大数据高频面试题-手写代码
手写代码
- 2.1 快排
- 2.2 归并
- 2.3 手写Spark-WordCount
- 2.4 冒泡排序
- 2.5 二分查找
- 2.6 二叉树之Scala实现
- 2.6.1 二叉树概念
- 2.6.2 二叉树的特点
- 2.6.3 二叉树的Scala代码实现
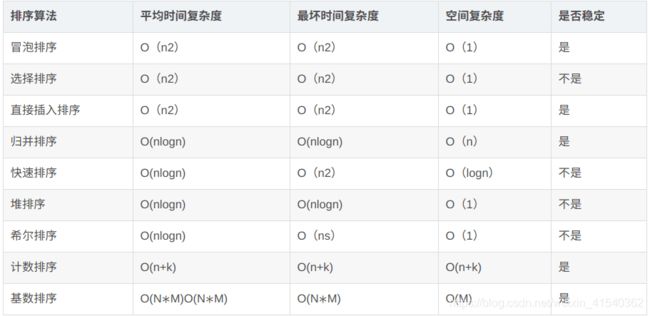
常见的几种排序
排序算法时间复杂度、空间复杂度、稳定性比较(动态图):
https://blog.csdn.net/yushiyi6453/article/details/76407640
2.1 冒泡排序
/**
* 冒泡排序 时间复杂度 O(n^2) 空间复杂度O(1)
*/
public class BubbleSort {
public static void bubbleSort(int[] data) {
System.out.println("开始排序");
int arrayLength = data.length;
for (int i = 0; i < arrayLength - 1; i++) {
boolean flag = false;
for (int j = 0; j < arrayLength - 1 - i; j++) {
if(data[j] > data[j + 1]){
int temp = data[j + 1];
data[j + 1] = data[j];
data[j] = temp;
flag = true;
}
}
System.out.println(java.util.Arrays.toString(data));
if (!flag)
break;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] data = { 9, -16, 21, 23, -30, -49, 21, 30, 30 };
System.out.println("排序之前:\n" + java.util.Arrays.toString(data));
bubbleSort(data);
System.out.println("排序之后:\n" + java.util.Arrays.toString(data));
}
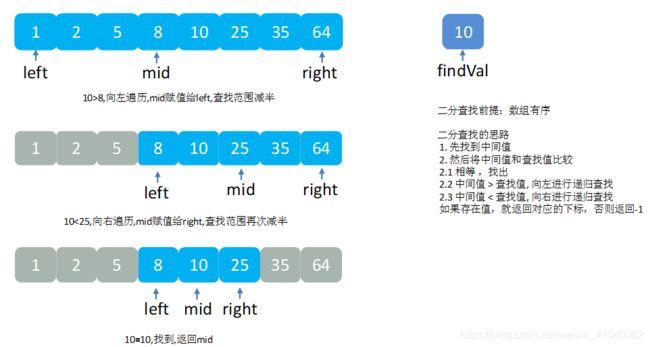
}2.2 二分查找
二分查找全流程
实现代码:
/**
* 二分查找 时间复杂度O(log2n);空间复杂度O(1)
*/
def binarySearch(arr:Array[Int],left:Int,right:Int,findVal:Int): Int={
if(left>right){//递归退出条件,找不到,返回-1
-1
}
val midIndex = (left+right)/2
if (findVal < arr(midIndex)){//向左递归查找
binarySearch(arr,left,midIndex,findVal)
}else if(findVal > arr(midIndex)){//向右递归查找
binarySearch(arr,midIndex,right,findVal)
}else{//查找到,返回下标
midIndex
}
}拓展需求:当一个有序数组中,有多个相同的数值时,如何将所有的数值都查找到。
代码实现如下:
/*
{1,8, 10, 89, 1000, 1000,1234} 当一个有序数组中,有多个相同的数值时,如何将所有的数值都查找到,比如这里的 1000.
