数据结构_实验4_快速排序
本人为编程小白,实验会有很多错误和不规范的地方,欢迎指出,仅供借鉴
1、 读懂理解〈数据结构〉教材中的冒泡排序的算法。
2、 基于冒泡排序,读懂理解快速排序的算法。
3、 编写冒泡排序、快速排序的程序,上机调试。
进行排序分析。构造多组数据,将编写的排序算法用多组数据进行测试,记录排序使用的时间:
a) 针对所实现的每种排序方法,产生多组随机数据进行多次排序试验,统计每次试验的性能,记录并计算每个算法的平均时间。
b) 针对所实现的每种排序方法,产生特殊数据进行排序试验,统计每次试验的性能,记录并计算每个算法的最好时间、最坏时间。
c) 针对各种排序方法,对同一组数据进行排序试验,统计每次试验的性能,记录并对比每种排序算法的执行时间。
需求分析
本实验目的为熟悉冒泡排序和快速排序,用代码实现这两种排序并比较两种排序方法在多组测试集下使用的时间。主要分为三个方面:
a) 针对所实现的每种排序方法,产生多组随机数据进行多次排序试验,统计每次试验的性能,记录并计算每个算法的平均时间。
b) 针对所实现的每种排序方法,产生特殊数据进行排序试验,统计每次试验的性能,记录并计算每个算法的最好时间、最坏时间。
c) 针对各种排序方法,对同一组数据进行排序试验,统计每次试验的性能,记录并对比每种排序算法的执行时间。
输入的形式和输入值的范围:无输入
输出的形式:①排序后结果②排序消耗的时间
程序所能达到的功能:排序并测试排序的相对时间
测试数据:
① 测试冒泡排序对0-10000内随机数组和有序数组的排序性能
② 测试快速排序对0-10000内随机数组和有序数组的排序性能
③ 测试冒泡排序和快速排序对对0-10000内随机数组的排序性能
④ 测试冒泡排序和快速排序对对0-10000内有序数组的排序性能
概要设计
详细设计
伪代码:
冒泡排序:
void BubbleSort(int* a,int size){
for(int i=0;i<size-1;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<size;j++){
if(a[j]<a[i]){
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
快速排序:
int Partition(int *a,int low,int high){
pivotkey = a[low];
while(low<high){
while(low<high&&a[high]>=pivotkey) high--;
a[low] = a[high];
while(low<high&&a[low]<=pivotkey) low++;
a[high] = a[low];
}
a[low] = pivotkey;
return low;
}
void QuickSort(int *a,int low,int high){
if(low<high){
pivotloc = Partition(a,low,high);
QuickSort(a,low,pivotloc-1);
QuickSort(a,pivotloc+1,high);
}
}
调试分析
存在有两个问题,第一是用clock函数来计算排序函数时间时,排序的数组范围太小,排序所用时间会为0,所以数组要足够大;第二是产生随机数的rand()函数在经过多次测试后无论%后跟的数有多大,最大只能产生一个32765左右的数,因此我们把数组的大小定为10000,产生随机数的范围也定为1-10000。
本测试中通常快速排序比冒泡排序所需要的时间少了两个数量级,但是在数组有序的情况下,快速排序所需要的时间变得和冒泡排序差不多了,说明快速排序退化成了冒泡排序。
用户使用说明
无输入,直接观察结果
测试结果
测试一:测试冒泡排序对0-10000内随机数组和有序数组的排序性能

测试二:测试快速排序对0-10000内随机数组和有序数组的排序性能

测试三:测试冒泡排序和快速排序对0-10000内随机数组的排序性能
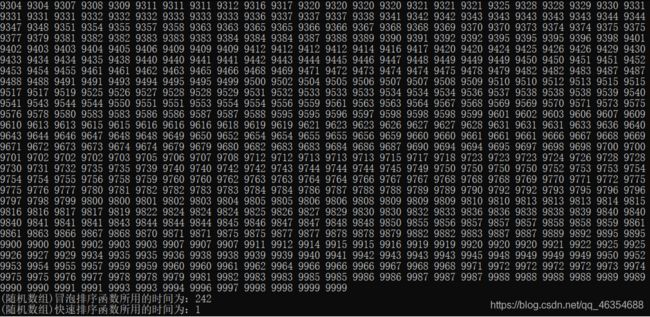
测试四:测试冒泡排序和快速排序对0-10000内有序数组的排序性能
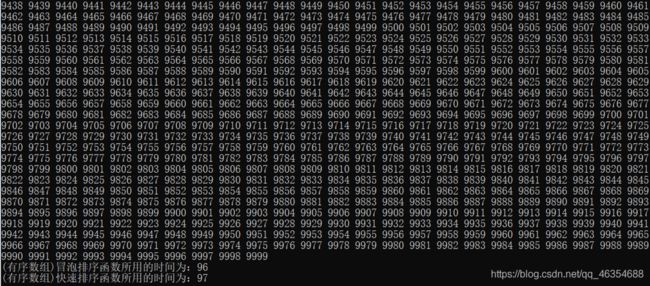
备注:程序运行结果很长很长,截图只显示了最后一部分数字
源代码
除主函数部分源代码:
#include 主函数:
① 测试冒泡排序对0-10000内随机数组和有序数组的排序性能
int main() {
int size = 10000;
int a[size];
int b[size];
//产生随机数
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
a[i] = rand()%10000;
}
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
b[i] = size-i;
