv;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
tv.watch();
}
}
//节目
class TV{
//演员表演,观众等待
//观众观看,演员等待
String voice;//表演的节目
boolean flag=true;
//表演
public synchronized void play(String voice){
if(!flag){
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("表演了:"+voice);
//通知观众观看
this.notifyAll();
this.voice=voice;
this.flag=!this.flag;
}
//观看
public synchronized void watch(){
if(flag){
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("观看了:"+voice);
this.flag=!this.flag;
//通知表演者表演
this.notifyAll();
}
}
线程池:ExecutorServer和Executors
- 经常创建和销毁、使用量特别大的资源,比如并发情况下的线程,对性能影响很大
- 提前创建好多个线程,放入线程池中,使用时直接获取,使用完后再放回去,可以避免反复创建和销毁
- 好处:
- 提高响应速度(减少创建新线程的时间)
- 降低资源消耗(重复利用)
- 便于进程管理
线程池:
- ExecutorService:真正的线程池接口。
- Executors:工具类、线程池的工厂类,用于创建并返回不同类型的线程池。
//测试线程池
public class PoolTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建服务。创建线程池
//newFixedThreadPool参数是线程池大小
ExecutorService service= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
//2.执行
service.execute(new MyThread());
service.execute(new MyThread());
service.execute(new MyThread());
//3.关闭连接
service.shutdown();
}
}
class MyThread implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
JUC并发编程
- JUC:java.utill.concurrent
- Java默认有2个线程 main + gc
- 并发编程:充分利用CPU的资源
- 并发:多线程操作同一个资源;快速交替执行
- 并行:多核CPU,多个线程同时执行;线程池
//获得CPU的核数
System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
Lock+Condition(同步监视器)
- 精准的通知和唤醒线程
- 设置多个监视器:
private Lock lock=new ReentrantLock();
private Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();
private Condition condition2= lock.newCondition();
private Condition condition3 = lock.newCondition();
//使用格式
//上锁
lock.lock();
//等待
condition1.await();
//唤醒第二个线程
condition2.signal();
//解锁
lock.unlock();
锁
- synchronized:锁的是方法的调用者:谁先拿到谁执行
- synchronized:普通方法不受影响
- synchronized:不同对象锁不管用
- static synchronized:静态方法,锁的是Class
- static synchronized:静态方法锁的是模板,实例化对象来自同一个模板。
读写锁
- 读的时候可以被多个线程同时读取
- 写的时候只能有一个线程去写
继续更新
集合类不安全
List不安全
- List是线程不安全的
- java.util.ConcurrentModificationException:并发修改异常
- List 下的Vector默认是安全的,底层是基于synchronized实现的,效率低
- 使用工具类:collections.synchronizedlist()转换为安全的
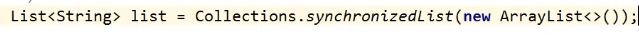
- 使用并发下的:concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList()
set不安全(HashSet)
-
HashSet底层是HashMap
-
同理set也存在并发修改异常:ConcurrentModificationException
-
解决方法:
HashMap不安全
三大常用辅助类
CountDownLatch(减法计数器)
- 数量减一: latch.countDown();
- 等待计数器归零: latch.await();:程序计数器的变为0的时候,再向下执行
//线程计数器
public class test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch latch=new CountDownLatch(6);
for (int i = 0; i <6 ; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
latch.countDown();
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
latch.await();
System.out.println("结束了");
}
}
CyclicBarrier(加法计数器)
- 允许一组线程全部等待彼此达到共同屏障点的同步辅助。
- 循环阻塞在涉及固定大小的线程方的程序中很有用,这些线程必须偶尔等待彼此。
- 调用await来加一·
//CyclicBarrier测试
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//主线程
CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier=new CyclicBarrier(7,()->{
System.out.println("召唤神龙!!!");
});
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"get one!");
try {
cyclicBarrier.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
Semaphore(信号量)
- 限流时使用
- 有限的空间内,让事情有序的进行
- acquire()获得,假设如果已经满了,等待被释放
- release()释放,会将当前的信号量释放+1,然后唤醒等待的线程作用,多个共享资源互斥的使用
- 并发限流,控制最大并发线程数
//测试Semaphore
public class test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//线程数量
Semaphore semaphore=new Semaphore(3);
for (int i = 0; i <6; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
try {
//acquire得到
semaphore.acquire();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"进入");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"离开");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//release释放
semaphore.release();
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}