//分析
1. 返回的结果是一个可变数组 ArrayBuffer
2. 在找到结果时,向左边扫描,向右边扫描 [条件]
3. 找到结果后,就加入到ArrayBuffer
*/
def binarySearch2(arr: Array[Int], l: Int, r: Int,
findVal: Int): ArrayBuffer[Int] = {
//找不到条件?
if (l > r) {
return ArrayBuffer()
}
val midIndex = (l + r) / 2
val midVal = arr(midIndex)
if (midVal > findVal) {
//向左进行递归查找
binarySearch2(arr, l, midIndex - 1, findVal)
} else if (midVal < findVal) { //向右进行递归查找
binarySearch2(arr, midIndex + 1, r, findVal)
} else {
println("midIndex=" + midIndex)
//定义一个可变数组
val resArr = ArrayBuffer[Int]()
//向左边扫描
var temp = midIndex - 1
breakable {
while (true) {
if (temp < 0 || arr(temp) != findVal) {
break()
}
if (arr(temp) == findVal) {
resArr.append(temp)
}
temp -= 1
}
}
//将中间这个索引加入
resArr.append(midIndex)
//向右边扫描
temp = midIndex + 1
breakable {
while (true) {
if (temp > arr.length - 1 || arr(temp) != findVal) {
break()
}
if (arr(temp) == findVal) {
resArr.append(temp)
}
temp += 1
}
}
return resArr
}2.3 快排
快速排序图解
代码实现:
代码实现:
/**
* 快排
* 时间复杂度:平均时间复杂度为O(nlogn)
* 空间复杂度:O(logn),因为递归栈空间的使用问题
*/
def quickSort(list: List[Int]): List[Int] = list match {
case Nil => Nil
case List() => List()
case head :: tail =>
val (left, right) = tail.partition(_ < head)
quickSort(left) ::: head :: quickSort(right)
}
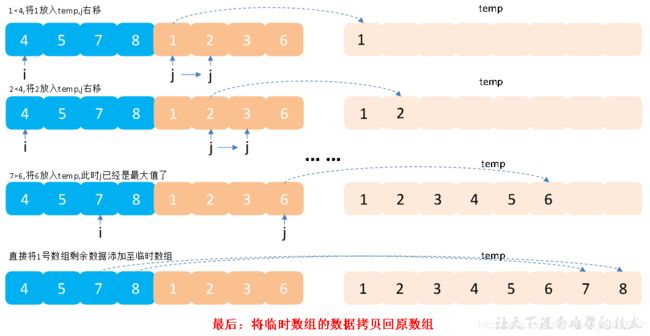
2.4归并
归并排序核心思想
核心思想:不断的将大的数组分成两个小数组,直到不能拆分为止,即形成了单个值。此时使用合并的排序思想对已经有序的数组进行合并,合并为一个大的数据,不断重复此过程,直到最终所有数据合并到一个数组为止。
归并排序治流程
代码实现:
/**
* 快排
* 时间复杂度:O(nlogn)
* 空间复杂度:O(n)
*/
def merge(left: List[Int], right: List[Int]): List[Int] = (left, right) match {
case (Nil, _) => right
case (_, Nil) => left
case (x :: xTail, y :: yTail) =>
if (x <= y) x :: merge(xTail, right)
else y :: merge(left, yTail)
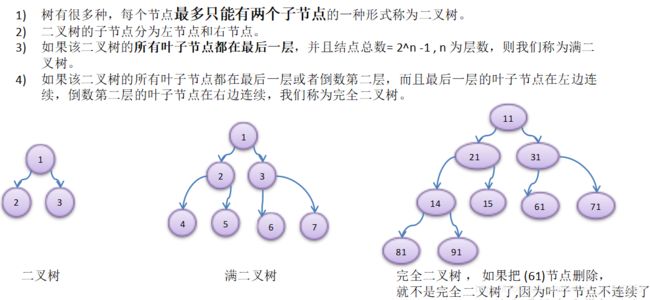
}2.5 二叉树之Scala实现
2.5.1 二叉树概念
2.5.2 二叉树的特点
1)树执行查找、删除、插入的时间复杂度都是O(logN)
2)遍历二叉树的方法包括前序、中序、后序
3)非平衡树指的是根的左右两边的子节点的数量不一致
4) 在非空二叉树中,第i层的结点总数不超过 , i>=1;
5)深度为h的二叉树最多有个结点(h>=1),最少有h个结点;
6)对于任意一棵二叉树,如果其叶结点数为N0,而度数为2的结点总数为N2,则N0=N2+1;
2.5.3 二叉树的Scala代码实现
定义节点以及前序、中序、后序遍历
class TreeNode(treeNo:Int){
val no = treeNo
var left:TreeNode = null
var right:TreeNode = null
//后序遍历
def postOrder():Unit={
//向左递归输出左子树
if(this.left != null){
this.left.postOrder
}
//向右递归输出右子树
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.postOrder
}
//输出当前节点值
printf("节点信息 no=%d \n",no)
}
//中序遍历
def infixOrder():Unit={
//向左递归输出左子树
if(this.left != null){
this.left.infixOrder()
}
//输出当前节点值
printf("节点信息 no=%d \n",no)
//向右递归输出右子树
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.infixOrder()
}
}
//前序遍历
def preOrder():Unit={
//输出当前节点值
printf("节点信息 no=%d \n",no)
//向左递归输出左子树
if(this.left != null){
this.left.postOrder()
}
//向右递归输出右子树
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder()
}
}
//后序遍历查找
def postOrderSearch(no:Int): TreeNode = {
//向左递归输出左子树
var resNode:TreeNode = null
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.postOrderSearch(no)