}
//计算时间复杂度
clock_t start,end;
start = clock();
BubbleSort(a,size);
end = clock();
double n=1000*(double)(end-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
start = clock();
BubbleSort(b,size);
end = clock();
double m=1000*(double)(end-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
cout<<"(随机数组)冒泡排序函数所用的时间为:"<<n<<endl;
cout<<"(有序数组)冒泡排序函数所用的时间为:"<<m<<endl;
return 0;
}
② 测试快速排序对0-10000内随机数组和有序数组的排序性能
int main() {
int size = 10000;
int a[size];
int b[size];
//产生随机数
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
a[i] = rand()%10000;
}
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
b[i] = size-i;
}
//计算时间复杂度
clock_t start,end;
start = clock();
QuickSort(a,0,size-1);
end = clock();
double n=1000*(double)(end-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
start = clock();
QuickSort(b,0,size-1);
end = clock();
double m=1000*(double)(end-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
cout<<"(随机数组)快速排序函数所用的时间为:"<<n<<endl;
cout<<"(有序数组)快速排序函数所用的时间为:"<<m<<endl;
return 0;
}
③ 测试冒泡排序和快速排序对0-10000内随机数组的排序性能
int main() {
int size = 10000;
int a[size];
int b[size];
//产生随机数
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
a[i] = rand()%10000;
b[i] = a[i];
}
//计算时间复杂度
clock_t start,end;
start = clock();
BubbleSort(a,size);
end = clock();
double n=1000*(double)(end-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
start = clock();
QuickSort(b,0,size-1);
end = clock();
double m=1000*(double)(end-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
cout<<"(随机数组)冒泡排序函数所用的时间为:"<<n<<endl;
cout<<"(随机数组)快速排序函数所用的时间为:"<<m<<endl;
return 0;
}
④ 测试冒泡排序和快速排序对0-10000内有序数组的排序性能
int main() {
int size = 10000;
int a[size];
int b[size];
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
a[i] = i;
b[i] = i;
}
//计算时间复杂度
clock_t start,end;
start = clock();
BubbleSort(a,size);
end = clock();
double n=1000*(double)(end-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
start = clock();
QuickSort(b,0,size-1);
end = clock();
double m=1000*(double)(end-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
cout<<"(有序数组)冒泡排序函数所用的时间为:"<<n<<endl;
cout<<"(有序数组)快速排序函数所用的时间为:"<<m<<endl;
return 0;
}
