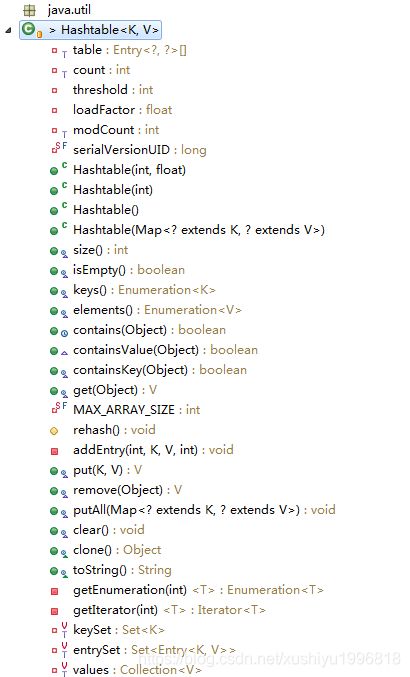
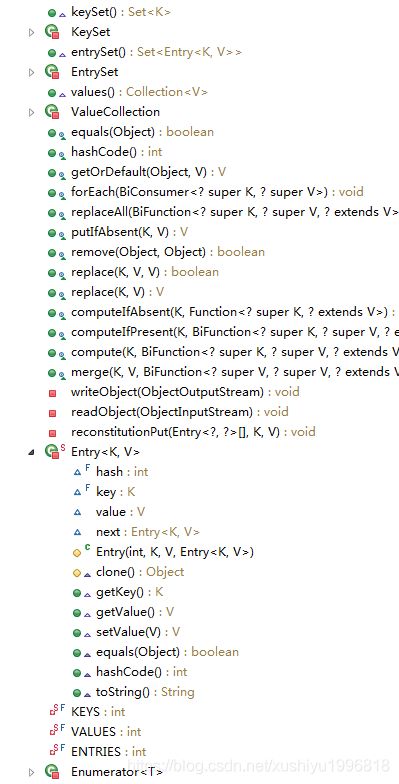
java容器 类HashTable源码分析
目录
简介
get
put,addEntry,rehash
remove
简介
/**
* 这个类实现了一个散列表,它将键映射到值。任何非空对象都可以用作键或值。
* 注意:是非空对象可以作为key和value。hashmap是所有对象,包括null,可以作为key和value。
*
* 要成功地从哈希表存储和检索对象,用作键的对象必须实现hashCode方法和equals方法。
*
* Hashtable实例有两个影响其性能的参数:初始容量和负载因子。
* 容量是哈希表中的桶数,初始容量只是创建哈希表时的容量。
* 注意,哈希表是打开的:在“哈希冲突”的情况下,一个bucket存储多个条目,这些条目必须按顺序搜索。
* 负载因子是一个度量哈希表在其容量自动增加之前允许的满度的度量。
* 初始容量和负载因子参数只是实现的提示。关于何时以及是否调用rehash方法的确切细节依赖于实现。
*
* G通常,默认的负载因子(.75)在时间和空间成本之间提供了很好的权衡。
* 较高的值减少了空间开销,但增加了查找条目的时间成本(这反映在大多数散列表操作中,包括get和put)。
*
* 初始容量控制了浪费的空间和需要重新哈希操作之间的权衡,后者非常耗时。
* 如果初始容量大于Hashtable将包含的最大条目数除以其负载因子,则不会发生任何重排操作。
* 但是,将初始容量设置得过高会浪费空间。
*
* 如果要将许多条目放入一个Hashtable中,那么以足够大的容量创建它可能比让它根据需要执行自动散列来扩展表更有效地插入条目。
*
* 本例创建一个数字散列表。它使用数字的名称作为键:
*
{@code
* Hashtable numbers
* = new Hashtable();
* numbers.put("one", 1);
* numbers.put("two", 2);
* numbers.put("three", 3);}
*
* To retrieve a number, use the following code:
*
{@code
* Integer n = numbers.get("two");
* if (n != null) {
* System.out.println("two = " + n);
* }}
*
* 返回的迭代器返回的集合的迭代器方法这门课的所有“集合视图方法”是快速失败:
* 如果哈希表结构修改创建迭代器后,任何时候以任何方式除非通过迭代器的删除方法,迭代器将抛出ConcurrentModificationException。
* 因此,在面对并发修改时,迭代器会快速而干净地失败,而不是在将来某个不确定的时间冒任意的、不确定的行为的风险。
* Hashtable的keys和elements方法返回的枚举不是快速失败的。
*
*
注意,不能保证迭代器的快速故障行为,因为通常来说,在存在非同步并发修改的情况下,不可能做出任何严格的保证。
* 故障快速迭代器在最大努力的基础上抛出ConcurrentModificationException。
* 因此,编写一个依赖于这个异常的正确性的程序是错误的:迭代器的快速故障行为应该只用于检测bug。
*
*
从Java 1.2开始,对该类进行了改进以实现Map接口,使其成为Java集合框架的成员。
* 与新的集合实现不同,Hashtable是同步的。
* 注意:hashtable的方法,除了构造器方法,和三个视图类方法,其余方法都是synchronized的,都是同步方法。
* 如果不需要线程安全的实现,建议使用HashMap代替Hashtable。
* 如果需要线程安全的高并发实现,那么建议使用java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap代替Hashtable。
*
* @author Arthur van Hoff
* @author Josh Bloch
* @author Neal Gafter
* @see Object#equals(java.lang.Object)
* @see Object#hashCode()
* @see Hashtable#rehash()
* @see Collection
* @see Map
* @see HashMap
* @see TreeMap
* @since JDK1.0
*/
public class Hashtable
extends Dictionary
implements Map, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
get
/**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key.equals(k))},
* then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise it returns
* {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
* @param key the key whose associated value is to be returned
* @return the value to which the specified key is mapped, or
* {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
* @see #put(Object, Object)
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public synchronized V get(Object key) {
Entry tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
// 先得到key的hashcode的前31位,然后mod tab.length 即取后x位
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
// 找到桶后,不断e=e.next循环
for (Entry e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
// 先判断hash,然后判断key是否equals
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return (V)e.value;
}
}
return null;
}
put,addEntry,rehash
/**
* Increases the capacity of and internally reorganizes this
* hashtable, in order to accommodate and access its entries more
* efficiently. This method is called automatically when the