}
if (resNode != null) {
return resNode
}
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.postOrderSearch(no)
}
if (resNode != null) {
return resNode
}
println("ttt~~")
if (this.no == no) {
return this
}
resNode
}
//中序遍历查找
def infixOrderSearch(no:Int): TreeNode = {
var resNode : TreeNode = null
//先向左递归查找
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.infixOrderSearch(no)
}
if (resNode != null) {
return resNode
}
println("yyy~~")
if (no == this.no) {
return this
}
//向右递归查找
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.infixOrderSearch(no)
}
return resNode
}
//前序查找
def preOrderSearch(no:Int): TreeNode = {
if (no == this.no) {
return this
}
//向左递归查找
var resNode : TreeNode = null
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.preOrderSearch(no)
}
if (resNode != null){
return resNode
}
//向右边递归查找
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.preOrderSearch(no)
}
return resNode
}
//删除节点
//删除节点规则
//1如果删除的节点是叶子节点,则删除该节点
//2如果删除的节点是非叶子节点,则删除该子树
def delNode(no:Int): Unit = {
//首先比较当前节点的左子节点是否为要删除的节点
if (this.left != null && this.left.no == no) {
this.left = null
return
}
//比较当前节点的右子节点是否为要删除的节点
if (this.right != null && this.right.no == no) {
this.right = null
return
}
//向左递归删除
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.delNode(no)
}
//向右递归删除
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.delNode(no)
}
}
}
定义二叉树,前序、中序、后序遍历,前序、中序、后序查找,删除节点
class BinaryTree{
var root:TreeNode = null
//后序遍历
def postOrder(): Unit = {
if (root != null){
root.postOrder()
}else {
println("当前二叉树为空,不能遍历")
}
}
//中序遍历
def infixOrder(): Unit = {
if (root != null){
root.infixOrder()
}else {
println("当前二叉树为空,不能遍历")
}
}
//前序遍历
def preOrder(): Unit = {
if (root != null){
root.preOrder()
}else {
println("当前二叉树为空,不能遍历")
}
}
//后序遍历查找
def postOrderSearch(no:Int): TreeNode = {
if (root != null) {
root.postOrderSearch(no)
}else{
null
}
}
//中序遍历查找
def infixOrderSeacher(no:Int): TreeNode = {
if (root != null) {
return root.infixOrderSearch(no)
}else {
return null
}
}
//前序查找
def preOrderSearch(no:Int): TreeNode = {
if (root != null) {
return root.preOrderSearch(no)
}else{
//println("当前二叉树为空,不能查找")
return null
}
}
//删除节点
def delNode(no:Int): Unit = {
if (root != null) {
//先处理一下root是不是要删除的
if (root.no == no){
root = null
}else {
root.delNode(no)
}
}
}2.6 手写Spark-WordCount
val conf: SparkConf =
new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("WordCount")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
sc.textFile("/input")
.flatMap(_.split(" "))
.map((_, 1))
.reduceByKey(_ + _)
.saveAsTextFile("/output")
sc.stop()2.7 手写Spark程序
要求:(a,1) (a,3) (b,3) (b,5) (c,4),求每个key对应value的平均值
rdd.combineByKey(v=>(v,1),(acc:(Int,Int),newV)=>(acc._1+newV,acc._2+1),(acc1:(Int,Int),acc2:(Int,Int))=>(acc1._1+acc2._1,acc1._2+acc2._2))
注:内容源自“尚硅谷”网络公开资源整理
—— 温故而知新,可以为师矣。