* number of keys in the hashtable exceeds this hashtable's capacity
* and load factor.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected void rehash() {
int oldCapacity = table.length;
Entry[] oldMap = table;
// overflow-conscious code
// 新的容量大小为2*old+1
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) {
if (oldCapacity == MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)
// Keep running with MAX_ARRAY_SIZE buckets
return;
newCapacity = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
Entry[] newMap = new Entry[newCapacity];
modCount++;
// threshold为capacity*load factor
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
table = newMap;
// 对oldMap的每个桶进行遍历
for (int i = oldCapacity ; i-- > 0 ;) {
// 从第一个元素开始遍历,不断old = old.next;
for (Entry old = (Entry)oldMap[i] ; old != null ; ) {
Entry e = old;
old = old.next;
// e对应的新的桶的位置
int index = (e.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % newCapacity;
// 将e放在新的桶的第一个位置,e.next为之前的第一个
// 循环完成后,旧桶的第一个会变成新桶的最后一个,因为它是第一个被放进去的
e.next = (Entry)newMap[index];
newMap[index] = e;
}
}
}
private void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int index) {
modCount++;
Entry tab[] = table;
if (count >= threshold) {
// Rehash the table if the threshold is exceeded
rehash();
tab = table;
hash = key.hashCode();
index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
}
// Creates the new entry.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry e = (Entry) tab[index];
// 在桶的第一个元素,创建新节点,然后新节点的next为原来的第一个节点
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
count++;
}
/**
* Maps the specified key to the specified
* value in this hashtable. Neither the key nor the
* value can be null.
*
* The value can be retrieved by calling the get method
* with a key that is equal to the original key.
*
* @param key the hashtable key
* @param value the value
* @return the previous value of the specified key in this hashtable,
* or null if it did not have one
* @exception NullPointerException if the key or value is
* null
* @see Object#equals(Object)
* @see #get(Object)
*/
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// 保证value不为null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry entry = (Entry)tab[index];
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
// 如get一样,先找到对应的节点,如果找到了,替换value
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
// 没找到,调用addEntry
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
}
remove
/**
* Removes the key (and its corresponding value) from this
* hashtable. This method does nothing if the key is not in the hashtable.
*
* @param key the key that needs to be removed
* @return the value to which the key had been mapped in this hashtable,
* or null if the key did not have a mapping
* @throws NullPointerException if the key is null
*/
public synchronized V remove(Object key) {
Entry tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry e = (Entry)tab[index];
for(Entry prev = null ; e != null ; prev = e, e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
// 找到节点
modCount++;
// 设置上一个节点的next
if (prev != null) {
prev.next = e.next;
} else {
tab[index] = e.next;
}
count--;
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = null;
return oldValue;
}
}
return null;
}